
Snow leopards^
Animal systems (just like like we do)
Circulatory system
to a snow leopard, is the same!
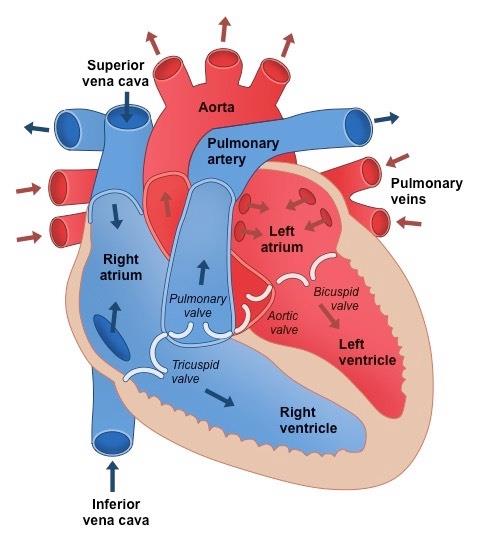
a 4 chambered heart, a closed circulatory system, arteries, veins and capillaries,
A system which circulates your blood, oxygen and nutrients throughout your body
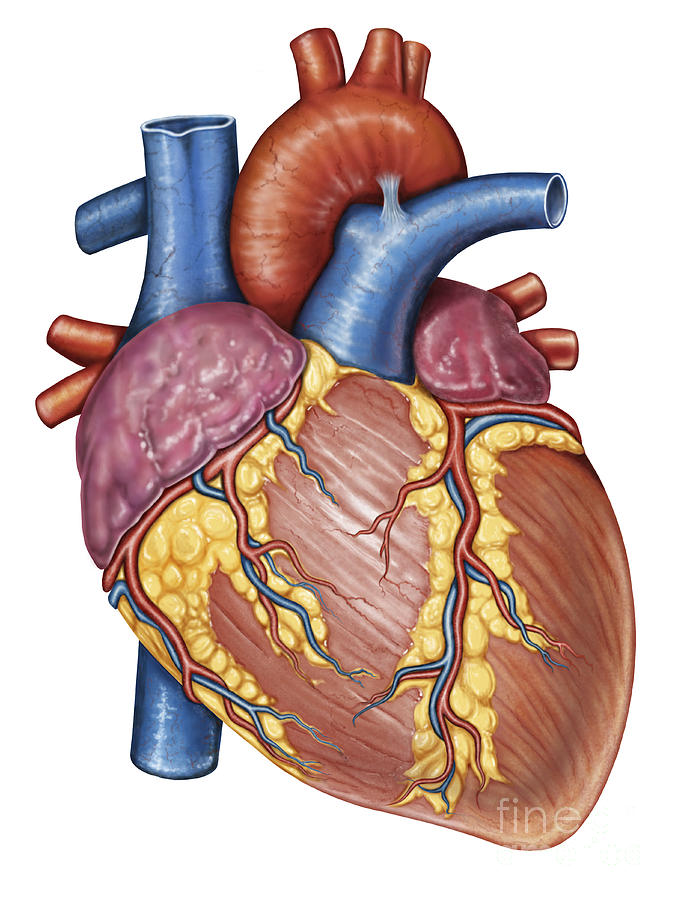
The heart
pumps blood throughout the body and is vital, human hearts are four chambered
The left ventricle
they then go through a valve to the left ventricle, and out your aorta (the biggest artery) to your body
the left atrium
is where the now oxygenated blood comes back from the lungs through the pulmonary veins
the right ventricle
the deoxygenated blood goes next through the valve, to the right ventricle, then out through the pulmonary artery to the lungs to carry back oxygen
the right atrium
