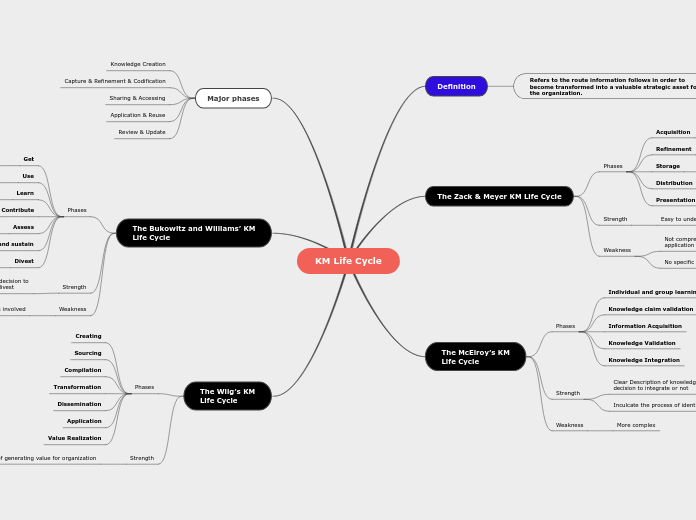
KM Life Cycle
Definition
Refers to the route information follows in order to become transformed into a valuable strategic asset for the organization.
The Zack & Meyer KM Life Cycle
Phases
Acquisition
Deals with sources
Refinement
Standardizing
Storage
physical or Digital
Distribution
The channel
Presentation
Context
Strength
Easy to understand and Simple to implement
Weakness
Not comprehensive in terms of
application of knowledge
No specific way pf capturing tacit knowledge
The McElroy’s KM
Life Cycle
Phases
Individual and group learning
Knowledge claim validation
Information Acquisition
Knowledge Validation
Knowledge Integration
Strength
Clear Description of knowledge evaluation and
decision to integrate or not
Inculcate the process of identifying knowledge
Weakness
More complex
Major phases
Knowledge Creation
Capture & Refinement & Codification
Sharing & Accessing
Application & Reuse
Review & Update
The Bukowitz and Williams’ KM
Life Cycle
Phases
Get
Seeking out information
Use
Combine information
Learn
learning from experiences
Contribute
Share what they have learned
Assess
Evaluate the intellectual capital
Build and sustain
Keep the organization viable and competitive
Divest
Maintain
Strength
New phases of learning and decision to
maintain this knowledge or divest
Weakness
No evaluation process involved
The Wiig’s KM
Life Cycle
Phases
Creating
Sourcing
Compilation
Transformation
Dissemination
Application
Value Realization
Strength
Details of generating value for organization