par zander rivers Il y a 1 année
612
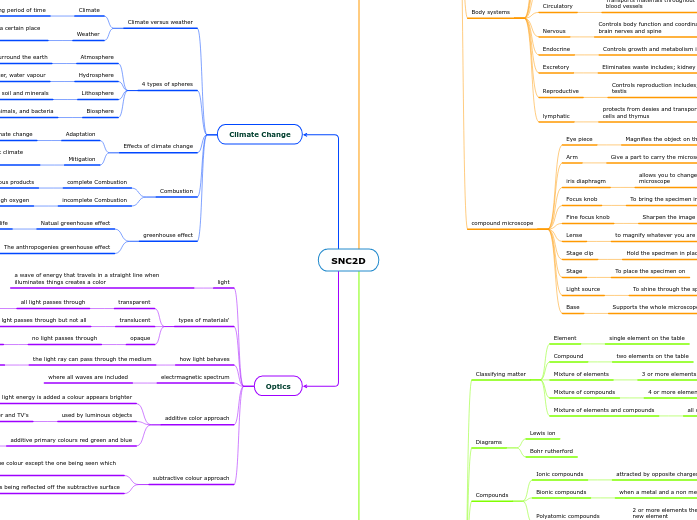
SNC2D
par zander rivers Il y a 1 année
612

Plus de détails
A microorganism is an organism so small that people cannot see them with the naked eye.
Microorganisms can be harmful and useful organisms.
Harmful microorganisms include fungi, bacteria, protozoa, etc.
They cause several diseases in human beings, animals, and plants, which can even lead to death.
The harmful microorganisms not only can damage the human body, but also the food we eat.
when mixing primary colours create secondary colours such as green magenta and cyan
ex:computer and TV's
What diseases can they cause?
transmited
Give examples of how the spread of harmful organisms can be prevented.
no light passes through
ex: wood and walls
some lght passes through but not all
ex:stained glass
all light passes through
ex: windows and a plate of glass
Give examples of how harmful organisms can spread.
Research about the main characteristics of the microorganisms and give examples!
Greenhouse gasses being produced by human activities such as burning Fossler fuels
Helps keep the earth at a temperature that can sustain life
When burring something without enough oxygen
A reaction that produces dangerous products
Changing things we do now a days to help prevent climate change in the future
Adjusting our lifestyle and activities to climate change
All plants, animals, and bacteria
Solid rock, soil and minerals
Liquid water, water vapour
Gasses that surround the earth
Enviornmental's conditions that are hopping in a certain place or time
average temperature in a reign or over a long period of time
Microorganisms help in the production of many food items, making medicines, keeping the environment clean, in manufacturing, and in research.
he process by which one or more chemical reactions are performed with the aim of converting a reactant or starting material into a product or multiple products.
During a reaction when the reaction makes teo different compounds
When a element in a reaction is replaced with another element
universal
phenolphthalein
magnesium
bromothymol blue
Blue litmus
Red litmus
Makes OH-
Conducts electricity
Contains metal
Bitter
Makes H2
Contains nonmetals
Conducts electricity's
Dissolves in water
Corrosive
Sour
Microorganisms have a role in waste disposal, agriculture, and nutrient recycling.
Give examples of these types.
2 or more elements the combined to each other to make a new element
when a metal and a non metal combined
attracted by opposite charges
Give examples of bacteria used in the pharmaceutical industry.
Give examples of Microorganisms in food production.
all of the above
4 or more elements that combined to each other
3 or more elements on the table
two elements on the table
single element on the table
There are five types of microorganisms. Out of these five, four can be free-living or parasitic.
There is one that can be only parasitic since it always reproduces inside other living things.
After enumerating them, click on the flags below to mark the ones which can be free-living and the ones that cannot.
Supports the whole microscope
To shine through the specimen for easier seeing
To place the specimen on
Hold the specimen in place
to magnify whatever you are looking at
Sharpen the image being produced though the eye piece
To bring the specimen into near focus
allows you to change the amount of light passing though the microscope
Give a part to carry the microscope by
Magnifies the object on the microscope
protects from desies and transports fats includes; white blood cells and thymus
Controls reproduction includes; ovaries tubes vagina penis testis
Eliminates waste includes; kidney skin bladder and urethra
Controls growth and metabolism includes
Controls body function and coordinates response includes; brain nerves and spine
Transports materials throughout the body includes; heart and blood vessels
Works with the skeletal system to help movement in the body includes; smooth cardiac
Supports body and allows movement includes; bones and cartilage
Ingestion, digestion, absorption of nutrients; includes mouth, esophagus, stomach, liver, and intestines rectum
Exchange of gases; includes Nose and mouth
The brain of the cell
Helps contain all the organelles in the cell (only in plant cells)
The powerhouse
Provides a gel like base to support the organelles
A micro machine for making proteins
Packages useful materials and sends them outside the cell
Breaks down food, waste and other materials.
Type of microorganism
Makes food for the cell
contains everything
This is the last stage of mitosis which is when the wall starts to be built in between the cells to make two new cells
This is the point where the duplicated cells start to part ways an move apart from each other
This is the point where the duplicated DNA and chromosomes are in the middle of the cell getting read to part
The phase of which the cells start to duplicate the DNA located in the nucleus to create two alike cells
The point of the cell cycle of which the cell has the most life
Nervous tissue
responds to stimuli and transmits and stores information.
Muscle tissue
allows movement
Connective tissue
supports and protects structures, forms blood, stores fat and fills empty space
Epithelial tissue
lines body cavities an outer surface of the body and produces sweat
Vascular tissue
transports sugars from the leaves to other parts of the plants
Epidermal tissue
allows the exchange of materials and gases into and out. Of the plants Ground tissue provides support for the stem and stores food and water and in the leaves this is where photosynthesis takes place
Meristematic
unspecialized tissue capable of dividing by mitosis Found in different parts of the plant Responsible for growing new parts of the plants