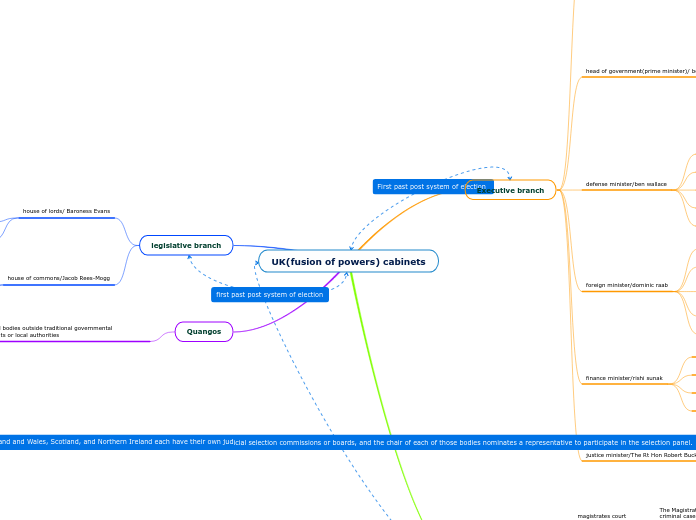
UK(fusion of powers) cabinets
Executive branch
head of state/queen elizabeth 2
The Queen cannot be prosecuted
Appointing the Prime Minister
Declaration of War
She CAN vote
She can veto any bill passed through Parliament
Although she is the crown, the government and state officials exercise the powers of the crown
head of government(prime minister)/ boris johnson
appoints cabinet
makes or ratifies major desicions
plans parlimentary business
arbitrates between departments
coordinates goverment
cannot change schedule of legislative decisions
parliamentary democracy
defense minister/ben wallace
Strategic military and defensive operations
Relations with international partnerships, including NATO
Defence policy (Trident), resourcing and planning
Communications on defence
cannot forsee short term military threats
foreign minister/dominic raab
British relations with foreign countries and governments
Promotion of British interests abroad.
Matters pertaining to the Commonwealth of Nations and the Overseas Territories
Oversight for the Secret Intelligence Service (MI6) and the Government Communications Headquarters (GCHQ).
cannot elect prime minister
finance minister/rishi sunak
Fiscal policy
Monetary policy
Ministerial arrangements
cannot mobilize the military
justice minister/The Rt Hon Robert Buckland
Her Majesty's Prison Service in England and Wales
Matters of probation
Oversight of the Judiciaries of the United Kingdom
cannot appoint cabinet memebers
Judicial branch
magistrates court
The Magistrates Court is one of the minor courts, and all criminal cases start here. This court isn't only for criminals, it's also for some civil matters, mainly focusing on family issues.
crown court
Crown Courts have power to deal with indictable offences, and also hear most appeals from magistrates' courts.
high court
The High Court deals at first instance with all high value and high importance civil law (non-criminal) cases, and also has a supervisory jurisdiction over all subordinate courts and tribunals, with a few statutory exceptions.
court of appeals
deals only with appeals from other courts or tribunals.
supreme court
The Supreme Court is the highest court of appeal for the whole of the UK.
legislative branch
house of lords/ Baroness Evans
Its most useful functions are the revision of bills that the House of Commons has not formulated in sufficient detail and the first hearing of noncontroversial bills that are then able, with a minimum of debate, to pass through the House of Commons.
approval of bills from the house of lords is not required
house of commons/Jacob Rees-Mogg
The Commons' functions are to consider through debate new laws and changes to existing ones, authorise taxes, and provide scrutiny of the policy and expenditure of the Government. It has the power to give a Government a vote of no confidence.
cannot elect queen
Quangos
nonelected bodies outside traditional governmental departments or local authorities