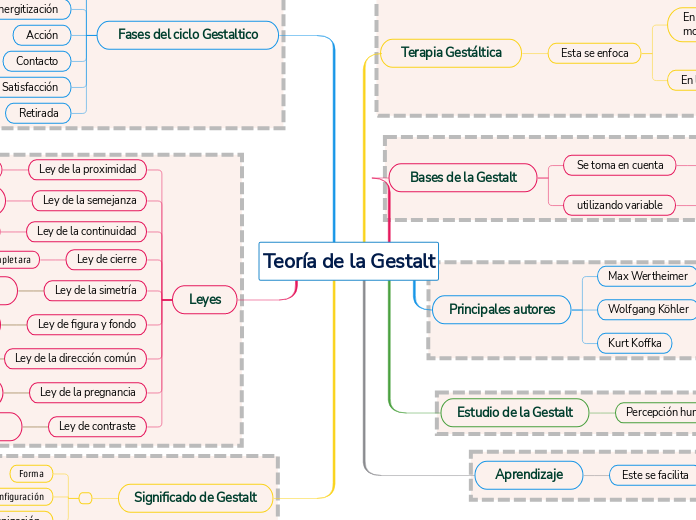
Teoría de la Gestalt
In linguistics, syntax is the set of rules, principles, and processes that govern the structure of sentences in a given language, usually including word order.
Significado de Gestalt
A compound sentence is a sentence that has at least two independent clauses joined by a comma, semicolon or conjunction. An independent clause is a clause that has a subject and verb and forms a complete thought.
Leyes
A complex sentence is a sentence that contains an independent clause and one or more dependent clauses.
An independent clause can stand alone as a sentence, but a dependent clause even though it has a subject and a verb cannot stand alone.
Ley de contraste
The object clause is a phrase on which a verb performs an action. It falls at the end of a sentence, and is governed by a verb or a preposition.
Elementos que se diferencian, tienden a contratar debido a sus singularidades
Ley de la pregnancia
An adverbial clause is a group of two or more words that function as an adverb in a sentence.
La percepción de formas incompletas asociándolas a formas conocidas
Ley de la dirección común
nuestra atención es enfocada en la dirección de los objetos
Ley de figura y fondo
Es la separación de el fondo y los elementos
Ley de la simetría
Es el percibir imágenes simétricas como iguales
Ley de cierre
Attributive clauses serve as an attribute to a noun (pronoun) in the main clause. This noun or pronoun is called the antecedent of the clause.
Si un contorno esta incompleto nuestra mente lo completara
Ley de la continuidad
An appositive clause follows another noun or noun phrase in apposition to it; that is, it provides information that further identifies or defines it.
nuestra mente tiende a seguir patrones aunque estos no existan
Ley de la semejanza
The subject clause is a dependent clause that acts as a subject.
figura parecidas ya sea por tamaño, forma o color se agruparan y percibirán como una totalidad
Ley de la proximidad
A predicative clause may be introduced by conjunctions - that, whether, whether... or, as, as if, as though, because, lest, the way - or connectives.
The latter may be conjunctive pronouns - who, whoever, what, whatever, which - or conjunctive adverbs - where, wherever, when, whenever, how, why.
Elementos cercanos son percibidos cómo grupo o un solo objeto
Fases del ciclo Gestaltico
Retirada
Satisfacción
Contacto
Acción
Energitización
Conciencia
Sensaciones
Aprendizaje
Este se facilita
Al asimilar, comprender e integrar las problemáticas presentadas
Estudio de la Gestalt
Percepción humana
See the example below and try to create your own simple sentences.
Tim drives.
Principales autores
Kurt Koffka
The attribute is defined as a quality or characteristic of a person, place or thing.
Wolfgang Köhler
The predicative is defined as an adjective or noun forming or contained in the predicate.
Its main trait is that it serves to express a property that is assigned to a 'subject'.
For e.g.: The dog is old.
Max Wertheimer
Traditional grammar defines the object in a sentence as the entity that is acted upon by the subject.
Bases de la Gestalt
utilizando variable
Fisiológicas
sociológicas
Cognitivas
Motivacionales
Se toma en cuenta
El campo biopsicosocial
Interacción organismo ambiente
Terapia Gestáltica
Esta se enfoca
En las dificultades del ahora
Aprendiendo y superando
Tomando conciencia y reposabilidad de nuestros sentimientos y acciones
Auto descubrimiento
crecimiento personal
En lo que se piensa y siente en el momento
concientizando la realidad, dándole mas importancia al "como" "porque" y "para que"