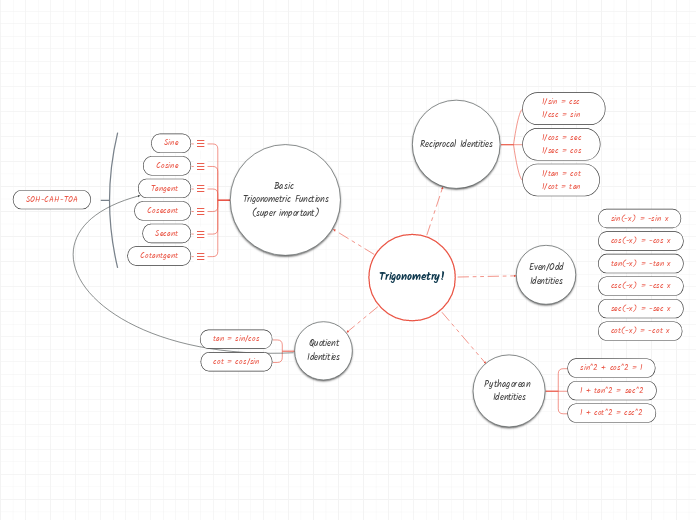
SOH-CAH-TOA
Trigonometry!
title here
Quotient
Identities
cot = cos/sin
tan = sin/cos
Basic
Trigonometric Functions
(super important)
Cotantgent
Abbreviation: COT
Cotangent is the reciprocal function of tangent.
Secant
Abbreviation: SEC
Secant is the reciprocal function of cosine.
(H/A)
Inverse: Arcsec or sec^-1
Cosecant
Abbreviated: CSC
Cosecant is the reciprocal of the sine function.
(H/O)
Inverse: Arccsc or csc^-1
Tangent
Abbreviated- TAN
Used to determine the ratio of a side opposite and a side adjacent of a given angle
(O/A)
Inverse: Arctan or Tan^-1
Cosine
Abbbreviated- COS
Used to determine the ratio of a side adjacent to a given angle
(A/H)
Inverse: Arccos or Cos^-1
Sine
Abbreviated: SIN
Used to determine the ratio of a side opposite of a given angle
(O/H)
Inverse: Arcsin or Sin^-1
Pythagorean
Identities
1 + cot^2 = csc^2
1 + tan^2 = sec^2
sin^2 + cos^2 = 1
Even/Odd
Identities
cot(-x) = -cot x
sec(-x) = -sec x
csc(-x) = -csc x
tan(-x) = -tan x
cos(-x) = -cos x
sin(-x) = -sin x
Reciprocal Identities
1/tan = cot
1/cot = tan
1/cos = sec
1/sec = cos
1/sin = csc
1/csc = sin