Macromolecules-Paxton Gunn
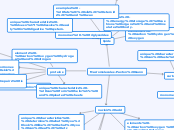
Macromolecules-Paxton Gunn
lipids
unique characteristics - doesn't dissolve easily in digestive system.
examples - fats, oils, steroids, and wax
Functions - energy storage, cushions organs, and insulates body.
monomer - triglycerides
carbohydrates
unique characteristics - can taste sweet
examples - Fructose, Lactose, Maltose, Sucrose and Glucose
Functions - quick energy, and energy storage.
elements - carbon hydrogen and oxygen
monomer - monosaccharides
proteins
unique characteristics - can form helix's and pleated sheets
Functions - builds and repairs tissue
examples - muscles, hormones, fingernails, skin, hair, and enzymes
monomer - amino acid
nucleic acid
Subtopic
unique characteristics - determine what you look like, what you can eat, etc
examples - RNA and DNA
Functions - storage of information
elements - carbon oxygen hydrogen and nitrogen
monomer - nucleotides