the deoxygenated blood comes in from our body, and goes through the superior and inferior vena cava (the biggest vein in the body)
The blood vessels (of which there are 3 types)
The artery
takes oxygenated blood away from heart and to your body
the vein
carries deoxygenated blood from body to heart
the capillary
takes oxygen, nutrients and blood throughout the body
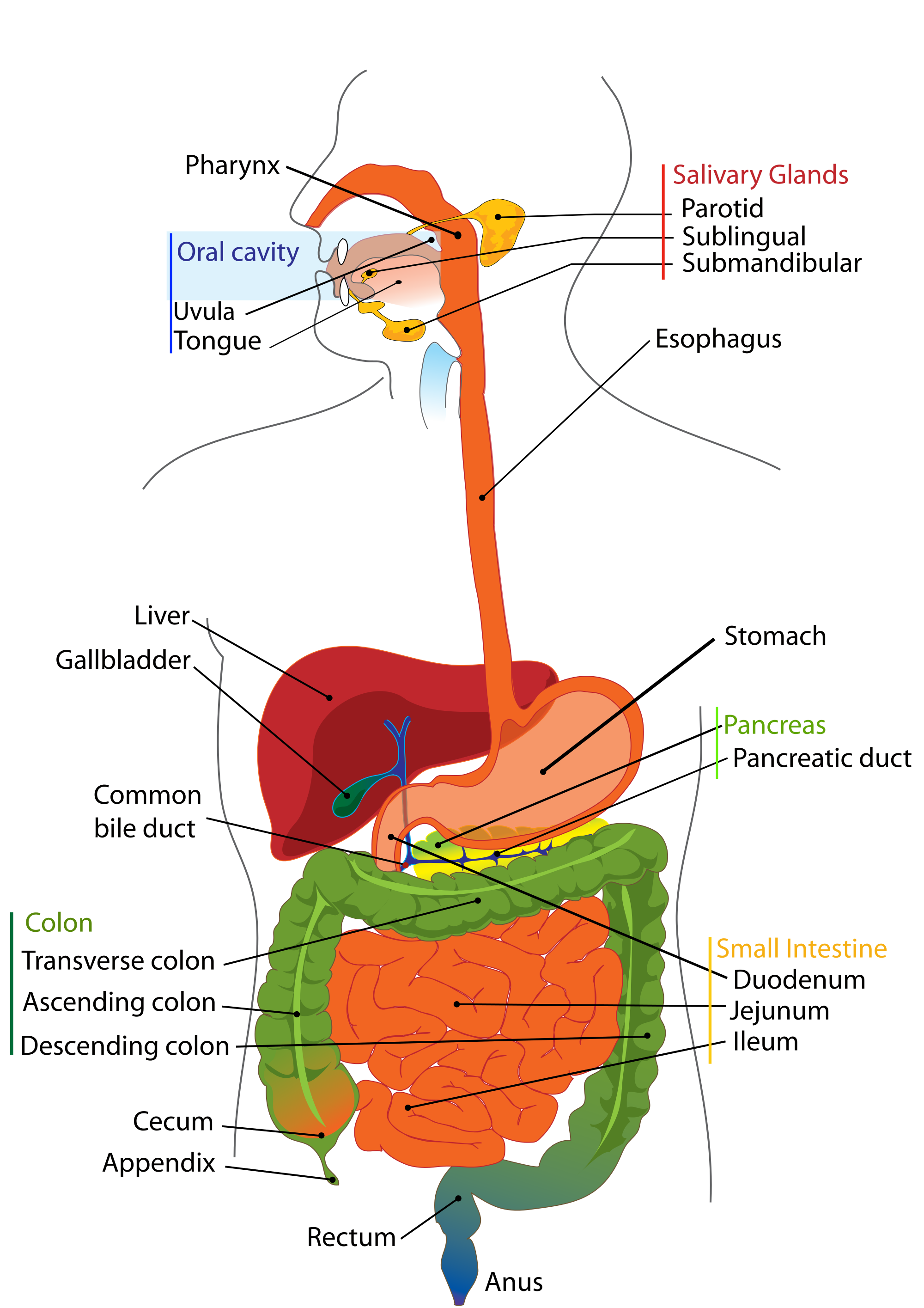
Digestive system
accessory organs
the salivary glands
producing saliva which has the enzyme amylase and this helps break down food in your mouth
the pancreas
of secreting juice into the duodenum, which include enzyme's, a base to neutralize stomach acid and hormones to regulate the storage of glucose
the gallbladder
stores bile made by liver and sends it to the duodenum
the liver
producing bile, removing alcohol and toxins from the body, storing vitamins and carbohydrates
the rectum
