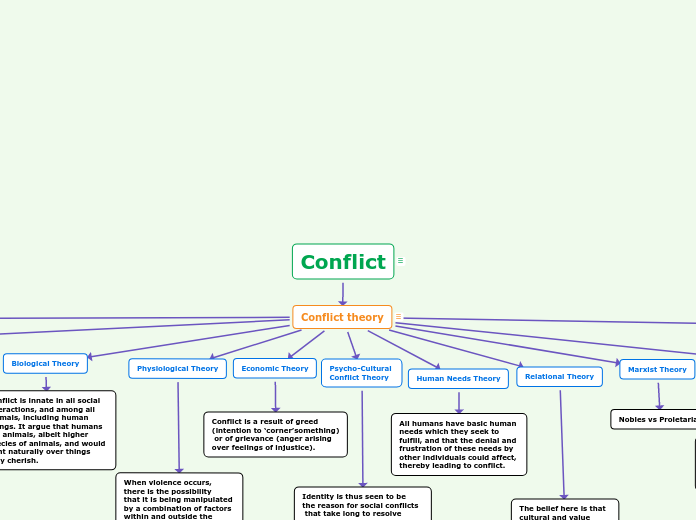
Conflict
Conflict theory
Structural Conflict Theory
Marxists
The solution to these types of
conflict to the Marxists is
that the contradictions will
end in a revolution-civil war.
Structuralisms
It attempts to explain
conflict as a product of the
tension that arises when
groups compete for scarce
recourses.
Realist Theory
Conflict has its roots in forces
that are inherent in human
nature, that human nature is
selfish, individualistic and
naturally conflictive.
Biological Theory
Conflict is innate in all social
interactions, and among all
animals, including human
beings. It argue that humans
are animals, albeit higher
species of animals, and would
fight naturally over things
they cherish.
Physiological Theory
When violence occurs,
there is the possibility
that it is being manipulated
by a combination of factors
within and outside the
individual’s control.
Economic Theory
Conflict is a result of greed
(intention to ‘corner’something)
or of grievance (anger arising
over feelings of injustice).
Psycho-Cultural
Conflict Theory
Identity is thus seen to be
the reason for social conflicts
that take long to resolve
despite the belief that
ethnicity is the biggest source
of identity-based conflicts.
Human Needs Theory
All humans have basic human
needs which they seek to
fulfill, and that the denial and
frustration of these needs by
other individuals could affect,
thereby leading to conflict.
Relational Theory
The belief here is that
cultural and value
differences are as well
as group interests all
influence relationships
between individuals
Systemic Theory
The position of this theory is
that reason(s) for any social
conflict lie in the social
context within which it
occurs.
Marxist Theory
Nobles vs Proletariat
Game Theory
Is the formal study of
decisionmaking where several
players must make choices
that potentially affect the
interests of the other players.