a juan angel fuentes sev 2 éve
259
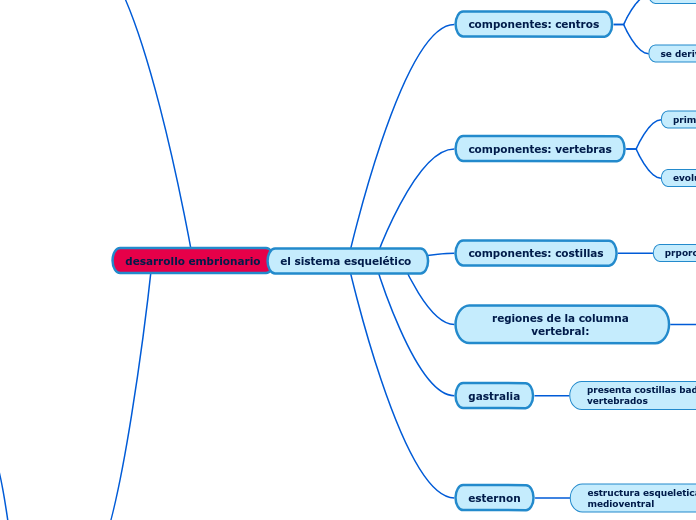
el sistema esquelético
a juan angel fuentes sev 2 éve
259

Még több ilyen
transmiten fuerza
aumenta la eficacia mecanica del musulo
proporciona aumento en la longitud de la espina
fuerza proporcional a la seccion transversal
su eje esta en pararalelo con su fuerza resultante
la impone los musculos axiales
la expina experimenta fuerza de compresion
llegan hasta los estremos de las espinas neurales
este problema lo contrarresta las aletas estabilizadoras
tiburon moderno
da ssporte al cuerpo
sisituyen a la notocordea en las formas moernas
los elementos vertebrales tienden a alargarse
tiburones primitivos con
arcos hemales y neurales estan en la notocorde
prominente notocornea con buen soporte
cadenas de arcos neurales sobre la notocordea
en los mixines y las lampreas
son piesas cartilaginosas
carecen de indicios vertebrales
notocordea patente
se encuentra una notocordea grande
proorciona el eje mecanico central del cuerpo
la celula da origen a esclerotomal
la mesenquima se condensa a nivel miosepto
la vaina se notocordea es cartilaginosa
se denominan arcualias
en la linea antracosauria
el pleurocentro tiene mas o menos el mismo tamaño que el intercentro
el pleurocentro se agranda
temnospondilos
tienen un predecesor con caracteristicas similares
pleurocentro desaparece
adquieren forma cilindrica
los intercentros aumentan de tamaño
vertebras raquitomas
formado por un arco neural y pleurocentro oseo
labrintodontos
las salamandras presentan oxilacion en su columna
presenta vertebras aspidospodila
evolucionaron de los ripidistos
lepospondilos
los anfibios presentan similitud n las vrtebras
presentan cola larga y pesada
debe su nombre a sus vertebras holospondila
presentan coola larga
la segunda es el axis
problema en el mantenimiento de la dureza
se forman vertebras cervicales
surgen los discos intervertebrales
forman racimos alargados
In physics, energy is the quantitative property that must be transferred to an object in order to perform work on, or to heat, the object. Energy is a conserved quantity; the law of conservation of energy states that energy can be converted in form, but not created or destroyed
Nuclear energy originates from the splitting of uranium atoms – a process called fission.
This generates heat to produce steam, which is used by a turbine generator to generate electricity. Because nuclear power plants do not burn fuel, they do not produce greenhouse gas emissions.
Write down the advantages and disadvantages of Nuclear Energy.
There are many different types of energy, which all fall into two primary forms – kinetic and potential.
Energy can transform from one type to another, but it can never be destroyed or created.
Gravitational energy is a form of potential energy.
It is energy associated with gravity or gravitational force, in other words, the energy held by an object when it is in a high position compared to a lower position.
Give examples.
Electrical energy is the movement of electrons, the tiny particles that make up atoms, along with protons and neutrons.
Electrons that move through a wire are called electricity.
Give another example of electrical energy.
Energy storage is the capture of energy produced at one time for use at a later time. A device that stores energy is generally called an accumulator or battery.
Flywheel energy storage (FES) works by accelerating a rotor to a very high speed and maintaining the energy in the system as rotational energy.
Write down the main components of a typical flywheel.
Thermal energy storage is achieved with widely differing technologies.
Depending on the specific technology, it allows excess thermal energy to be stored and used hours, days, months later, at scales ranging from the individual process, to building or town.
What are 3 types of thermal energy?