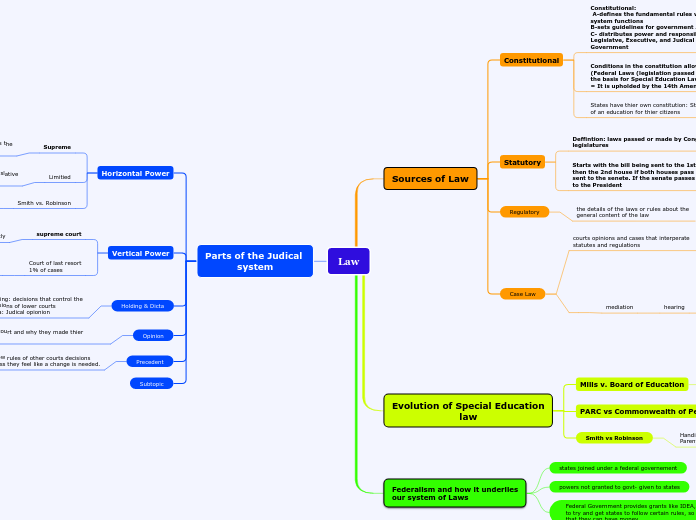
Law
Sources of Law
Constitutional
Constitutional:
A-defines the fundamental rules which the american system functions
B-sets guidelines for government Actions
C- distributes power and responsibility among the Legislatve, Executive, and Judical branches of Government
Conditions in the constitution allow for Statutes (Federal Laws (legislation passed by congress). This is the basis for Special Education Laws (IDEA & 504)
= It is upholded by the 14th Amendment
States have thier own constitution: States instruct the supply of an education for thier citizens
Statutory
Deffintion: laws passed or made by Congress and state legislatures
Starts with the bill being sent to the 1st house
then the 2nd house if both houses pass it it is
sent to the senete. If the senate passes it goes
to the President
If the president says no
then it goes through process
again.
Regulatory
the details of the laws or rules about the
general content of the law
Case Law
courts opinions and cases that interperate
statutes and regulations
mediation
hearing
appeal
Supreme
9 judges
nation/other states pay attention
Appealate
3 judges
nieghboring states pay attention
District
1 judge
discovery stage
Evolution of Special Education
law
Mills v. Board of Education
Special Education under 14th Amendment
PARC vs Commonwealth of Pennsylvania
Special Education under 14th Amendment
Smith vs Robinson
Handicapped Children's Protection Act-
Parents collect attorney's fees
Federalism and how it underlies
our system of Laws
states joined under a federal governement
powers not granted to govt- given to states
Federal Government provides grants like IDEA,
to try and get states to follow certain rules, so
that they can have money.
Parts of the Judical
system
Horizontal Power
Supreme
Court interpretes the
constitution
Harder to change
Limitied
Courts interprete legislative
laws
laws can be changed
or altered if disagreed
with
Smith vs. Robinson
IDEA
Vertical Power
supreme court
Judges and justices, see if
they applied the law correctly
fact finding
Court of last resort
1% of cases
appelate of intermediate court
12 judeges- 3 hear the case
trial court/ District
court
Holding & Dicta
Holding: decisions that control the
decisions of lower courts
Dicta: Judical opionion
Opinion
States the ruling of the court and why they made thier decision
Precedent
Follow rules of other courts decisions
unless they feel like a change is needed.
Subtopic