a Breon Brinkley-Bowens 5 éve
576
Tissue Types
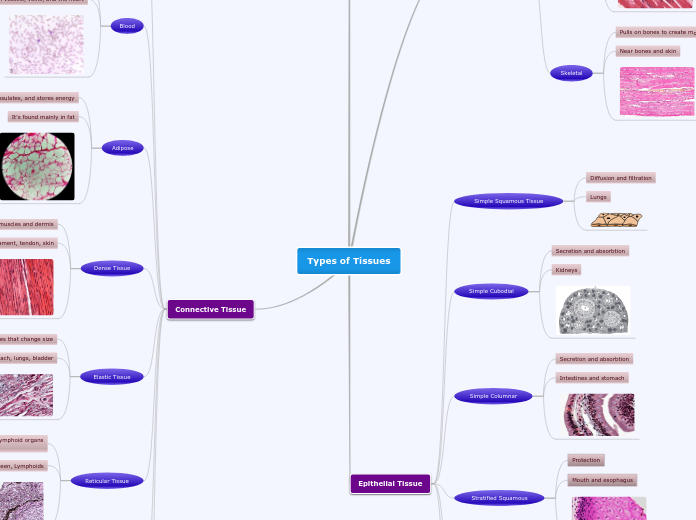
There are various types of tissue in the body, each with distinct functions, locations, and appearances. Nervous tissue, found in the spinal cord and brain, is responsible for receiving stimuli and transmitting impulses.