of storing stool until it goes out through the anus
the small intestine
the small intestine gets digestive juices from the pancreas and gallbladder, the first part is the duodenum where enzymes come in, the jejunum is where the digestion continues and absorbtion starts, the illeum is where the nutrients are absorbed into the bloodtsream by vili, which are covered in capillaries
the large intestine
of absorbing water and vitamins and eliminating waste
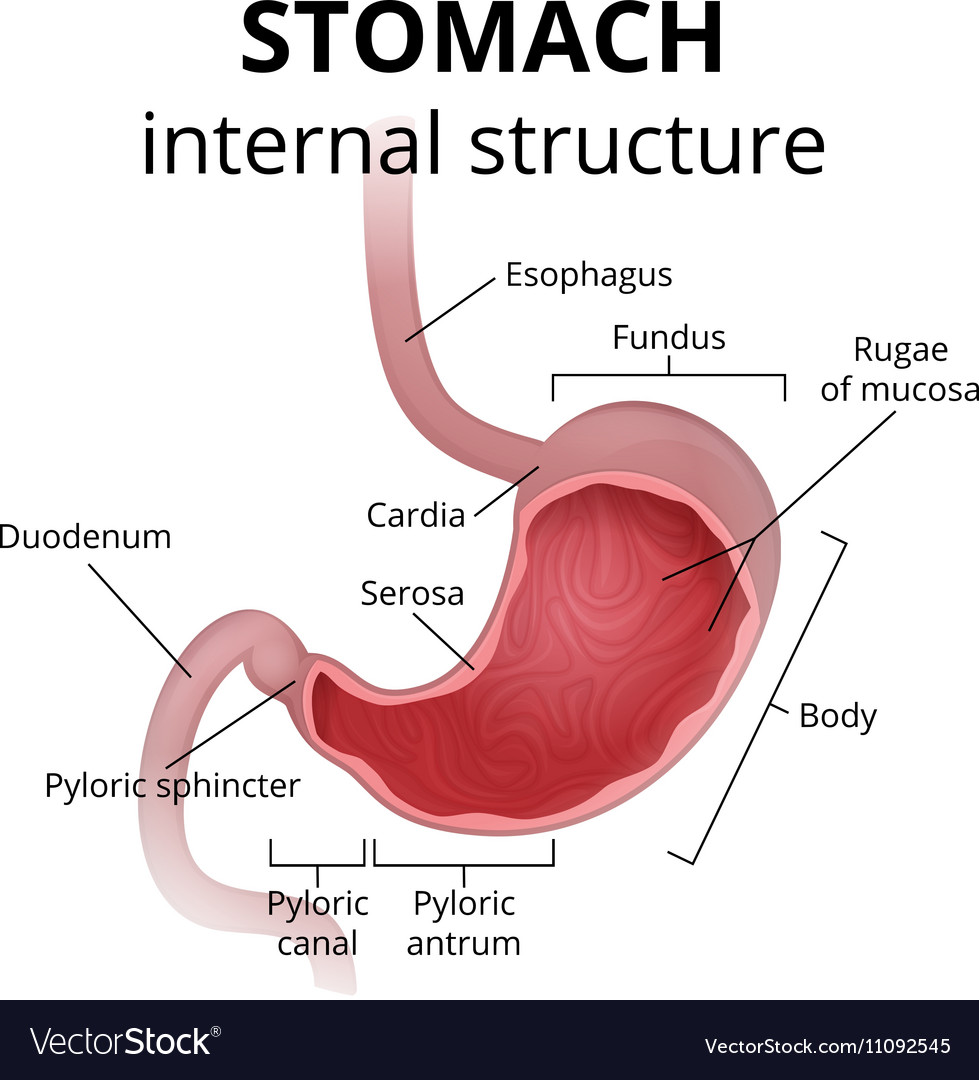
the stomach
creating stomach acid or digestive juices that break down your food, then the digested food called chyme, goes to your small intestine
the esophagus
the esophagus, with the help of peristalsis, which is the contraction of muscles to push the food down your esophagus to your stomach
the mouth
the mouth is where the food is chewed and bile is released by the gallbladder

