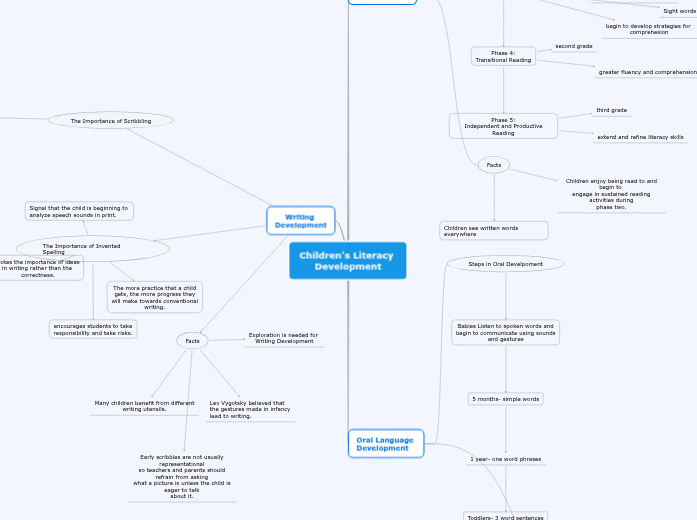
Children's Literacy
Development
Reading
Development
Reading Development Phases
Phase 1:
Awareness and Exploration
Phase 2:
Experimental Reading
Phase 3:
Early Reading
Phase 4:
Transitional Reading
Phase 5:
Independent and Productive Reading
third grade
extend and refine literacy skills
second grade
greater fluency and comprehension
First grade
being reading simple stories
begin to develop strategies for
comprehesion
Sight words and fluency
Kindergarten
Basic understandings of print:
top to bottom, left to right
letters and letter-sound
relationships
Birth- Preschool
logographic knowledge
Pretend-reading
Begin to identify some letters
and letter-sound relationships
Facts
Children see written words everywhere
Children enjoy being read to and begin to
engage in sustained reading activities during
phase two.
Oral Language
Development
Steps in Oral Develpoment
Babies Listen to spoken words and
begin to communicate using sounds
and gestures
5 months- simple words
1 year- one word phrases
Toddlers- 3 word sentences
Preschool- larger vocabulary from listening
to others and reading books
sentences become longer/more complex
begin to talk about their experiences
Facts
the rate of vocabulary development is strongly
influenced by how much the child is exposed to
oral communication from parents.
Toddlers often come up with original speech
utterances that are not copies of adult verbalizations,
so it is argued that this is evidence of an independent
emerging language system.
By the time that children enter Kindergarten, many
may have a vocabulary of 10,000 words or more.
By age 3, children of professional families know about
1100 words, children of working-class families know
about 750 words, and children of welfare-recipient families
know just 500 words.
Writing
Development
The Importance of Scribbling
Early Scribbling
Controlled Scribbling
Scribble Drawing
Name Scribbling
the intent is to make their
writing look like words
pictographic in expression
between 4 and 6
scribbles have meaning
begin to understand the difference
between drawing and writing. They
start to use letters, usually beings
with their name.
systematic, repeated marks
(circles, lines, dots.squares)
between 3 and 6
also called scribble writing
random marks on paper
learn that whatever is in
their hands is what makes
the marks.
The Importance of Invented Spelling
Signal that the child is beginning to
analyze speech sounds in print.
The more practice that a child
gets, the more progress they
will make towards conventional
writing.
Notes the importance of ideas
in writing rather than the
correctness.
encourages students to take
responsibility and take risks.
Facts
Many children benefit from different
writing utensils.
Lev Vygotsky believed that
the gestures made in infancy
lead to writing.
Exploration is needed for
Writing Development
Early scribbles are not usually representational
so teachers and parents should refrain from asking
what a picture is unless the child is eager to talk
about it.