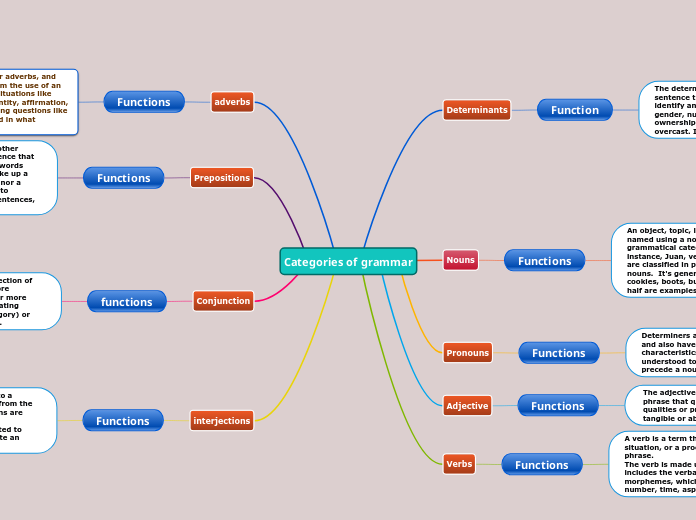
Categories of grammar
Determinants
Function
The determiners are aspects of the sentence that are included in the name to identify and restrict its meaning, such as gender, number, spatial position, ownership, and so on. The day started off overcast. In the yard, the students had fun.
Example
Articles (a, an, the), cardinal and ordinal numbers (first, second, third...), demonstratives (this, that, these, those), partitives (some of, piece of, and others), quantifiers (most, all, and others), difference words (other, another), and possessive determiners (my).
Nouns
Functions
An object, topic, location, or concept is named using a noun, which is a grammatical category or word class. For instance, Juan, vehicle, home, etc. Nouns are classified in proper and common nouns. It's generally a single word, but cookies, boots, bus stop, and hour and a half are examples of nouns.
Example
Person: boy, gentleman, student, David, Loren. place: farm, school, city, countryside, Peru, Colombia. thing: chair, vehicle, apple, donkey, concert, hate, cat, pencil.
Pronouns
Functions
Determiners and pronouns are connected and also have unusual sentence distribution characteristics. In fact, all pronouns are understood to be determiners that do not precede a noun.
Example
I, you, she, he , it we , they. Her, his, him, us, them , our etc.
Adjective
Functions
The adjective is a word or portion of a phrase that qualifies a noun by expressing qualities or properties given to it, whether tangible or abstract.
Example
Fantastic,Perfect, Huge.
Verbs
Functions
A verb is a term that describes an action, a situation, or a process that occurs in a phrase.
The verb is made up of a lexeme, which includes the verbal meaning, and morphemes, which represent the person, number, time, aspect, mode, and accent.
Example
Irregular verbs
regular verbs
adverbs
Functions
A verb, an adjective, other adverbs, and even sentences derive from the use of an adverb. Adverbs explain situations like mode, location, time, quantity, affirmation, doubt, and so on, answering questions like when?, where?, how?, and in what situation?
Example
Eventually, Perfectly
Prepositions
Functions
Its aim is to introduce a term, in other words, a nominal group or a sentence that provides an ordered collection of words combines the many parts that make up a sentence. It has neither a gender nor a number: single or plural, in order to produce logical and meaningful sentences, prepositions must be used.
Example
Along, Behind, Beside, Below
Conjunction
functions
Conjunctions are words or a collection of terms used to connect two or more components in a phrase or two or more sentences, which can be coordinating (when they share the same category) or subordinating (when they don't).
Example
Dilemmas. For example: or, or.
Adversative. For example: but, although, on the contrary, instead, however, despite.c
Explanatory. For example: that is, that is, this is.
interjections
Functions
Interjection is a term that refers to a certain type of phrase. It derives from the Latin word interiectio. Interjections are made up of elements that allow exclamatory sentences to be created to communicate feelings or to indicate an appellative speech behavior.
Examples
Awesome! Oh! My God! That´s interesting!