Respiratory system
the nose/mouth
bringing in the air, to our windpipe/trachea
/Alveoli-56a14da83df78cf772696d4f.jpg)
the alveoli
gas exchange occurs, from capillary to alveoli, via diffusion to get the co2 out, or from alveoli to capillary, where oxygen attaches to hemoglobin and with the help of the heart, sends it all throughout the body
the bronchioles
the air passes to the alveoli
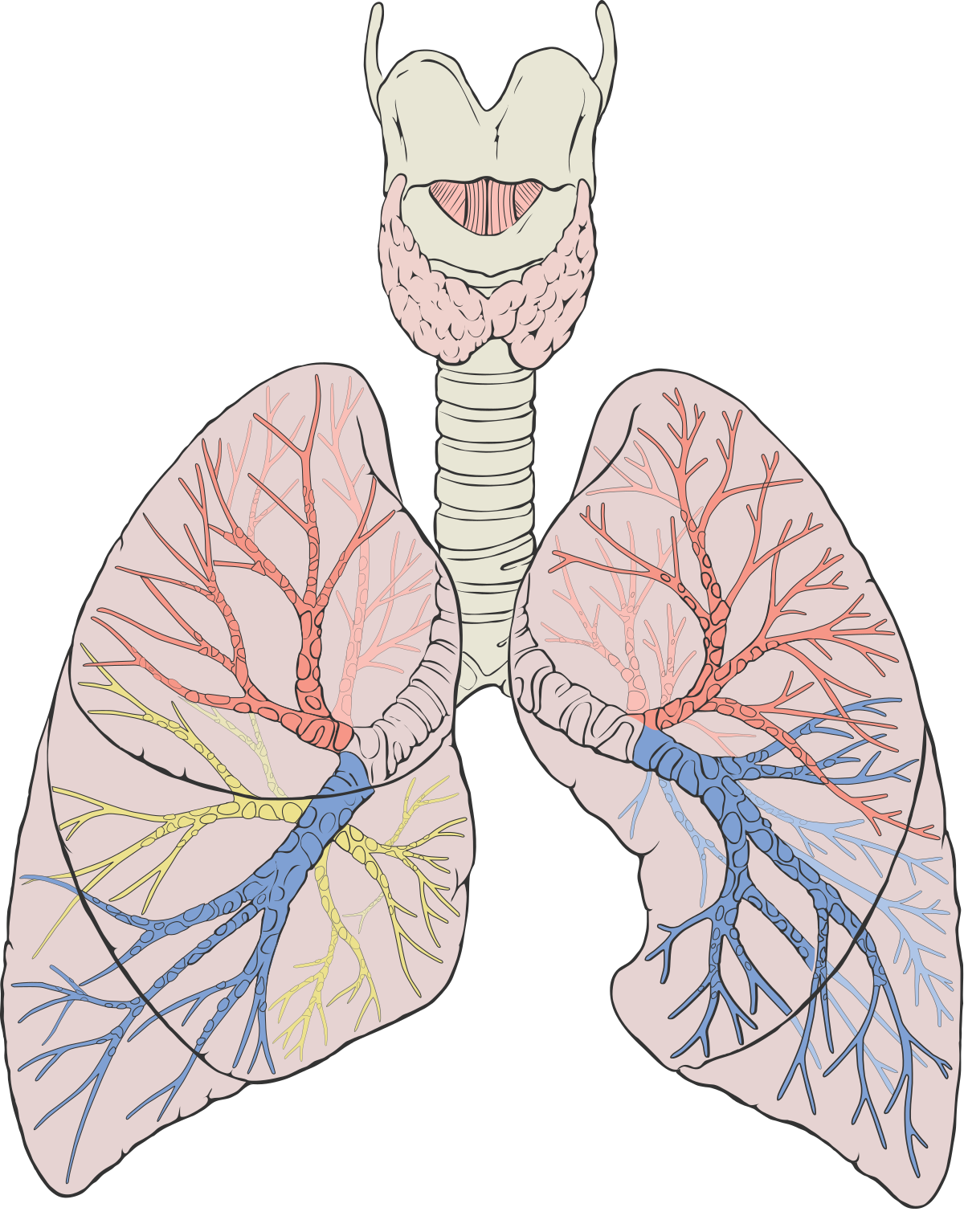
the lungs
the left and right bronchi lead to, inside that, we have the next step, the bronchioles
the bronchi
tubes that connect to each lung on each side
the trachea
a long pipe lined with cartilage and sends the air down to your bronchi,

