a Raabia Ansari 3 éve
533
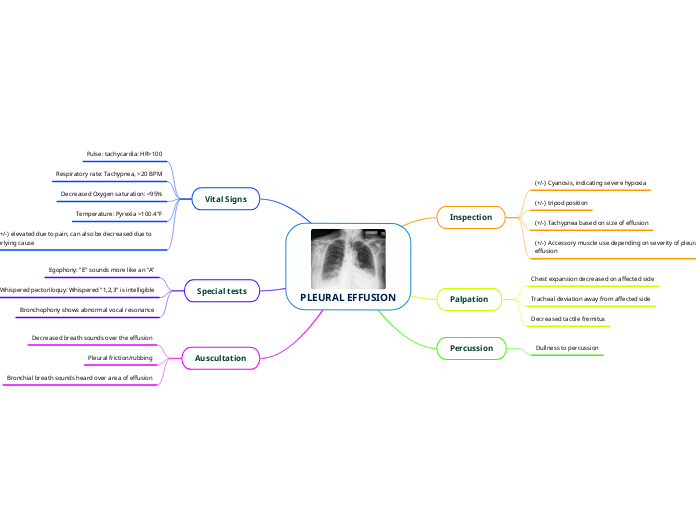
PLEURAL EFFUSION
PLEURAL EFFUSION
Auscultation
Bronchial breath sounds heard over area of effusion
Pleural friction/rubbing
Decreased breath sounds over the effusion
Special tests
Bronchophony shows abnormal vocal resonance
Whispered pectoriloquy: Whispered "1,2,3" is intelligible
Egophony: "E" sounds more like an "A"
Vital Signs
BP: (+/-) elevated due to pain, can also be decreased due to underlying cause
Temperature: Pyrexia >100.4°F
Decreased Oxygen saturation: <95%
Respiratory rate: Tachypnea, >20 BPM
Pulse: tachycardia: HR>100
Percussion
Dullness to percussion
Palpation
Decreased tactile fremitus
Tracheal deviation away from affected side
Chest expansion decreased on affected side
Inspection
(+/-) Accessory muscle use depending on severity of pleural effusion
(+/-) Tachypnea based on size of effusion
(+/-) tripod position
(+/-) Cyanosis, indicating severe hypoxia

