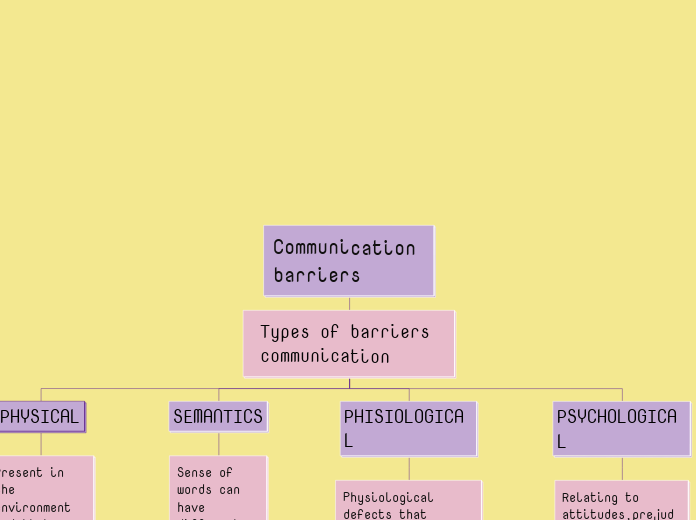
Communication barriers
Types of barriers communication
PHYSICAL
Present in the environment and that prevent good communication
FOR EXAMPLE
Noise,ligting, distance,failure of means to broadcast a message:telephone, projector, acoustics,tape recorder,acreen

SEMANTICS
Sense of words can have different meanungs different interpretations
FOR EXAMPLE
If the sender says:"come as quickly as possible", the receiver could interpret it as "immediately"or "soon, but not urgent
PHISIOLOGICAL
Physiological defects that affect the senses of the sender as well as the receiver hinder the clear transmission and reception of messages
FOR EXAMPLE
Hearing,visual, writing,reading

PSYCHOLOGICAL
Relating to attitudes,prejudices, moods emotional states of the sender or receiver
FOR EXAMPLE
Fear,joy sadness, anger

COMMUNICATION MODELS
CONTAMINATED MODELS
The victimiser
Is the accuser
Authoritarian
Attitude of superiority
look for defects
criticeze and blame others
Use phrases
It¨s your fault
I¨m right
It is as I say and period
You are always wrong

The victim
It¨s my fault
Everything happens to me
Relationsnalist or calculator
Adopt a correct attitude
sensible
Sereme
Over reasonable
Cold
without reflection of emotions
Use intellectual language to deal with the threat
Resort to dating
Scientifec explanations
Emit sentences like
According to that author
As provided by law

Evasive or distracting
Ignorw thw threat
Seek mechanisms to focus attention on another topic
disperses
Is elusive
Avoid confrontation
It does not resolve conflicts

Conciliator or appeaser
Virginia Satir tells us about a functional congruent communucation model the person is aware of her thoughts and emotions expresses himself honestly
Frank
direct
clear
respectful
His body and verbal language are :
coherent
set limits
not afraid of confrontation
Reach win win agreements
Does not blame or judme

HEALTHY MODELS
People communicate we do it not only with words but
With al our being
With the body
The face
The look
Tone of voice
Our principles
values

Effective communication we must consider three doors
True
Need
Warmth or affection

Speaking truthfully is essential to building healthy relationships which is why we must discard so- called "White or White lies" because the truth always comes aout
We have frequently heard expressions "The important thing is not what is said ,but how it is said""Adrop honey is better than a barrel of venegar

Non-verbal communication
Nonverbal communication is one in which the sender and receiver do not use words to convey the messages
Types of nonverbal communication
Proxemics:
It is the study of the use and perception of social and personal space to communicate
The anthropologist Edward Hall (1968) distinguishes the following types of space:
Fixed space:
marked by immovable structures, such as the barriers of countries.
Semi-fixed space:
space around the body. This can be invaded (staring at someone, occupying two seats with bags when people are standing).
Distance types
INTIMATE DISTANCE:
between 15 and 45 cm. a lot of confidence, communication is done through the look, the touch. Private intimate area less than 15 cm.
PERSONAL DISTANCE:
between 46 and 120 cm. At work, meetings, assemblies, parties, friendly conversations.
SOCIAL DISTANCE:
between 120 and 360 cm. This distance separates us from strangers.Example: the saleswoman of a store.
PUBLIC DISTANCE:
occurs at more than 360 cm. And it has no limit. Eg: conferences or talks.

Kinesics:
It refers to body language, gestures and movements that accompany communication to enhance it; They are used to convey ideas and feelings.
The expressionGestures (hands, arms, head…)The facial expression.The look.The smile.displacement

Paralinguistics:
Study of oral, auditory, tactile or visual signs. These non-linguistic variations where sounds are present and words are absent.
For example:
Crying.Laughter.The tone of voice (intensity and volume).The rhythm (pause or haste).

Artifact:
It deals with the study of objects and accessories in an environment or context of communication.
There are 4 types of objects:
Integrated:
used for a specific purpose.
For example
table, podium.

Incidental:
those that affect the recipients, even if they are not part of a plan to use them.
For example
fan, lamp.

Revealed:
they are the ones that the communicator uses with emphasis, shows the receivers.
For example
projector, video.
:format(jpg)/f.elconfidencial.com%2Foriginal%2Fa23%2F757%2F09f%2Fa2375709f80795e88646130220043300.jpg)
Hidden objects:
those that are not detected by the public, but their use has been planned
For example
a bouquet of flowers, tablecloths, pens, water, glasses