more lung capacity and larger nasal cavaties to get more air, as they live high up in mountais, with less oxygen and their noses warm the air before it goes down to the lungs
domain: eukarya
Animilia
Chordata
Mammalia
carnivora
felidae
panthera

unicia

Biodiversity
3 layers

ecosystem diversity
the different/ variety of habitats found in a location

genetic diversity
the variety of genes in a species

species diversity
the variety of species in a ecosystem
Taxonomy
kingdom
Eukarya
plantae
bryophyta
all non-vascular plants on land, including mosses, liverworts and hornworts
pteridophyta (ferns)
Vascular plants that do not produce seeds nor flowers (so fern leafs)
coniferophyta
The seeds of this group are called “naked” (not contained in an ovary or fruit), this group includes Conifers, Pines, Spruces,
anthophyta
plants that produce flowers (flowering plants), seeds are in ovary/fruit.
Fungi
mushroom, yeast, mold, is heterotrophic and multicellular
Animilia
Nematoda
roundworms, non segmented, usually parasitic
Cnidaria
things like jellyfish, coral, anemones (radial symmetry)
Plathelminthes
flat, tapeworms, soft bodied invertebrate, also have bilateral symmetry
Porifera
sponges or usually in the sea, and have pores
is Prokarya
(domain) Bacteria
modern bacteria
(domain) Archaea
archaea means archaic or ancient bacteria, they live in extreme environments
Phylum
class
order
family
genus
species
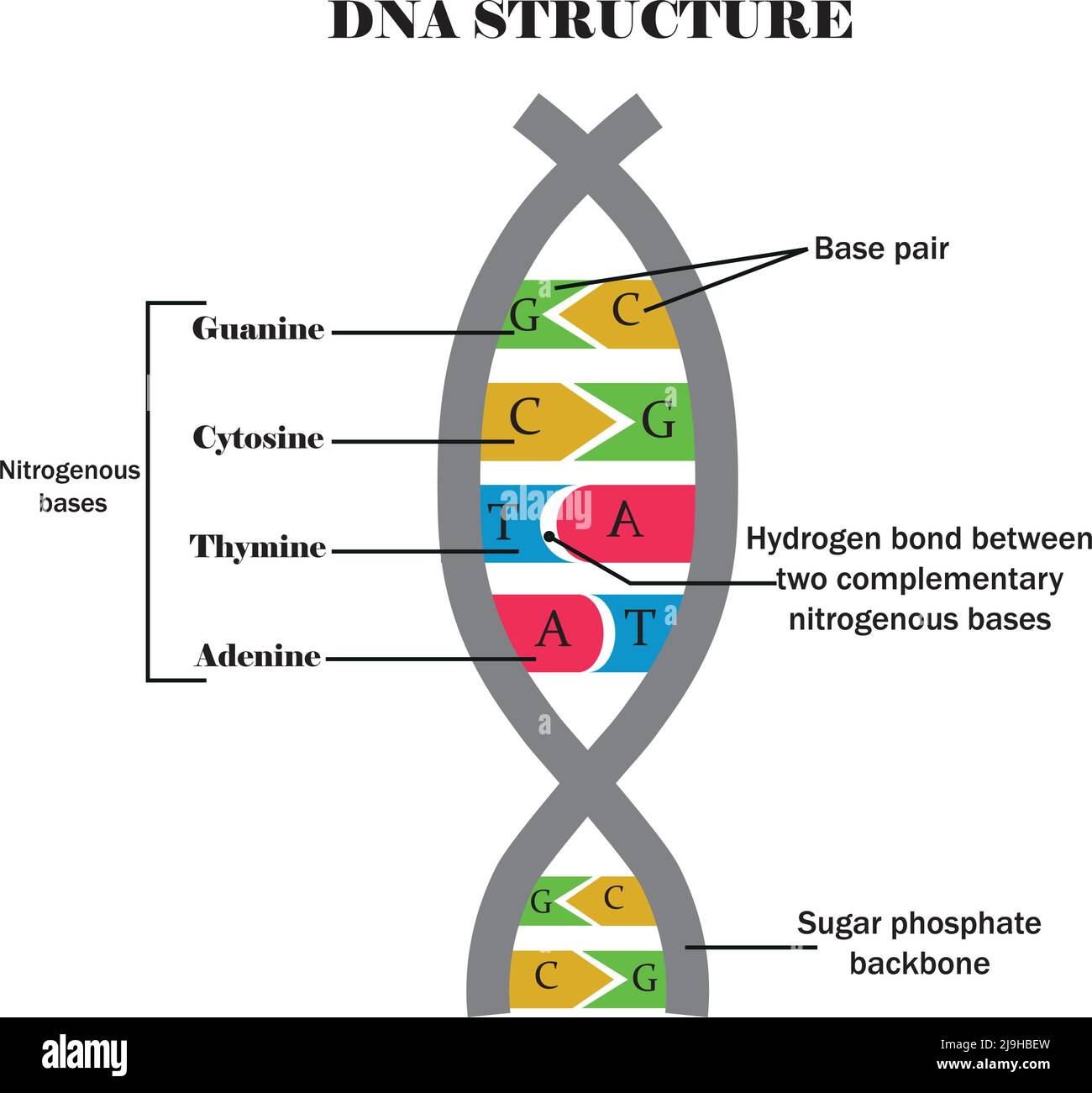
genetics
DNA
meiosis
mitosis
is the process of cells duplicating
PMAT
Anaphase
Telophase
Metaphase
Prophase
a sugar, a nitrogenous group and a phosphate group

ATGC, A can only pair with C and G can only pair with C
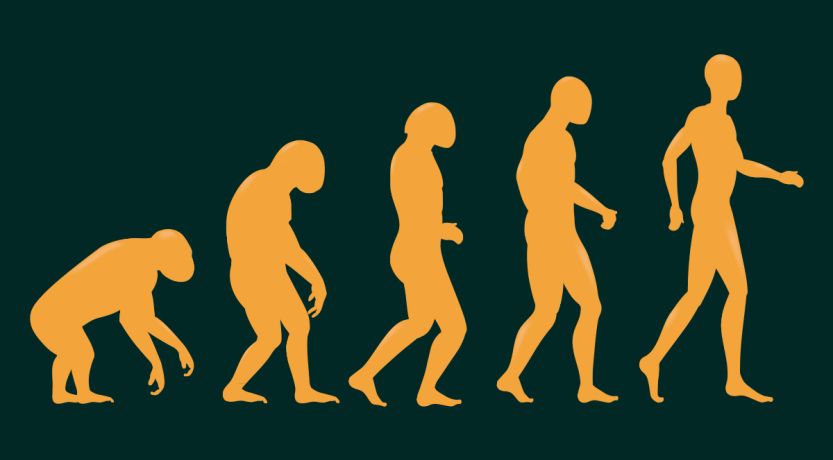
Evolution
A common ancestor

