Matter and Measuremnt
Characteristics of different states of matter
The definition of a Liquid: definite size but no definite shape. Molecules are loosely linked.
What is the change of a Liquid to a Solid? Freezing or Solidification
What is the change of a Liquid to a Gas? Evaporation
the definition of a solid is: that it has a definite size definite shape. Molecules are tightly packed together.
What is the change of a Solid to a Liquid? Melting
What is the change of a Solid to a Gas? Sublimation
the definition go Gas: no definite size and no definite shape. Molecules move freely.
What is the change of a Gas to Liquid? Condensation
what is the change from gas to solid? deposition

Physical and Chemical property
Physical properties can be observed or measured without changing the composition of matter. Physical properties are used to observe and describe matter.
Melting Point: As solid matter is heated it eventually melts or changes into a liquid state at the melting point.
Ice (a solid form of water) melts at 0 oC and changes to the liquid state. Boiling Point: As the liquid matter is heated further it eventually boils or vaporizes into a gas at the boiling point.
Liquid water boils and changes into a gas, usually called steam or water vapor at 100 oC. In all three states the same molecules of water (H2O) are present.
Physical properties include: appearance, texture, color, odor, melting point, boiling point, density, solubility, polarity, and many others.
A physical change takes place without any changes in molecular composition. The same element or compound is present before and after and during the change the change.
Chemical properties are properties that can be measured or observed only when matter undergoes a change to become an entirely different kind of matter.
Reactivity is a part of chemical properties because it is the ability of matter to combine chemically with other substances. Some kinds of matter are extremely reactive; others are extremely unreactive.
For example, the ability of iron to rust can only be observed when iron actually rusts. When it does, it combines with oxygen to become a different substance called iron oxide. Iron is very hard and silver in color, whereas iron oxide is flakey and reddish brown. Besides the ability to rust, other chemical properties include reactivity and flammability.
Examples of Chemical Change are: toxicity.
oxidation.
flammability.
heat of combustion.
enthalpy of formation.
chemical stability under specific conditions.
radioactivity.
1.1 What is matter?

Matter is any object that has mass and can take you space/volume
All things — living and nonliving — are made of matter, and all matter is composed of tiny particles called atoms
Matter stores energy: the atoms and molecules represent stored energy. The type of energy is chemical energy stored in food. Matter and energy travel together in food along food chains.
Matter can exist in three states: Liquid, solid, gas
Matter can change states, commonly as a result of temperature and pressure
Chemistry is the study of matter
Distinguishing the difference between properties
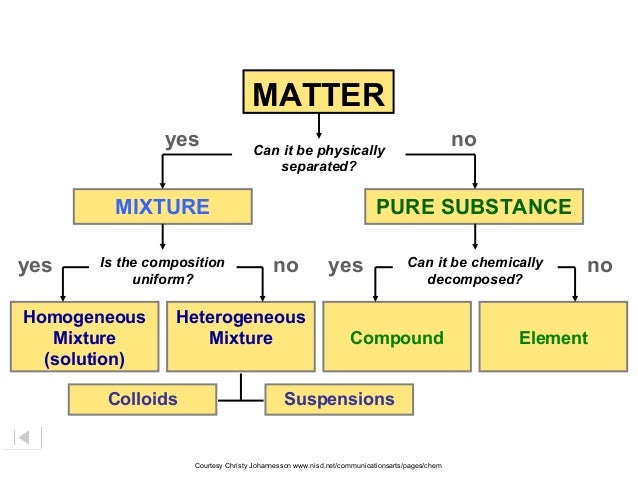
mixtures and pure substance
Mixtures are composed of more than one substance andcan be physically separated
example of a Mixture is salad dressing
pure substances are composed of only one substance and cannot be physically separated (e.g. water)
Element and compound
elements are made up of atoms of the same kind (e.g. the carbon element is made up of carbon atoms)
Compounds are made up of two or more different kinds of atoms
Examples of compounds are water (H2O) and table salt (NaCl)
Homogeneous and heterogeneous
Homogenous mixtures have uniform composition (e.g. sugar in water). The smaller component (sugar) is completely dissolved in the larger component (water)
Homogenous mixtures have uniform composition (e.g. sugar in water). The smaller component (sugar) is completely dissolved in the larger component (water)