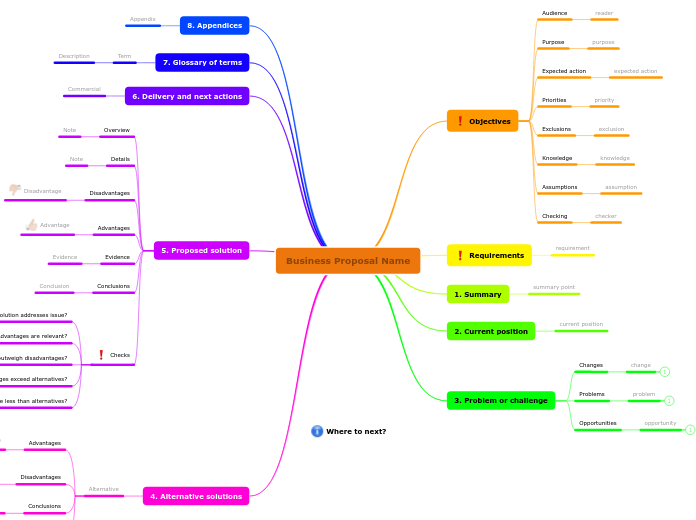
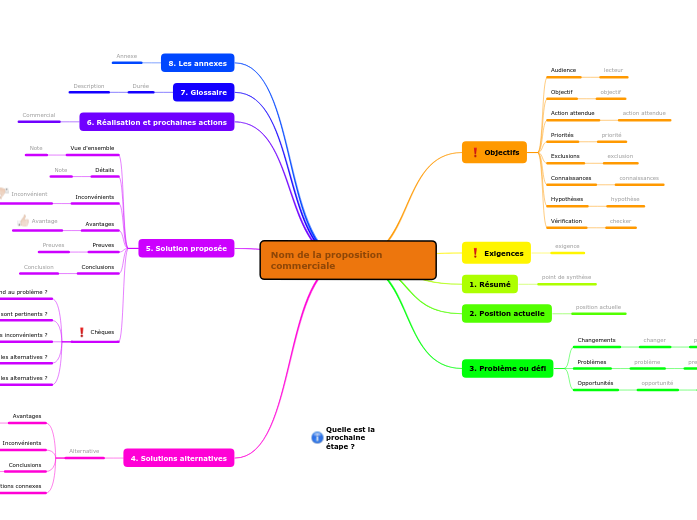
This professional business proposal structure mind map will help you land and close the deal with a new customer.
The quality of a strong proposal always depends on how you present your proposal. Set your objectives and identify your audience, define your purpose and priorities, express your assumptions and knowledge and find someone who can check all of the mentioned above.
Begin your document with a summary of your agenda, then check the current position of your customers and identify their problems to which your product or service is the solution.
Include alternative solutions and state the advantages and disadvantages from the clients’ point of view.
After considering all of the above, start developing your suggested solution, including the benefits and drawbacks of your product or service. The actual delivery and the following actions are the final steps and will prove to your clients that they can rely on you.
Where to next?
Where to next?
Before finalizing your proposal, check through it again to ensure that all the information you are providing supports the objectives you originally set out and is relevant from the reader's point of view.
When you have gathered most of the material for your proposal, you can transfer it to a linear document for presentation. You can do this in Mindomo by converting topics into text in the topic notes for export to a linear document.
Good luck with your proposal!
Business Proposal Name
What is your business proposal about?
Give it a name. Type it in.
4. Alternative solutions
Alternative
What other options could solve the problem? Add an alternative.
Related information
Related information about the options that have been identified might be needed.
Add resource(s)
Resource
Summarize your alternative points.
Add a conclusion
Disadvantages must be accurately stated from your client's point of view.
Add a disadvantage
Advantages must be accurately stated from your client's point of view.
Add an advantage
5. Proposed solution
Checks
Disadvantages are less than alternatives?
Are the disadvantages of your solution less significant than the disadvantages of the alternatives?
Advantages exceed alternatives?
Are the advantages of your solution more significant and relevant than the advantages of the alternatives?
Advantages outweigh disadvantages?
Do the advantages of your solution outweigh the disadvantages?
Advantages are relevant?
Are the advantages of your solution fully relevant to the client?
Solution addresses issue?
Does your solution comprehensively and effectively address the requirements, issue or opportunity?
Check
YesNoMore work needed
Conclusions
Summarise your points about your solution.
Add a conclusion
Conclusion
Evidence
What evidence can you provide that your proposed solution will work?
Add evidence
Advantages
Ensure that the advantages you identify are relevant to the client, from their point of view.
Add an advantage
Advantage
Disadvantages
Acknowledge disadvantages early and deal with them in your proposal.
Add a disadvantage
Disadvantage
Details
Match up the solution with the issue or opportunity that you are addressing.
Add detail(s)
Overview
Develop the key points of your proposed solution.
Add a note
Note
6. Delivery and next actions
Describe the further actions for a commercial and a non-commercial proposal.
What are the next steps?
Commercial
Add delivery details for a commercial proposal.
7. Glossary of terms
Do you need a glossary for any specific technical terms you are using?
Term
Add a term.
Description
Add the description for it.
8. Appendices
Include any detailed data in appendices rather than break up the flow of the proposal.
Identify the contents of an appendix for your proposal.
Appendix
Add an appendix.
3. Problem or challenge
Opportunities
opportunity
Identify an opportunity that requires action to be taken, which your solution will address. Add an opportunity.
Add any supporting information or evidence of changes. Type it in.
Problems
problem
Identify a problem that requires action to be taken, which your solution will address. Add a problem.
Changes
change
Identify a change or a trend in the current situation, that requires action to be taken. Add a change.
evidence
Add any supporting information or evidence of changes.
2. Current position
Describe the current position that your client is in.
This creates some common ground, which is a good platform for discussing your solution.
current position
1. Summary
Summarize your proposal at the beginning of the document. Add a sum-up.
summary point
Requirements
What do you know about the client's requirements?
Is your proposal in response to an inquiry?
Has there been provided a Request for Proposal (RFP) or other resources that you can work with?
If you have relevant materials in other files, you can attach them to this topic.
This section should not be included in the proposal.
requirement
Objectives
Defining clear objectives is the key to building a good proposal.
What are your objectives?
This section should not be included in the proposal.
Checking
Who can check your objectives?
Identify who else can check the objectives and assumptions of this proposal. Add checker.
checker
Assumptions
What assumptions have you made?
Are there things that you hope are true, but you cannot check? Add an assumption.
assumption
Knowledge
How much will the client know?
Add an assessment of the reader's knowledge.
knowledge
Exclusions
What should you leave out?
What can you assume is not relevant, or not a priority? Add an exclusion.
exclusion
Priorities
What is important? Add a priority.
priority
Expected action
What action(s) are you aiming for?
What do you want the client to do, as a result of this proposal?
expected action
Purpose
What is the purpose of your proposal?
What will your proposal lead to?
purpose
Audience
Who is the audience for this proposal?
Who will read it and act upon it?
reader