Natural selection

Charles Darwin
made rules for natural selection
individuals within a population differ (they can't all be the same)
only traits that can be selected by nature are heritable (they can be passed down)
some individuals are more successful at surviving and reproducing than others
the most fit trait will be the most likely to be passed down
the idea that those most fit or the best adapted to their environment will be the ones to live, reproduce and pass on those beneficial traits
many other types of selection
directional selection
when an extreme version of a trait is favoured, which results in a shift away from the norm
stabilizing selection
selection against traits that are different from the current population norm
Disruptive selection
favouring two or more traits that are different from the current population norm

sexual selection
female mate choice
when a female favours a certain physical, or behavioral trait, which is then the trait that is mostly passed down, as the best "mate" would be one with such a trait and mostly reproduced with
male-male competition
when male's fight each other to show their power/strength and whoever comes out stronger would get the female mate
vicariance
the change or separation of land masses, which split apart species and made them evolve differently (the animals didn't move, the land did)
dispersal
a species is pressured by overcrowding or some other sort of pressure which forces individuals to leave a certain are
Genetic drift
when there's a change in the gene pool due to the population reducing by chance, there are 2 types
bottleneck effect
is when a large amount of the population is wiped out due to natural disasters or human interference
founders effect
is when a small number from a population move and colonize a habitat
Mutation
A change in the DNA sequence of a body, this can be a deletion, base pair substitution, or insertion
harmful mutation
a mutation that harms a species
neutral mutations
mutations that have no affect
germline/somatic mutations
when the mutation will get passed down
when the mutation will no be passed down, so no evolution
beneficial mutations
any mutation that benefits a species
of evidence
fossils

any ancient remains of an animal or it's track. preserved in rock, mineral or another substance, so it could be footprints, bones, teeth, feces or whole insects
DNA
used by looking at the DNA sequence of different species and seeing how similar/different they are
biogeoghraphy
the movement of land masses, which distributed species/spread them apart
comparative anatomy
comparing the body structure of different species to see what's similar/different
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH-ZoeHansen-WhatDoestheAppendixDo-Standard-222109eb919745429d3d12fb913ea580.jpg)
vestigial features
features that evolved and now serve no purpose but once did

analogous features
features that don't come from the same origin but have similar purposes

homologous features
a structure that started with a same origin but may now serve different purposes
embryology
the study of the forming or development of an embryo and fetus, we usually compare how 2 different embryo's look
snow leopards and tigers both diveraged from the miacid around 3.9 million years, then snow leopards branched from tigers 3.2 million years after

Plants
Primary producers in almost all food chains
Subtopic
Subtopic
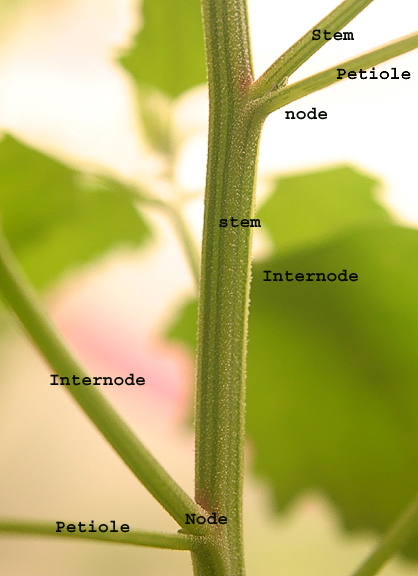
stems and transport
absorb vital minerals through the soil
take the glucose that is created during photosynthesis
can store water and carbohydrates
cacti
gives support
connect vascular tissues in the leaf to the root
maximizes the light exposure
photosynthesis
the carbon dioxide that comes through the leafs stoma, which is in he top, the cells that make up the surface are called epidermal cells, then goes through the mesophyll, then to the pallisade cells absorb the light from the sun

