a Sahil Sandhu 3 éve
247
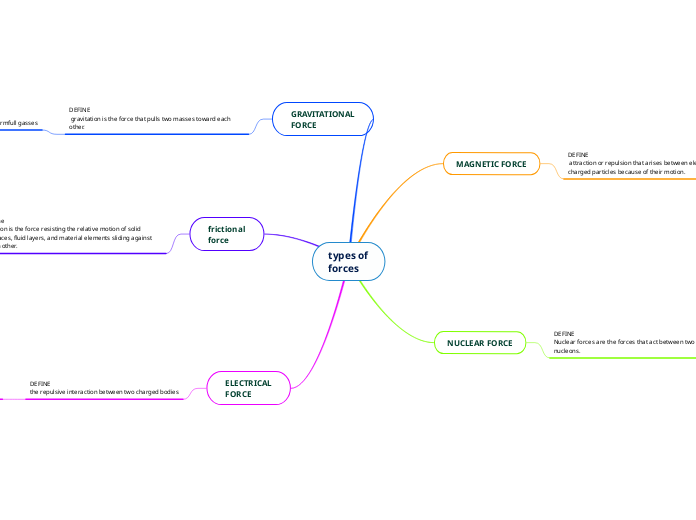
types of forces
a Sahil Sandhu 3 éve
247

Még több ilyen
UNITS It is measured in newton
Advantages Very high collection efficiencies, even for very small particles DISADVANTAGE Cannot control gaseous emissions
USES thr charge in electrical bulb
facts Objects with the same charge, both positive and both negative, will repel each other, and objects with opposite charges, one positive and one negative, will attract each other
units the unit of friction is newton
ADVANTAGE it helps to support ledder against the wall DISADVANTAGE Heat is generated at this surface of contact due to the opposing force of friction.
uses it is used in car brakes
FACTS it can generate static electricity
UNITS newton
ADVANTAGE it allows earth to retain its gravity DISADVANTAGE earth will end up heating of sun from far away if no gravitational force
USES it helps in keep all the planets to stay in their own orbit
units of nuclear force 10,000 N
Pros of nuclear energy Cons of nuclear energy Carbon-free electricity Uranium is technically non-renewable Small land footprint Very high upfront costs
uses The nuclear force has an essential role in storing energy that is used in nuclear power and nuclear weapons
facts The strong nuclear force is one of four fundamental forces in nature. The strong force is 'felt' between nucleons (protons and neutrons)
unit of H is amperes per metre
advantages Magnetic forces can be used to aid humans through technology Disadvantages : Magnetism starts to decrease (and can be permanently lost) at 80°C*
uses Magnetic fields can be used to make electricity
facts magnetic force, attraction or repulsion that arises between electrically charged particles because of their motion.