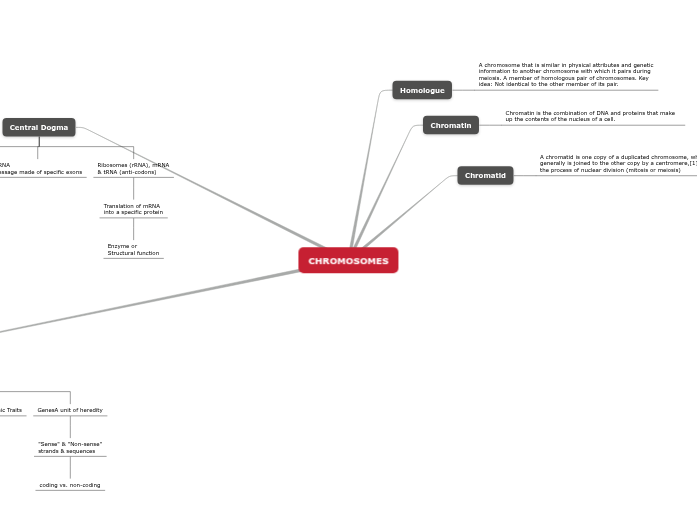
CHROMOSOMES
Homologue
A chromosome that is similar in physical attributes and genetic information to another chromosome with which it pairs during meiosis. A member of homologous pair of chromosomes. Key idea: Not identical to the other member of its pair.
Chromatin
Chromatin is the combination of DNA and proteins that make up the contents of the nucleus of a cell.
Chromatid
A chromatid is one copy of a duplicated chromosome, which generally is joined to the other copy by a centromere,[1] for the process of nuclear division (mitosis or meiosis)
Central Dogma
DNA (Gene)
Transcription
Introns (not translated)
& Exons (translated)
mRNA
message made of specific exons
Ribosomes (rRNA), mRNA
& tRNA (anti-codons)
Translation of mRNA
into a specific protein
Enzyme or
Structural function
Heredity
Cell Division
Mitosis
Somatic CellClones
Binary fission (prokaryotes)
Fetal development (eukaryotes)
Growth or Repair (eukaryotes)
Meiosis
Gametic Cell (Sperm or Egg)
Mendelian Laws ofSimple Inheritance
Dominance
Independent Assortment
Segregation
Co-dominance
Incomplete Dominance
Multiple Alleles &Polygenic Traits
GenesA unit of heredity
"Sense" & "Non-sense"
strands & sequences
coding vs. non-coding