a zulhafiz shafiq 12 éve
618
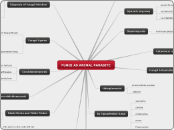
FUNGI AS ANIMAL PARASITE
a zulhafiz shafiq 12 éve
618

Még több ilyen
epidermophyton
microsporum
histoplasma capsulatom
coicedeides immitis
blastomycete dermatitis