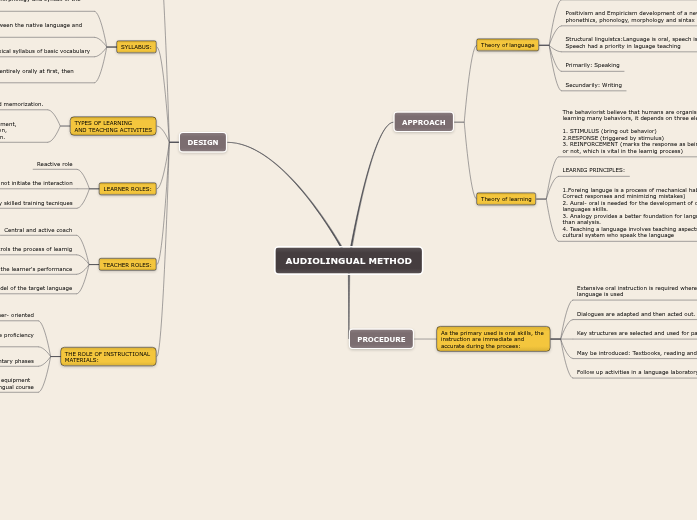
AUDIOLINGUAL METHOD
APPROACH
Theory of language
Audioligualism (1950) derived from structural linguistics
Positivism and Empiricism development of a new intrest in phonethics, phonology, morphology and sintax
Structural linguistcs:Language is oral, speech is language. Speech had a priority in laguage teaching
Primarily: Speaking
Secundarily: Writing
Theory of learning
The behaviorist believe that humans are organism capable of learning many behaviors, it depends on three elements:
1. STIMULUS (bring out behavior)
2.RESPONSE (triggered by stimulus)
3. REINFORCEMENT (marks the response as being appropriate or not, which is vital in the learnig process)
LEARNIG PRINCIPLES:
1.Foreing languge is a process of mechanical habit formation( Correct responses and minimizing mistakes)
2. Aural- oral is needed for the development of other languages skills.
3. Analogy provides a better foundation for language learning than analysis.
4. Teaching a language involves teaching aspects of the cultural system who speak the language
PROCEDURE
As the primary used is oral skills, the instruction are immediate and accurate during the procees:
Extensive oral instruction is required where the target language is used
Dialogues are adapted and then acted out.
Key structures are selected and used for pattern drills.
May be introduced: Textbooks, reading and writing activities.
Follow up activities in a language laboratory or vocabulary
DESIGN
OBEJTIVES:
Short-Range Objectives:
Listening comprehension
Accurate pronunciation
Recognition of speech symbols
The hability to reproduce these symbols in writing
Long-range objectives:
Language of the native speaker. Knowledge of a second language.
Language is primarily speech in Audiolingual theory
SYLLABUS:
Contains items of phonology, morphology and syntax of the language.
Analysis of the differences between the native language and the target language
Lexical syllabus of basic vocabulary
The language may be present entirely orally at first, then written presentations.
TYPES OF LEARNING
AND TEACHING ACTIVITIES
Diologues:Used for repetition and memorization.
Drills:Repetition,Inflection, replacement,restatement, completion, transposition, expansion, contraction, transformation, integration rejoinder, restoration.
LEARNER ROLES:
Reactive role
They do not initiate the interaction
They can be directed by skilled training tecniques
TEACHER ROLES:
Central and active coach
Controls the process of learnig
Monitors and controls the learner's performance
Model of the target language
THE ROLE OF INSTRUCTIONAL
MATERIALS:
Teacher- oriented
Help the teacher developing language proficiency
on the student
The text book is not used in the elementary phases
The recorder and the audiovisual equipment
are the central role in the audiolingual course