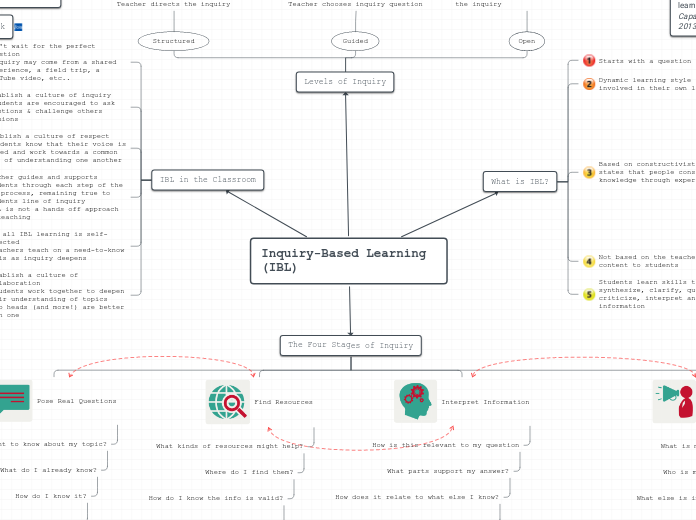
Inquiry-Based Learning (IBL)
Levels of Inquiry
Structured
Teacher directs the inquiry
Teacher provides question and step
by step instructions
Important to teach students the process
Guided
Teacher chooses inquiry question
Students establish direction and methods of their inquiry
Teacher guides the inquiry
Open
Students take lead in establishing
the inquiry
Teacher has supportive role
Requires higher order thinking
The Four Stages of Inquiry

Pose Real Questions
What do I want to know about my topic?
What do I already know?
How do I know it?
What do I need to know?
What could the answer be?

Find Resources
What kinds of resources might help?
Where do I find them?
How do I know the info is valid?
Who is responsible for the info?
What other info is there?

Interpret Information
How is this relevant to my question
What parts support my answer?
How does it relate to what else I know?
What parts do not support my answer?
Does it raise new questions?

Report Findings
What is my main point?
Who is my audience?
What else is important?
How does it connect?
How do I use media to express my message?
What is IBL?
Starts with a question
Dynamic learning style as students are involved in their own learning
Based on constructivist theory that states that people construct their own knowledge through experience

CONSTRUCTIVISTS believe that students learn better when they:
- Ask questions
- Investigate solutions
- Create new knowledge as they gather information
- Discuss their discoveries and explanations
- Reflect on new knowledge
Not based on the teacher delivering content to students
Students learn skills to research, synthesize, clarify, question, debate, criticize, interpret and evaluate information
IBL in the Classroom
Don't wait for the perfect
question
-inquiry may come from a shared experience, a field trip, a YouTube video, etc..
Establish a culture of inquiry
-students are encouraged to ask
questions & challenge others opinions
Establish a culture of respect
-students know that their voice is
valued and work towards a common
goal of understanding one another
Teacher guides and supports students through each step of the IBL process, remaining true to students line of inquiry
-IBL is not a hands off approach to teaching
Not all IBL learning is self-directed
-teachers teach on a need-to-know basis as inquiry deepens
Establish a culture of collaboration
-students work together to deepen
their understanding of topics
-two heads (and more!) are better
than one
Coupled Inquiry =
Teachers start with one level and move to another level during the inquiry process

Inquiry-based learning is an approach to teaching and learning that places students’ questions, ideas and observations at the centre of the learning experience.
Capacity Building Series, Inquiry Learning, May 2013, p. 2