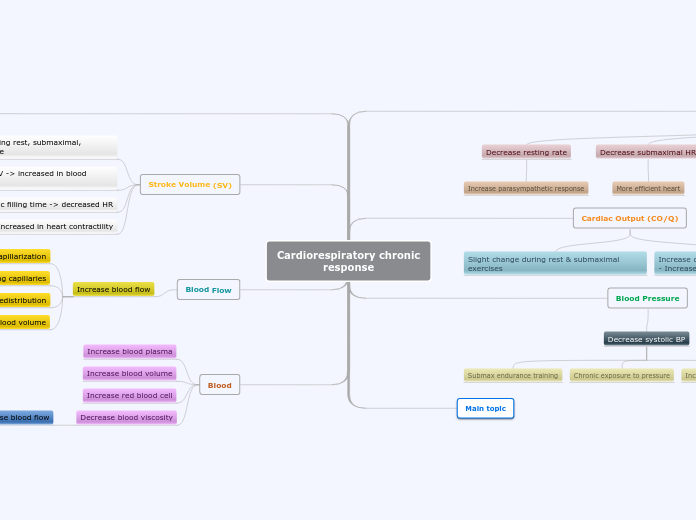
Cardiorespiratory chronic
response
Chronic exercise (heart rate)
Decrease resting rate
Increase parasympathetic response
Decrease submaximal HR
More efficient heart
Decrease maximal HR
Optimum SV to maximize CO
Decrease steady state HR (faster)
Decrease recovery HR (faster)
Cardiac Output (CO/Q)
Slight change during rest & submaximal exercises
Increase during maximal exercises
- Increase in SV
Blood Pressure
Decrease systolic BP
Submax endurance training
Chronic exposure to pressure
Increase arteriole dilation at active muscle
Main topic
Main toc
Stroke Volume (SV)
Increase SV during rest, submaximal, maximal exercise
Increased in EDV -> increased in blood plasma
Greater diastolic filling time -> decreased HR
Increased in heart contractility
Blood Flow
Increase blood flow
Increase capillarization
Increase opening of existing capillaries
Increase in blood redistribution
Increase blood volume
Blood
Increase blood plasma
Increase blood volume
Increase red blood cell
Decrease blood viscosity
Increase blood flow