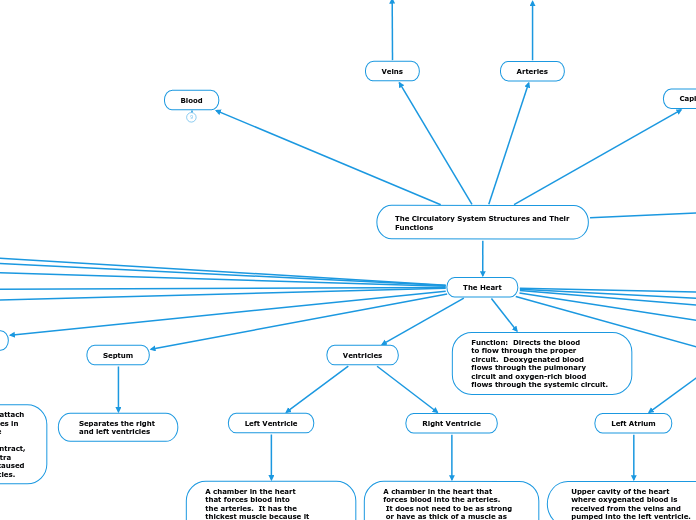
The Circulatory System Structures and Their Functions
The Heart
Septum
Separates the right
and left ventricles
Ventricles
Left Ventricle
A chamber in the heart
that forces blood into
the arteries. It has the
thickest muscle because it
needs to pump blood throughout
the entire body through the
systemic circuit.
Right Ventricle
A chamber in the heart that
forces blood into the arteries.
It does not need to be as strong
or have as thick of a muscle as
the left ventricle because it pumps
blood into the lungs in the
pulmonary circuit.
Atria
Left Atrium
Upper cavity of the heart
where oxygenated blood is
received from the veins and
pumped into the left ventricle.
Right Atrium
Upper cavity of the heart
where deoxygenated blood is
received from the veins and
pumped into the right ventricle.
Valves: the semilunar (pulmonary) valve,
atrioventricular (tricuspid) valve,
atrioventricular (mitral) valve,
and the semilunar (aortic) valve
Their function is to make
sure that blood flows in only
one direction when each
chamber contracts.
Chordae Tendineae
Tough, string-like cords that attach
to the special papillary muscles in
the ventricles. They keep the
tricuspid and mitral valves in
place when the ventricles contract,
and are needed to provide extra
support due to the pressure caused
by the pumping of the ventricles.
Function: Directs the blood
to flow through the proper
circuit. Deoxygenated blood
flows through the pulmonary
circuit and oxygen-rich blood
flows through the systemic circuit.
Aorta
Carries oxygenated blood
away from the heart, to the
rest of the body. It is the
largest artery in the body.
Arteries To Head and Arms:
the brachiocephalic trunk,
the left common carotid artery,
and the left subclavian artery
These arteries carry blood
upwards towards the head
and arms.
Inferior Vena Cava
Delivers deoxygenated blood
from the lower body into the
heart. It is a vein
Pulmonary Arteries
Carry deoxygenated blood from
the heart to the lungs.
Superior Vena Cava
Delivers deoxygenated blood
from the upper body into the
heart. It is a vein.
Atrioventricular Node (AV Node)
Receives electrical impulses
from the SA Node and directs
them to the walls of the
ventricles down the Purkinje
fibres.
Sinoatrial node (SA Node)
A group of cells located in
the wall of the right atrium
that generate electrical
signals to control the rhythm
of the heart
Myogenic Muscles
Muscle fibres of the heart
that contract without being
stimulated to do so by an
external nerve cell. This
causes the heart to beat.
Lungs
Carbon dioxide travels from the blood to the air within the lungs and oxygen travels from the air into the blood. This oxygenates the blood.
Arteries
Vessels carrying blood
away from the heart
Veins
Vessels carrying blood
toward the heart