Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things
Organism
Prokaryote
Definition
Without a Nucleus
Example
Bacteria
Eukaryote
Definition
With a Nucleus
Example
Human
Single-Celled Organism
Example
Amoeba
Plant Cell
Animal Cell
Cells
Parts of a Cell
Cell Structures
Structures Common to Plant and Animal Cells
Cytoplasm
Water material containing organelles
Cell Membrane
Permeable membrane layering the cell
Nucleas
Contains genetic information to control cell activity
Mitochondria
glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water + usable energy
Contains enzymes that convert stored
energy into usable energy
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Tubes for transportation of materials
throughout the cell
Golgi Bodies
Collect and process materials to be
removed from the cell
Vacuoles
Membrane sac containing fluid
Structures in Plant Cells Only
Cell Wall
porous structure found outside cell membrane,
provides support and protection from physical injury
Vacuole
Single large membrane sac containing fluid
to keep cells plump
Chloroplasts
carbon dioxide + water + energy → glucose + oxygen
Absorb light energy used in photosynthesis
Cell Division Parts
Chromosomes
A structure in the cell made of DNA
Chromatid
One of two identical DNA strands that
make up a chromosome
Centromere
Structure that holds the chromatids together
Nuclear Membrane
Spindle Fibres
The Cell Cycle
Interphase
Cell Growth
Cellular Respiration
DNA duplication
Cell Division
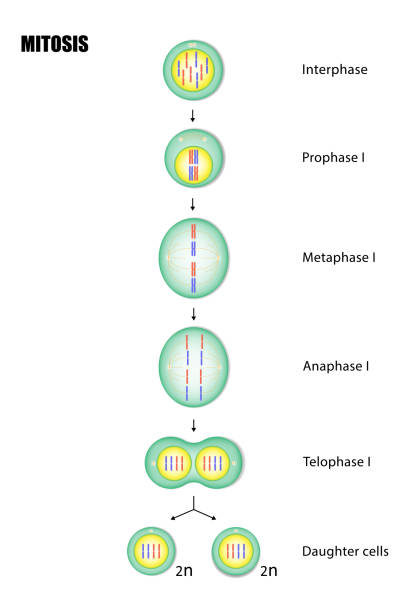
Mitosis
Definition
Division of the nucleus' contents
Prophase
DNA strands condense and become
visible chromosomes
Metaphase
Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell
Anaphase
Centromere splits and sister chromatids separate
to opposite sides of the cell, becoming daughter chromosomes
Telophase
New nuclear membrane forms around each group
of daughter chromosomes
Cytokinesis
Animal Cell
Cell membrane is pinched off in center
Plant Cell
Plate develops new cell wall
Uncontrolled Cell Division
Cancer
Causes
Mutation
Definition
Random changes occurring in DNA
Carcinogen
Environmental factors that cause mutations
Treatments
Surgery
Physically removing cancerous tissue
Chemotherapy
Drug treatment prevents cancer cells
from dividing
Radiation
Damages and prevents cell division
using ionizing radiation
Biphotonics
Detects and treats cancer through use
of beams of light
Stem Cells
Definition
An undifferentiated cell that can
divide into specialized cells
Embryonic Stem Cell
Can differentiate into any
kind of cell
Tissue Stem Cells
Only able to differentiate into
certain types of cells
Cellular Differentiation
