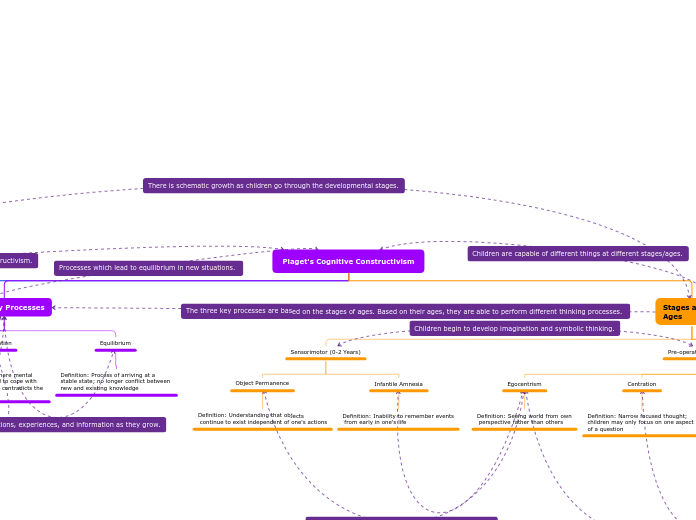
Piaget's Cognitive Constructivism
Schema Theory
Schema
Definition: Unit of knowledge,
understanding, skills
Beliefs
Definition: Connects different
knowledge to make meaningful links
between discrete pieces of info
Literary Connections
Methods: Text-to-self,
Text-to-text, and Text-to-world
Three Key Processes
Assimiliation
Definition: Process where new
information is incorporated into
existing schemas
Accomodation
Definition: Process where mental
structures are altered to cope with
new experiences that contradicts the
existing model
Equilibrium
Definition: Process of arriving at a
stable state; no longer conflict between
new and existing knowledge
Stages at Ages
Sensorimotor (0-2 Years)
Object Permanence
Definition: Understanding that objects
continue to exist independent of one's actions
Infantile Amnesia
Definition: Inability to remember events
from early in one's life
Pre-operational (2-7 Years)
Egocentrism
Definition: Seeing world from own
perspective rather than others
Centration
Definition: Narrow focused thought;
children may only focus on one aspect
of a question
Reversibility
Definition: Ability to recognize that
numbers/objects can be changed
and return to original condition
Theory of Mind
Definition: An understanding of mental
states such as feelings, desires, and
beliefs and the causal role they play in
human behaviour
False Belief
Definition: Realization that people
can hold beliefs that are not true
Joint Attention and Lying
Concrete Operational (7-11 years)
Definition: Children able to use
logical thought about physical operations
Conservation
Definition: Able to realize that
two equal quantities are the same
even if the appearance of one changes
Formal Operation (11+/Adolescence)
Definition: Able to think abstractly
although it is limited by lack of depth
and breadth in knowledge