Types of RNA Nucleotides
adenine, cytosine, uracil, and guanine
Types of DNA Nucleotides
adenine, thymine , guanine, and cytosine
Dinucleotide
CoA
- Coenzyme A
- used to move a molecule to an enzyme
FAD
- Flavin adenine dinucleotide
- used in different sets of reactions that remove hydrogen from another molecule, for example in different parts of cellular respiration
NADP+
- Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
- is used in different sets of reactions that remove hydrogen from another molecule, for example in photosynthesis
NAD+
- nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
- used in reactions that remove hydrogen from another molecule, for example in parts cellular respiration
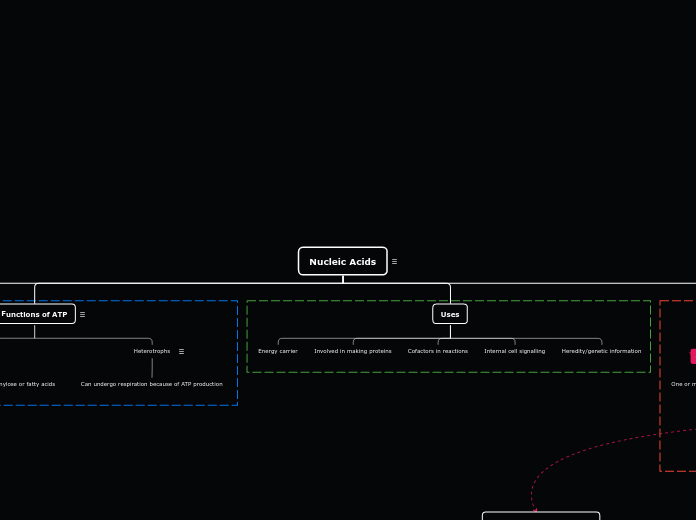
Nucleic Acids
- ATP (adenosine triphosphate)
- have more predictable rules for which nitrogenous bases are attracted to each other than proteins
Structure
Nucleotide
- The monomer of nucleic acids
- connected between their phosphate group and a hydroxyl group on the 5-carbon sugar to make a phosphodiester bond.
Nitrogenous base
There are 5 common nitrogenous bases: guanine, adenine, cytosine, thymine, and uracil.
Pyrimidines
- In RNA pyrimidines include cytosine and uracil
- In DNA pyrimidines include cytosine and thymine
Purines
- In RNA purines include adenine and guanine
- In DNA purines include adenine and guanine
5-carbon sugar
RNA
- the polymer ribonucleic acid
- used as the genetic molecule in many viruses
- used to turn off genes
- folded in such a way so that the bottom of the molecule can attach to other RNA molecules
DNA
- the polymer deoxyribonucleic acid
Double strand
- made up of 2 polymers
- When two strands come together, though, they always line up and connect with one strand inverted compared to the other
Single strand
- made up of 1 polymer
- can fold up on themselves to make functional shapes.
One or more phosphate functional groups
Uses
Heredity/genetic information
Internal cell signalling
Cofactors in reactions
Involved in making proteins
Energy carrier
Functions of ATP
In plants, sunlight energy is captured as ATP
In consumers enzymes convert the energy consumed into ATP
Heterotrophs
- organisms that consume biological molecules to produce energy
Can undergo respiration because of ATP production
Autotrophs
- organisms that can produce biological molecules from simpler molecules like CO2 and H2O using light or chemical energy
stores energy in the form of amylose or fatty acids
grows new tissue
Plays a Role in Food Systems
- includes|: growing, harvesting, transporting, marketing, consumption, and disposal of food
- energy in cells and organisms is carried and stored in different forms
- the amount of energy we can get is limited because of limitations
Limitations to the Food System
Waste
- a third of food produced is wasted
Malnutrition
- 794 million people suffer from hunger
- 2 billion people do not get sufficient vitamins and minerals
- 9 billion people over eat, 600 million of these people are obese leading to type 2 diabetes
Too Rich in fat, sugar, salt, and meat
- this diet impacts our health and the environment
- leads to health diseases
- green house gas emissions are raised from meat production
- food is less diverse
Natural Resources are Under Pressure
- sources of fresh water are running dry
- existing water sources are becoming polluted
- 33% of soils are degraded
- biodiversity is threatened --> tropical forests disappearing, plants and animals endangered
- climate change intensifies these issues