leafs
teas
herbs
treating diseases like leukimia
for cuts and bruises
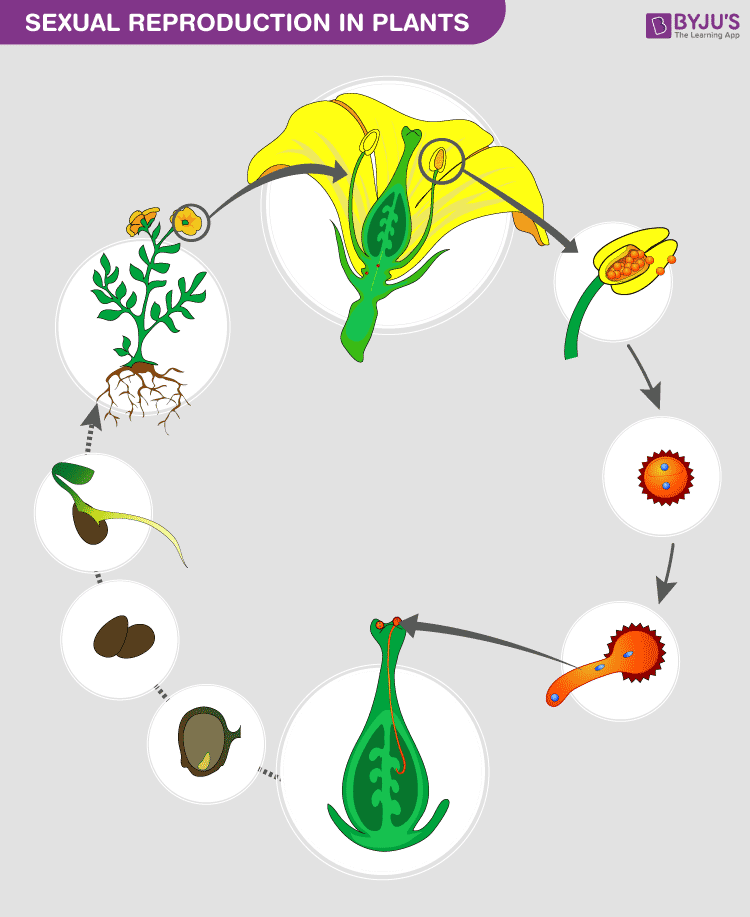
Sexually reproduce
starts off with pollination, which happnes by the wind, water or pollinators
Fertilization happens, pollen tubes carry male gametes to ovules in the ovary, forming a zygote
Fruit Development starts! The ovary becomes fruit, protecting seeds.
Seed Dispersal happens, Seeds spread by wind, water, animals, or other means, later, Germination starts, seeds grow into new plants under favorable conditions.
aesexually reproduce
this can happen by, budding, fragmentation, spore formation and vegetative propagation
Subtopic
Subtopic
many purposes
eating (for food)
in agriculture
in dyes or chemicals
contribute to biodiversity
in many medicines
creating a clean environment (eg. trees)
fighting against climate change and absorbing co2, releasing oxygen
providing herbivores with food, no plants, no herbivores who rely on them
water to land, from being simple to more complex

Many types of plants
cell walls
walls right outside the membrane in plants to give structure and support
autotrophic
an organism that produces it's own food using light
alteration
Eukaryotic
an organism that has a nucleus and membrane organelles

