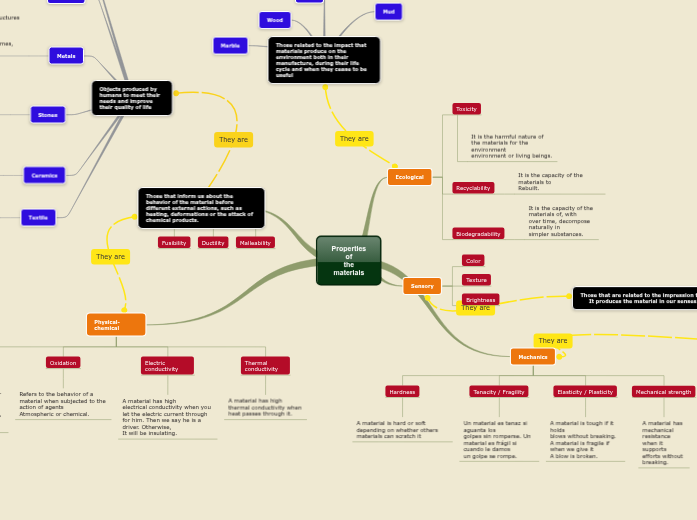
Properties of
the materials
Ecological
Toxicity
It is the harmful nature of the materials for the environment
environment or living beings.
Recyclability
It is the capacity of the materials to
Rebuilt.
Biodegradability
It is the capacity of the materials of, with
over time, decompose naturally in
simpler substances.
Sensory
Color
Texture
Brightness
Mechanics
Hardness
A material is hard or soft depending on whether others
materials can scratch it
Tenacity / Fragility
Un material es tenaz si aguanta los
golpes sin romperse. Un material es frágil si cuando le damos
un golpe se rompe.
Elasticity / Plasticity
A material is tough if it holds
blows without breaking. A material is fragile if when we give it
A blow is broken.
Mechanical strength
A material has mechanical resistance
when it supports efforts without breaking.
Technological
Fusibility
Ductility
Malleability
Physical-chemical
Transparency
According to the behavior of the materials
against the light they are classified as: transparent, translucent and
opaque.
Oxidation
Refers to the behavior of a
material when subjected to the action of agents
Atmospheric or chemical.
Electric conductivity
A material has high
electrical conductivity when you let the electric current through
for him. Then we say he is a driver. Otherwise,
It will be insulating.
Thermal conductivity
A material has high
thermal conductivity when heat passes through it.
Objects produced by humans to meet their needs and improve their quality of life
Wood
It is used as fuel, for
paper industry, for the manufacture of
furniture, building elements
Plastics
They are used to manufacture
pipes, packaging, toys, containers,
cable sheathing
Metals
They are used for structures and
machine parts, tools,
components
electronic window frames,
furniture
Stones
They are normally used as materials
of construction.
Ceramics
A brick and a tile, a botijo, a crockery
and even a sink are products
made with ceramic materials
Textile
Wool, cotton, are textile materials
silk, linen, or nylon and lycra.