Coasts
Land Forms Produced by Coastal Processes
Cliffs and shore platforms
A cliff is formed when waves repeatedly pound against a rocky coast. Causing the weakend rocks to form lines of weakness. Waves erode the coast to cut a notch along the lines of weakness. The notch may be eroded to form a cave. The overhanging part of the notch or cave eventually collapses.
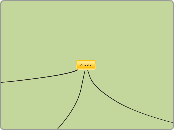
Headlands
Formation of headlands
More resistant rocks will form headlands
Bays
Less resistant rocks froms bays
Beaches
Beaches form when waves tides, or currents bring and deposits materials onto the shore.
Spits
When longshore cirrents encounter a bay or a bend in the coast with shallow sheltered water, the materials will be deposited along the direction of the long shore drift.This is known as a spit.
Tombolos
A tombolo is an extention of the coastline made up of mainly sand and other materials tha join an offshore island to main land
Coastal Protection measures
Hard engineering
Hard engineering refers to the construction of structures such as seawalls, beackwaters, groynes and gabions

Seawalls
Effectiveness
A seawall is usually made out of concrete, which absorbs the energy of the wave
Ineffectiveness
As waves break against the sea wall, the wave is redirected backwards resuslting in a strong backwash which would wear away the base of the seawall causing it to weaken and eventually collasp[e

Breakwaters
Ineffectiveness
Breakwaters are unable to provide complete protection as the leave areas of the coast unprotected, which are more prone to erosion.
Effectiveness
breakwaters are granite walls built parallelto the coast. It creates a zone of shallow water between itself and the coast, such that the waves will break before reaching the coast.

Groynes
Effectiveness
A groyne is a low wall built at right angles to prevent materials from being transported away by the longshore drift .Transported materials accumulate on the side of the groynefaceing the longshore drift.
Ineffectives
The materials deposits by the longshore drift would not be replenished at the other side of the groyne. Hence the beach further down the coast may be eroded away.
Gabions
Gabions are rocks stored in wire chages to form a wall to protect the coast from erosion and other coastal protection such as seawalls
Ineffectivesness
Gabions are temporial features as they last ony to about 15 years whereas seawalls, breakwaters and groynes lasts for about 30 years.
Gabions are much cheaper compared to other coastal protection measures such as seawalls, breakwaters and groynes.
Gabions can be easily destroyed by powerfull waves during storms and the wire rusts easily.
Soft engineering
Soft Engineering is involves applying the knowledge of natural process to stabilise the coast and reduce erosion
Stabilising coastal dunes
Effectivenesss
Planing vegetation such as marram grass along coasts, roots of vegetation trap and bind the sand together, preventing sand from being blown inland
Ineffectivenesss
Human activities sucha as property development ad recreational activities have to be minimised along these coasts
Planting Mangroves along the shores
Effectivenesss
Planting mangroves helps to protect coasts from erosion as many moagrove trees have prop roots or kneed roots that anchor the tress frimly in the soil
Ineffectivenesss
As young mangrove trees are fragile, mangrove planting requires cooperation of the local people living in the area.
Beach nurishment
Effectivenesss
Adding large amounts of sand to a beach that have been eroded from a beach to replenish sand eroded by the longshore drift.
Ineffectivenesss
Lasts only for about 10 years
Cost is high for beach quality sand
Encouraging growth of coral reefs
Effectivenesss
Reduces coastal erosion by reducing speeds of waves as they approach the shores.
Inffectivenesss
It requires constant effort from various groups of people
Corals can only grow well in clear waters
Coastal Processes
Erosion
Currents as agents of erosion
During high tides, water extends up the coast.
During low tides, the water retreats down the coast
Waves as an agent of erosion
large waves cause coastal erosion
High-energy waves have a backwash stronger than the swas.Causing more materials to be removed from the beach instead of being deposited.
A wave is a rising and falling movement of the water surface.It is usually produced by winds blowing across the sea or ocean
Transport
Waves and currents as agents of transportation
Waves approaches the coast at an angle, the swash carries sediments up onto the coast at that angle. The backswash then carries the sediments back into the sea
Longshore Drift
Deposition
Waves as an agent of deposition
Low-energy waves have a swash that is stronger than the backwash. this occurs on a gently slopping beach. When the backwash returns to the sea, some sediments are left on the coast. Low-energy waves are also called constructive waves.