The process of creating a specialized cell
to perform specific functions
Microscope
Parts of a Microscope
Body Tube
Holds the ocular lens
Nosepiece
Holds the objective lenses
Objective Lens
Different lenses with different levels of magnification
serve to magnify the object
Stage Clips
Hold the slides in place on the stage
Stage
Where the slides is placed
Diaphragm
Controls the amount of light passing
through the slide
Illuminator
Provides light through the stage onto the slides
Ocular Lens
Magnifies the image created by the objective lens
Magnfication
Ocular Lens Magnification x Objective Lens Magnification
Arm
Connects base to nosepiece and eyepiece
Coarse Focus
Moves the stage to general focus
Fine Focus
Moves stage in small increments
Base
Support of the microscope
Systems
Organ Systems
Organs
Tissue
Epithelial Tissue
Definition
Tightly packed cells that cover
body surfaces and internal organs
Connective Tissue
Definition
Specialized tissue that provides
support and protection
Muscle Tissue
Definition
Group of specialized tissues
containing proteins that can contract
and enable movement
Nerve Tissue
Definition
Specialized tissue that conducts electrical
signals from one part of the body to another
The Circulatory System
Blood
Definition
Connective tissue that circulate
throughout the body
Types
Red
Contain hemoglobin to transport
oxygen throughout the body
White
Recognize and destroy harmful
bacteria and viruses
Platelet
Assist in blood clotting
Plasma
Protein-rich liquid which carries
blood cells
Heart
Definition
Contracts to pump blood throughout the body
Heart Attack
Coronary arteries become blocked, preventing
flow of blood and oxygen
Blood Vessels
Arteries
Thick-walled blood vessel that
carries blood away from the heart
Veins
Blood vessel that returns blood to the heart
Capilleries
Thin-walled blood vessel that enable the
exchange of gas, nutrients and waste
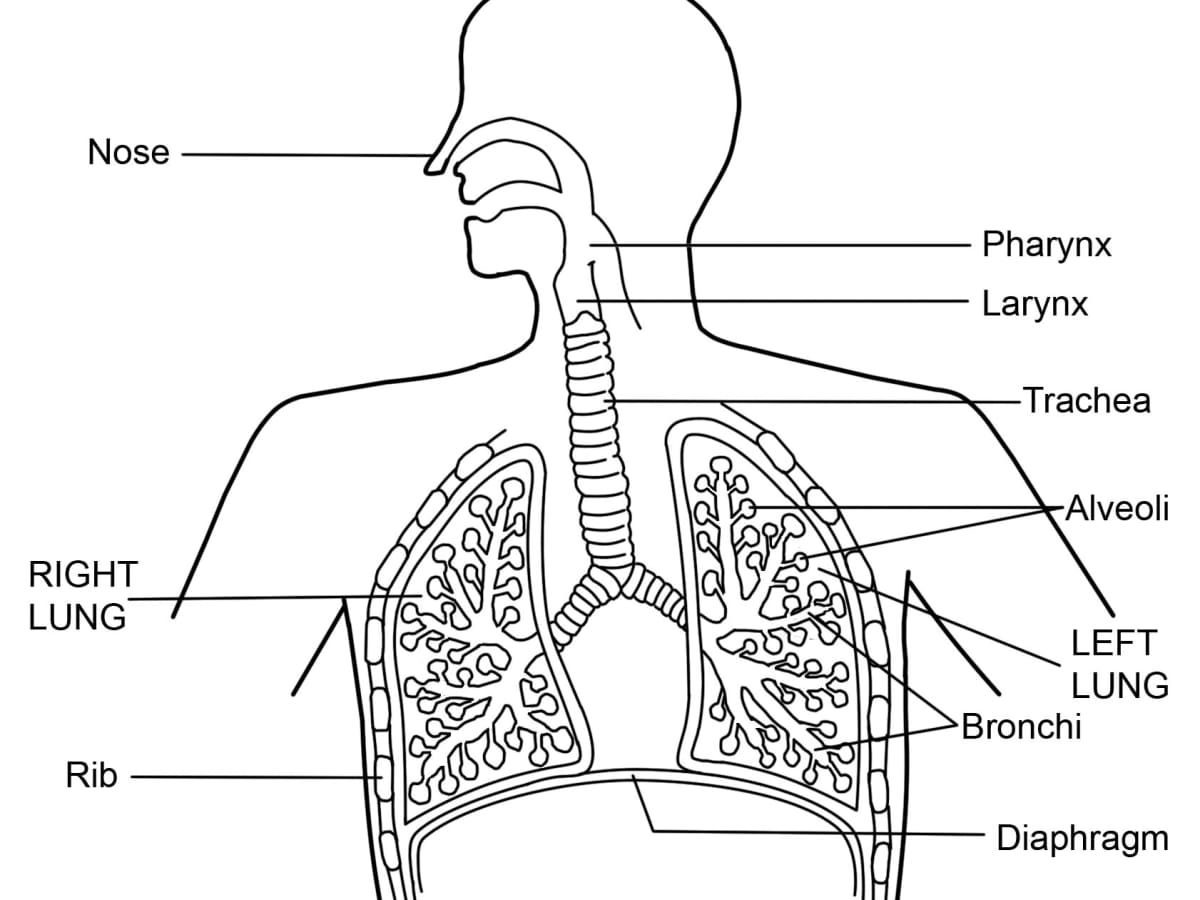
Respiratory System
Nasal Cavity
Definition
Allows air to enter the body
Mouth
Definition
Allows air to enter the body
Pharynx
Definition
Tube that air flows down to reach the trachea
Trachea
Definition
Separates into two different branches
called bronchi
Bronchus
Definition
Deliver air into the lungs
Lung
Definition
Holds oxygen to enter the bloodstream
through diffusion
The Nervous System
Central Nervous System
Definition
Part of the nervous system consisting
of the brain and the spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System
Definition
Part of the nervous system consisting of the
nerves that connect the body to the nervous system
Nerve Tissue
Neurons
Send information around the body using
electrical signals