Wireless sensor networks
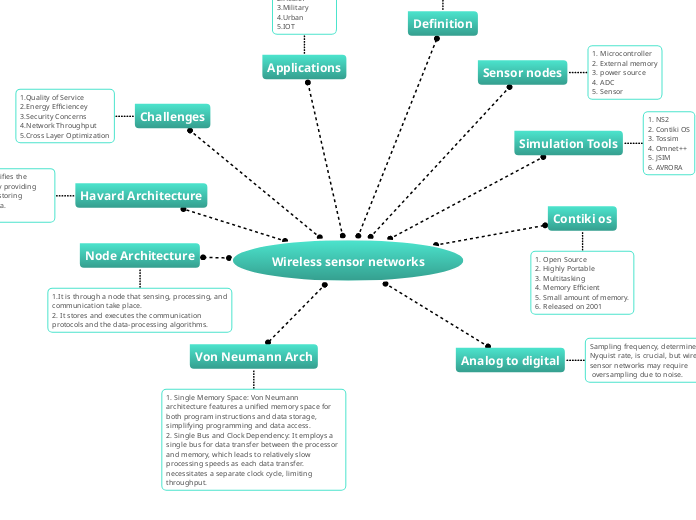
Definition
WSN is an infrastructureless network
that is deployed in a large no.of.sensors
in an adapt manner that is used to monitor the system or physical environmental conditions.
Sensor nodes
1. Microcontroller
2. External memory
3. power source
4. ADC
5. Sensor
Simulation Tools
1. NS2
2. Contiki OS
3. Tossim
4. Omnet++
5. JSIM
6. AVRORA
Contiki os
1. Open Source
2. Highly Portable
3. Multitasking
4. Memory Efficient
5. Small amount of memory.
6. Released on 2001
Analog to digital
Sampling frequency, determined by
Nyquist rate, is crucial, but wireless
sensor networks may require
oversampling due to noise.
Applications
1.Environmental
2.Health
3.Military
4.Urban
5.IOT
Challenges
1.Quality of Service
2.Energy Efficiencey
3.Security Concerns
4.Network Throughput
5.Cross Layer Optimization
Havard Architecture
The Harvard architecture modifies the
Von Neumann architecture by providing
separate memory spaces for storing
program instructions and data.
Node Architecture
1.It is through a node that sensing, processing, and communication take place.
2. It stores and executes the communication protocols and the data-processing algorithms.
Von Neumann Arch
1. Single Memory Space: Von Neumann architecture features a unified memory space for both program instructions and data storage, simplifying programming and data access.
2. Single Bus and Clock Dependency: It employs a single bus for data transfer between the processor and memory, which leads to relatively slow processing speeds as each data transfer. necessitates a separate clock cycle, limiting throughput.