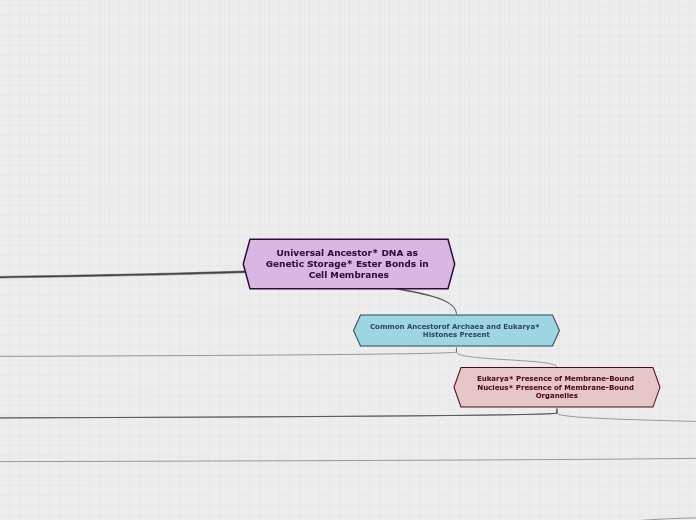
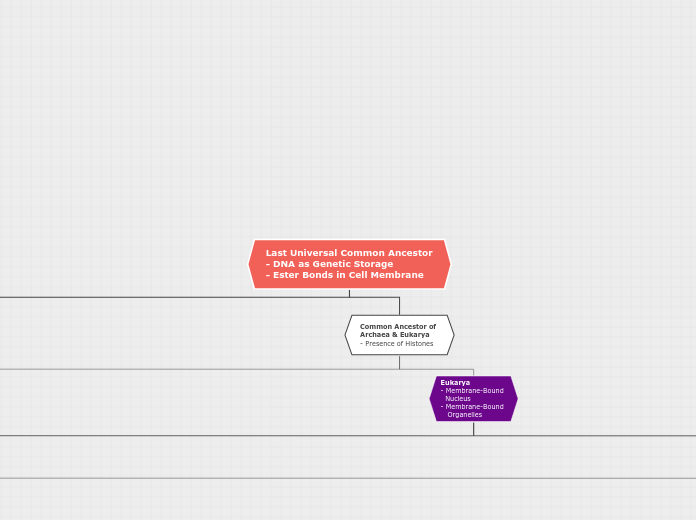
Universal Ancestor* DNA as Genetic Storage* Ester Bonds in Cell Membranes
Common Ancestorof Archaea and Eukarya* Histones Present
Eukarya* Presence of Membrane-Bound Nucleus* Presence of Membrane-Bound Organelles
Unikonta
Opisthokonta* Single posterior flagellum on swimming cells* Absorptive heterotrophy
Common ancestor ofFungi and Nucleariids
Nucleariids
Nucleariid(Nuclearia thermophila)
Fungi* Multicellularity* Chitin cell wall* Zygotic life cycle
Fly Agaric(Amanita muscaria)
Black Bread Mold(Rhizopus stolonifer)
Common ancestor ofAnimalia and Choanoflagellates
Choanoflagellates
Choanoflagellates(Desmarella moniliformis)
Animalia* Multicellularity* Mobility* Gametic life cycle
Eumetazoa* Tissues
Bilateria* Bilateral symmetry* Triploblasty* Cephalization
Protostomia* Spiral and determinate cleavage* Blastopore becomes the mouth
Ecdysozoa* Ecdysis
Arthropoda* Modified appendages that are jointed and come in pairs
Common ancestor ofHexapoda and Crustacea(Pancrustaceans)
Crustacea* Highly specialized appendages* Two pairs of antennae
Chesapeake Blue Crab(Callinectes sapidus)
Hexapoda* Have wings without sacrificing any legs
Monarch butterfly(Danaus plexippus)
Chelicerata* Clawlike feeding appendages which serves as pincers or fangs
Southern Black Widow(Latrodectus mactans)
Nematoda* Roundworms
Roundworm(Caenorhabditis elegans)
Lophotrochozoa* Trochophore larvae* Lophophore
Platyhelminthes* Flatworms* Acoelomates *blind gut
Rhabditophorans* Fresh water and marine species
Free-living Rhabditophorans
Pseudobiceros sp.
Cestoda* Parasites
Pork Tapeworm(Taenia solium)
Trematoda* Parasites
Sheep Liver Fluke(Fasciola hepatica)
Common ancestorof Annelida and Mollusca
Mollusca* Soft-bodied organisms with hard protective shells
Bivalva* Shell divided into two hinged halves
Soft Shell Clam(Mya arenaria)
Cephalopoda* Foot has become modified into a muscular excurrent siphon and part of the tentacles* No hard shell
Humboldt squid(Dosidicus gigas)
Gastropoda* Move at a snail's pace by a rippling motion of their foot or by means of cilia
Golden Apple Snail(Pomacea canaliculata)
Annelida* Body resembles a series of fused rings
Common Earthworm(Lumbricus terrestris)
Deuterostomia* Radial and indeterminate cleavage* Blastopore becomes the anus
Common Ancestor ofHemichordata and Echinodermata
Echinodermata* Water vascular system
Holothuroidea* Lack spines
California sea cucumber(Apostichopus californicus)
Echinoidea* No arms
Purple Sea Urchin(Strongylocentrotus purpuratus)
Ophiuroidea* Flexible arms
Serpent Star(Ophiura ophiura)
Asteroidea* Arms with tube feet that resemble suction cups
Giant Sea Star(Pisaster giganteus)
Chordata* Notochord* Hollow dorsal nerve cord* Post anal tail* Pharyngeal slits
Cephalochordata* Lancelets
Branchiostoma lanceolatum
Cnidaria* Radial symmetry* Diploblasty
Common ancestor ofHydrozoa and Scyphozoa
Hydrozoa* Alternate between the polyp and medusa forms
Pennaria disticha
Scyphozoa* Produce a medusa(jellies)
Moon Jelly(Aurelia aurita)
Anthozoa* Occur only as polyps(sea anemones and corals)
Elkhorn coral(Acropora palmata)
Porifera
Giant Barrel Sponge(Xestospongia muta)
Amebozoa* Movement with pseudopodia
Slime molds
SAR clade
Rhizaria* Filose pseudopodia
Foraminiferas
Radiolarians
Common Ancestor of Stramenopila and Alveolata* Secondary plastids
Alveolata* Membranous vesicles on cell membrane
Dinoflagellate
Stramenopila*Tripartite flagellar hair
Diatoms
Giant Kelp(Macrocystis pyrifera)
Excavata* Feeding groove* Secondary plastid
Euglenoids
Archaeplastida* Primary plastid
Common Ancestorof Chlorophytes, Charophytes and Land Plants
Common Ancestorof Charophytes and Land Plants
Land Plants* Sporic life cycle* Embryos* Apical meristems* Gametangia* Sporangia* Desiccation-resistant spores
Liverworts
Common Liverwort (Marchantia polymorpha)
Charophytes
Braun's stonewort(Chara Braunii)
Chlorophytes
Rhodophytes
Archaea* Ether Bonds in Cell Membranes
Methanobrevibacter smithii
Bacteria* Presence of Peptidoglycan in Cell Wall
Escherichia coli