par Helena Nodilo Il y a 4 années
498
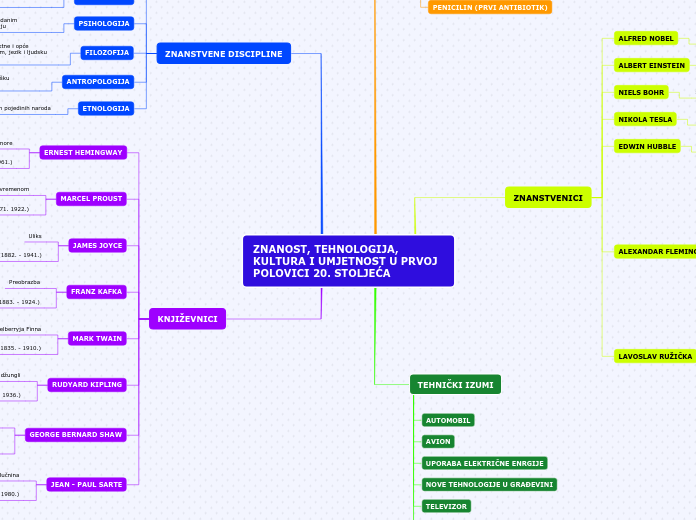
ZNANOST, TEHNOLOGIJA, KULTURA I UMJETNOST U PRVOJ POLOVICI 20. STOLJEĆA
par Helena Nodilo Il y a 4 années
498

Plus de détails
In linguistics, syntax is the set of rules, principles, and processes that govern the structure of sentences in a given language, usually including word order.
Attributive clauses serve as an attribute to a noun (pronoun) in the main clause. This noun or pronoun is called the antecedent of the clause.
An appositive clause follows another noun or noun phrase in apposition to it; that is, it provides information that further identifies or defines it.
The subject clause is a dependent clause that acts as a subject.
A predicative clause may be introduced by conjunctions - that, whether, whether... or, as, as if, as though, because, lest, the way - or connectives.
The latter may be conjunctive pronouns - who, whoever, what, whatever, which - or conjunctive adverbs - where, wherever, when, whenever, how, why.
The object clause is a phrase on which a verb performs an action. It falls at the end of a sentence, and is governed by a verb or a preposition.
See the example below and try to create your own simple sentences.
Tim is driving the red car.
See the example below and try to create your own simple sentences.
Tim is the driver.
See the example below and try to create your own simple sentences.
Tim is driving the car with his mother.
See the example below and try to create your own simple sentences.
Tim drives the car.
See the example below and try to create your own simple sentences.
Tim drives.
An adverbial is an individual word (that is, an adverb), a phrase, or a clause that can modify a verb, an adjective, or a complete sentence.
A complex sentence is a sentence that contains an independent clause and one or more dependent clauses.
An independent clause can stand alone as a sentence, but a dependent clause even though it has a subject and a verb cannot stand alone.
Subtopic
Radilo se o svojevrsnom slučajnom otkriću. Naime, on je imao razmjerno neuredne navike u laboratoriju. Kad se te godine vratio s godišnjeg odmora koji je proveo s obitelji, u laboratoriju je primijetio hrpu kultura bakterija koje je prethodno ostavio. Neke od kultura bile su zagađene gljivicama. Fleminga je zaintrigirala činjenica da kolonije bakterija stafilokoka nisu rasle u neposrednoj okolini gljivica.Nakon analize tih bakterijskih kultura Fleming je zaključio da jedna vrsta gljivica, točnije plijesan iz roda Penicillium sprečava razvoj bakterija. Iz te je plijesni izlučio tvar koju je nazvao penicillin, upravo prema spomenutom latinskom nazivu roda plijesni Penicillium.
Prije otkrića penicilina, mnogi su ljudi umrli ili nisu izliječili ni od najjednostavnijih infekcija.
prvi antibiotik - ušao u uporabu 1941.
Alexander Fleming (1928.)
The attribute is defined as a quality or characteristic of a person, place or thing.
The predicative is defined as an adjective or noun forming or contained in the predicate.
Its main trait is that it serves to express a property that is assigned to a 'subject'.
For e.g.: The dog is old.
Traditional grammar defines the object in a sentence as the entity that is acted upon by the subject.
The indirect object identifies the person/thing for whom/which the action of the verb is performed.
The indirect object is usually a person or a thing.
The predicate of a sentence is the part that modifies the subject in some way. Because the subject is the person, place, or thing that a sentence is about, the predicate must contain a verb explaining what the subject does and can also include a modifier.
The subject of a sentence is the person, place, thing, or idea that is doing or being something. You can find the subject of a sentence if you can find the verb.
Ask the question, 'Who or what 'verbs' or 'verbed'?' and the answer to that question is the subject.
A compound sentence is a sentence that has at least two independent clauses joined by a comma, semicolon or conjunction. An independent clause is a clause that has a subject and verb and forms a complete thought.
An adverbial clause is a group of two or more words that function as an adverb in a sentence.