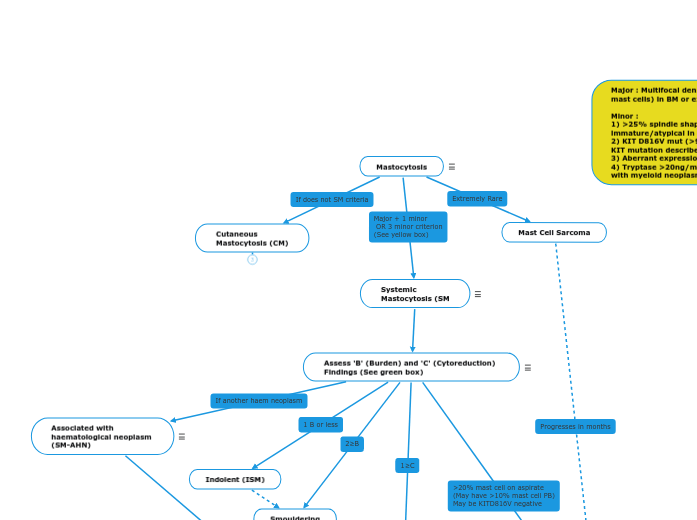
Assess 'B' (Burden) and 'C' (Cytoreduction) Findings (See green box)
B Findings>30% bone marrow involvement and tryptase >200ng/mLDysplasia or proliferation in other lineages, but does not meet definition of another myeloid neoplasm. And with relatively normal blood count. Hepatomegaly (without liver dysfunction), Splenomegaly (without hypersplenism), lymphadenopathyC FindingsMast cell infiltration related cytopenia (Hb < 100, PLT < 100, ANC < 1.0)Hepatomegaly with impaired liver function, portal hypertension, ascites. Osteolytic lesions (with or without fractures)Palpable splenomegaly with hypersplenismMalabsorption due to GI mast cell infiltrate.
Associated with
haematological neoplasm
(SM-AHN)
CMML most common, but can be MDS, MPN, MDS/MPN, AMLLymphoma and myeloma rare.KITD816V common, and can be detected in the non-mast cell neoplasm as well.
Major : Multifocal dense infiltrate (≥15 mast cells) in BM or extracut. organ
Minor :
1) >25% spindle shape, or >25% immature/atypical in BM
2) KIT D816V mut (>90% +ve, nb other KIT mutation described)
3) Aberrant expression CD25 +/- CD2
4) Tryptase >20ng/mL unless associated with myeloid neoplasm.
Midotaurin (ORR 60%)
Cladribine (ORR 50%)
?Avapritinib (ORR 77%)
?AlloSCT
rKIT D816V resistant to Imatinib and masatinibBut for KIT D816V negative patients imatinib can be usedMidostaurinPivotal Phase 2 TrialAvapritinibPhase 1 trialUncertain whether these medication actually change OS. Difficult to determine due to heterogeneity of patients with AHN. It is believed that OS is determined by AHN rather than ASM.
B Findings
>30% bone marrow involvement and tryptase >200ng/mL
Dysplasia or proliferation in other lineages, but does not meet definition of another myeloid neoplasm. And with relatively normal blood count.
Hepatomegaly (without liver dysfunction), Splenomegaly (without hypersplenism), lymphadenopathy
C Findings
Mast cell infiltration related cytopenia (Hb < 100, PLT < 100, ANC < 1.0)
Hepatomegaly with impaired liver function, portal hypertension, ascites.
Osteolytic lesions (with or without fractures)
Palpable splenomegaly with hypersplenism
Malabsorption due to GI mast cell infiltrate.