a Vireshwar Jagdeo 2 éve
177
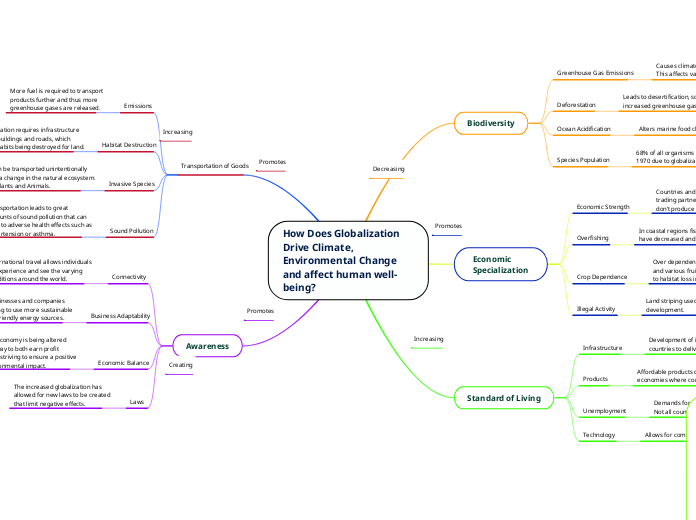
How Does Globalization Drive Climate, Environmental Change and affect human well-being?
Globalization has profound impacts on climate, environmental change, and human well-being. It promotes economic growth while pushing for environmentally friendly practices through new laws and business adaptability.
Megnyitás
Decreasing Creating Increasing Promotes How Does Globalization Drive Climate, Environmental Change and affect human well-being? Awareness Laws The increased globalization has
allowed for new laws to be created
that limit negative effects. Economic Balance The economy is being altered
in a way to both earn profit
while striving to ensure a positive
environmental impact. Business Adaptability More businesses and companies
are looking to use more sustainable
and eco-friendly energy sources. Connectivity International travel allows individuals
to experience and see the varying
conditions around the world. Transportation of Goods Sound Pollution Transportation leads to great
amounts of sound pollution that can
lead to adverse health effects such as
hypertension or asthma. Invasive Species Species can be transported unintentionally
and cause a change in the natural ecosystem.
Ex. Fungi, Plants and Animals. Habitat Destruction Transportation requires infrastructure
such as buildings and roads, which
leads to habits being destroyed for land. Emissions More fuel is required to transport
products further and thus more
greenhouse gases are released. Standard of Living Technology Allows for communication at minimal cost, time and effort. Unemployment Demands for higher-skilled work with lower wages.
Not all countries and regions can accommodate for this. Products Affordable products due to competition in domestic economies where companies reduce product price. Infrastructure Development of infrastructure enables to
countries to deliver their services to the people. Economic
Specialization Illegal Activity Land striping used to create more area for
development. Crop Dependence Over dependence on coffee, cacao,
and various fruits, has contributed
to habitat loss in tropical regions. Overfishing In coastal regions fish populations
have decreased and oceanic pollution has increased. Economic Strength Countries and regions can use
trading partners for goods they
don’t produce themselves. Biodiversity Species Population 68% of all organisms have decreased since
1970 due to globalization. Ocean Acidification Alters marine food chains and food supply to humans. Deforestation Leads to desertification, soil erosion, fewer crops, flooding, and increased greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. Greenhouse Gas Emissions Causes climate change by trapping heat.
This affects various species especially in arid climates