DATA STRUCTURE
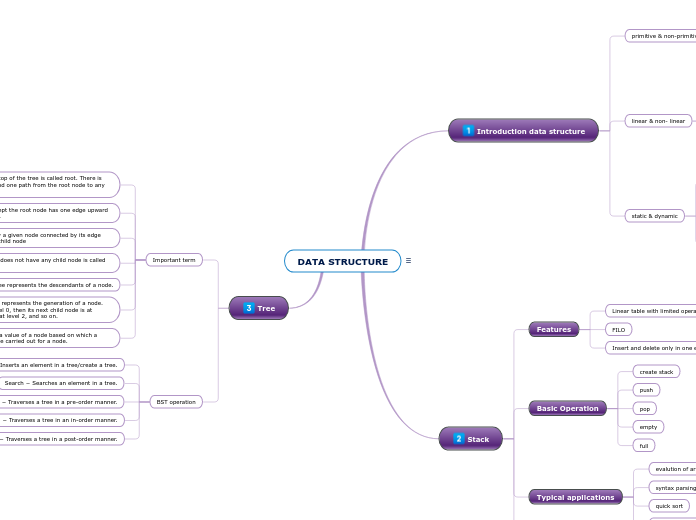
Introduction data structure
primitive & non-primitive
primitive
Basic data structures that are directly operated upon by machine level instructions.
The primitives data type are basic data type that are available
non primitive
Complicated data structures that are derived
from the primitive data structures
These data types are used to store group of
values.
linear & non- linear
Linear
Traverses the data elements sequentially, in which
only one data element can directly be reached.
non-linear
Every data item is attached to several other data
items in a way that is specific for reflecting
relationships. Example : tree and graph
graph
static & dynamic
static
Size is fixed at compile time, and
does not grow or shrink at runtime.
Can be inefficient as the memory for
the data structure has been set aside
dynamic
size is not fixed at compile time and that
can grow and shrink at run time to make
efficient use of memory.
Makes the most efficient use of memory
as the data structure only uses as much
memory as it needs
Stack
Features
Linear table with limited operations
FILO
Insert and delete only in one end
Basic Operation
create stack
push
pop
empty
full
Typical applications
evalution of arithmetic expression
syntax parsing and checking
quick sort
memory management
Storage representation
code
logical mode
Tree
Important term
Root − The node at the top of the tree is called root. There is only one root per tree and one path from the root node to any node.
Parent − Any node except the root node has one edge upward to a node called parent.
Child − The node below a given node connected by its edge downward is called its child node
Leaf − The node which does not have any child node is called the leaf node.
Subtree − Subtree represents the descendants of a node.
Levels − Level of a node represents the generation of a node. If the root node is at level 0, then its next child node is at level 1, its grandchild is at level 2, and so on.
keys − Key represents a value of a node based on which a search operation is to be carried out for a node.
BST operation
Insert − Inserts an element in a tree/create a tree.
Search − Searches an element in a tree.
Preorder Traversal − Traverses a tree in a pre-order manner.
Inorder Traversal − Traverses a tree in an in-order manner.
Postorder Traversal − Traverses a tree in a post-order manner.