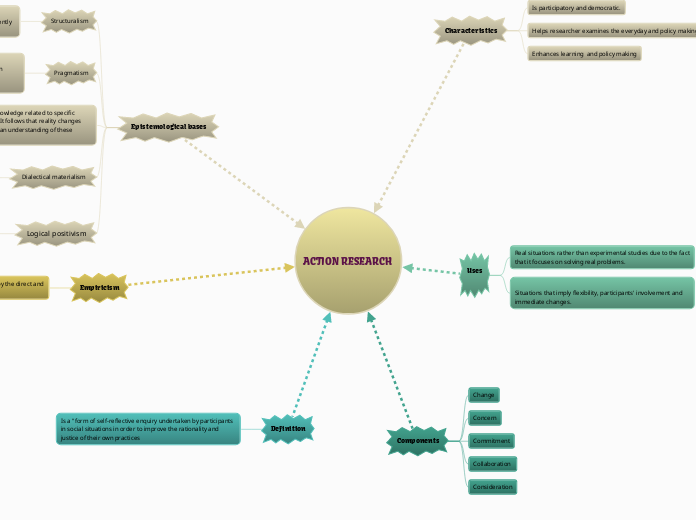
ACTION RESEARCH
Characteristics
Is participatory and democratic.
Helps researcher examines the everyday and policy making
Enhances learning and policy making
Uses
Real situations rather than experimental studies due to the fact that it focuses on solving real problems.
Situations that imply flexibility, participants' involvement and immediate changes.
Components
Change
Concern
Commitment
Collaboration
Consideration
Epistemological bases
Structuralism
This focuses on knowledge and theory as two sharpy separated domains. It means real objects exist independently of knowledge, and knowledge occurs by itself.
Pragmatism
This verifies the union of knowledge and reality based on experimental practice
This views on production of knowledge related to specific historical and social contexts. It follows that reality changes constantly, then knowledge is an understanding of these changes
Dialectical materialism
This views on production of knowledge related to specific historical and social contexts. It follows that reality changes constantly, then knowledge is an understanding of these changes
Logical positivism
This begins with the postulation of a hypothesis which has to be tested rigorously. There can be more than one interpretation of the reality, but all variables have to be controlled.
Empiricism
This maintains that man produces knowledge by the direct and neutral observation of reality.
Definition
Is a "form of self-reflective enquiry undertaken by participants in social situations in order to improve the rationality and justice of their own practices