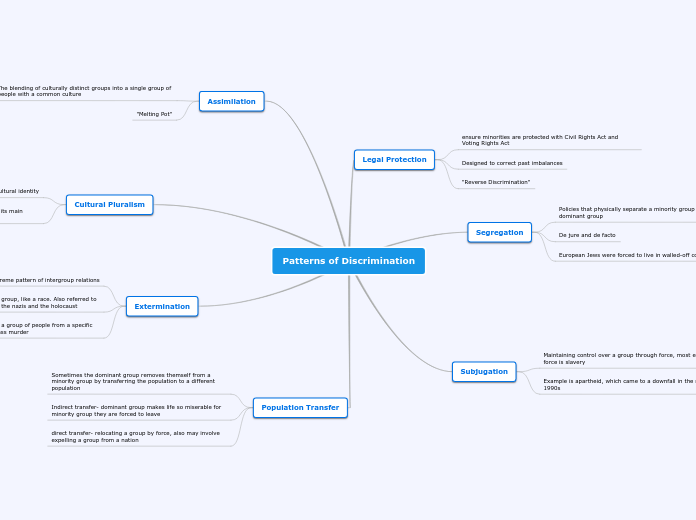
Patterns of Discrimination
Legal Protection
ensure minorities are protected with Civil Rights Act and Voting Rights Act
Designed to correct past imbalances
"Reverse Discrimination"
Segregation
Policies that physically separate a minority group from the dominant group
De jure and de facto
European Jews were forced to live in walled-off communities
Subjugation
Maintaining control over a group through force, most extreme force is slavery
Example is apartheid, which came to a downfall in the mid 1990s
Assimilation
The blending of culturally distinct groups into a single group of people with a common culture
"Melting Pot"
Cultural Pluralism
Allows each group to keep its cultural identity
Switzerland has 3 national languages for each of its main ethnic groups
Extermination
Most extreme pattern of intergroup relations
Goal is the destruction of a group, like a race. Also referred to as a genocide, for example the nazis and the holocaust
Ethnic cleansing: removing a group of people from a specific area through terror and mass murder
Population Transfer
Sometimes the dominant group removes themself from a minority group by transferring the population to a different population
Indirect transfer- dominant group makes life so miserable for minority group they are forced to leave
direct transfer- relocating a group by force, also may involve expelling a group from a nation