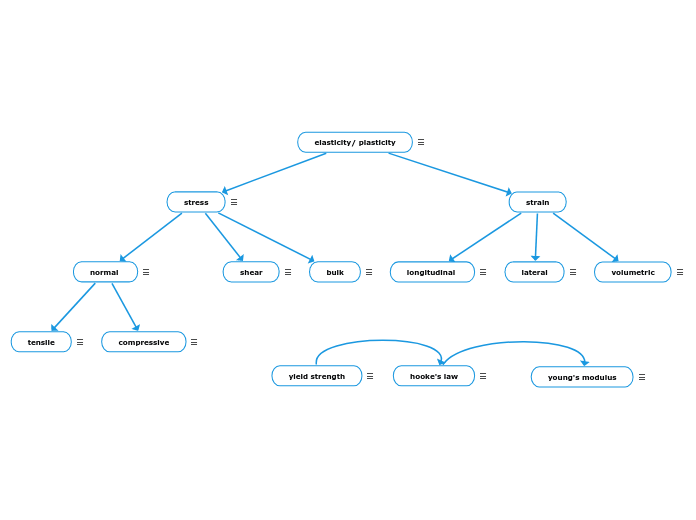
elasticity/ plasticity
Elasticity is the property of a body to recover its original configuration (shape and size) when you remove the deforming forces. Plastic bodies do not show a tendency to recover to their ori ginal configuration when you remove the deforming forces.Plasticity is the property of a body to lose its property of elasticity and acquire a permanent deformation on the removal of deforming force.
stress
stress is the force acting on the unit area of a material.
normal
When a force acts perpendicular (or "normal") to the surface of an object, it exerts a normal stress
tensile
Tensile Stress = Force / Cross-sectional Area. Tensile stress measures the strength of a material; therefore, it refers to a force that attempts to pull apart or stretch a material
compressive
Compressive stress is a force that causes a material to deform to occupy a smaller volume.
shear
When a force acts parallel to the surface of an object, it exerts a shear stress.
bulk
bulk stress causes a change in the volume of the object or medium and is caused by forces acting on the body from all directions, perpendicular to its surface.
strain
longitudinal
Change in the length to the original length of an object. It is caused due to longitudinal stress
lateral
The lateral strain is the ratio of change in the diameter of the wire to its change in diameter in longitudinal direction.
volumetric
Volumetric strain is defined as the ratio of change in volume of a body to its original volume due to the application of some external deforming forces
hooke's law
Hooke's law states that the strain of the material is proportional to the applied stress within the elastic limit of that material
young's modulus
The Young's modulus (E) is a property of the material that tells us how easily it can stretch and deform and is defined as the ratio of tensile stress (σ) to tensile strain (ε).
yield strength
The magnitude of the stress at which the transition from elastic to plastic occurs is known as the yield strength