1
Bacteria
Archea
Shape: Cocci - circular
Bacilli -
Single-Celled prokaryotic
NO Nucleus or cell membrane or organelle
Have a very rigid cell wall
Capable of withstanding super rough environmental conditions
Archaebacteria
They're the oldest organism on the planet
Lives in the most inhospitable areas
Lives in very hot, salty, and acidic conditions
Bacteria
Single-celled prokaryotic organisms
NO Nucleus or membrane-bound organelles
Also have several chemical types of cell walls
Eubacteria
Single-celled prokaryotes
Classified by their shape, their response to stains and the arrangements
They contain Plasmids
Eukaryotes
Animalia
Vertebrates: backbone in its
internal skeleton
Invertebrates: does no have
a backbone in its internal skeleton
Fungi
Fungi Imperfecti
(Phylum Deuteromycota)
Usually do not reproduce
sexually and are very diverse

Penicillium
Chytrids
(Phylum Chytridomycota)
-Mostly unicellular and
aquatic (spores have
flagella)
-Can be parasites or
live on decaying
plants or insects

Synchytrium endobioticum
Zygospore Fungi
(Phylum Zygomycota)
-Multi-cellular and
terrestrial
- Usually asexual
-When sexual they use
zygospores which protects
contents from drying

Rhizopus
Sac Fungi
(Phylum Ascomycota)
- Develop sacs, asci, during
sexual reproduction
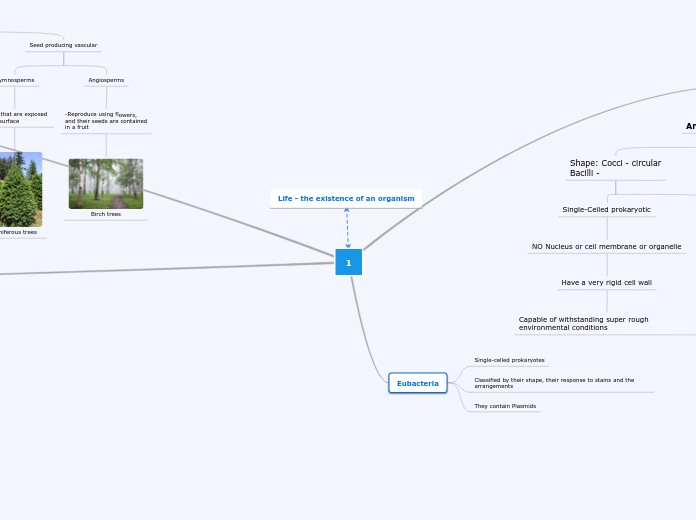
Yeast cells
Club Fungi
(Phylum Basidiomycota)
-Release hyphae,"basidia"

Mushrooms
Protista
Fungi-like:
-they absorb nutrients from
other organisms, living or
dead.
Cellular slime molds
-One nucleus each
- form pseudoplasmodium
when food is scarce
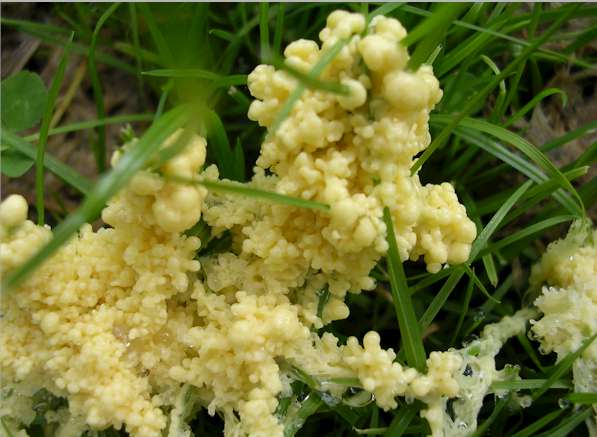

Plasmodial slime molds
- Contains many nuclei
-feed by engulfing small
particles
of food into their
cytoplasm

Water molds
- Filamentous organisms
- extend threads into their
host and release digestive
enzymes and absorb the
resulting nutrients.

Animal-like (Protozoa):
-they consume other organisms
for food
Flagellates
-Use flagellum for food
and movement (tail-like)
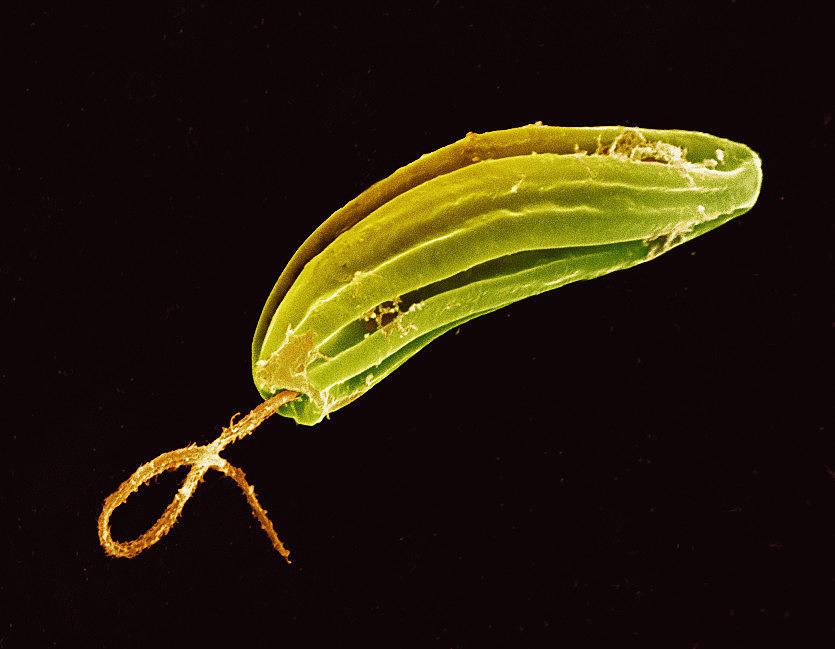

Cercozoans
- Use pseudopods for
feeding and locomotion

Amoeba
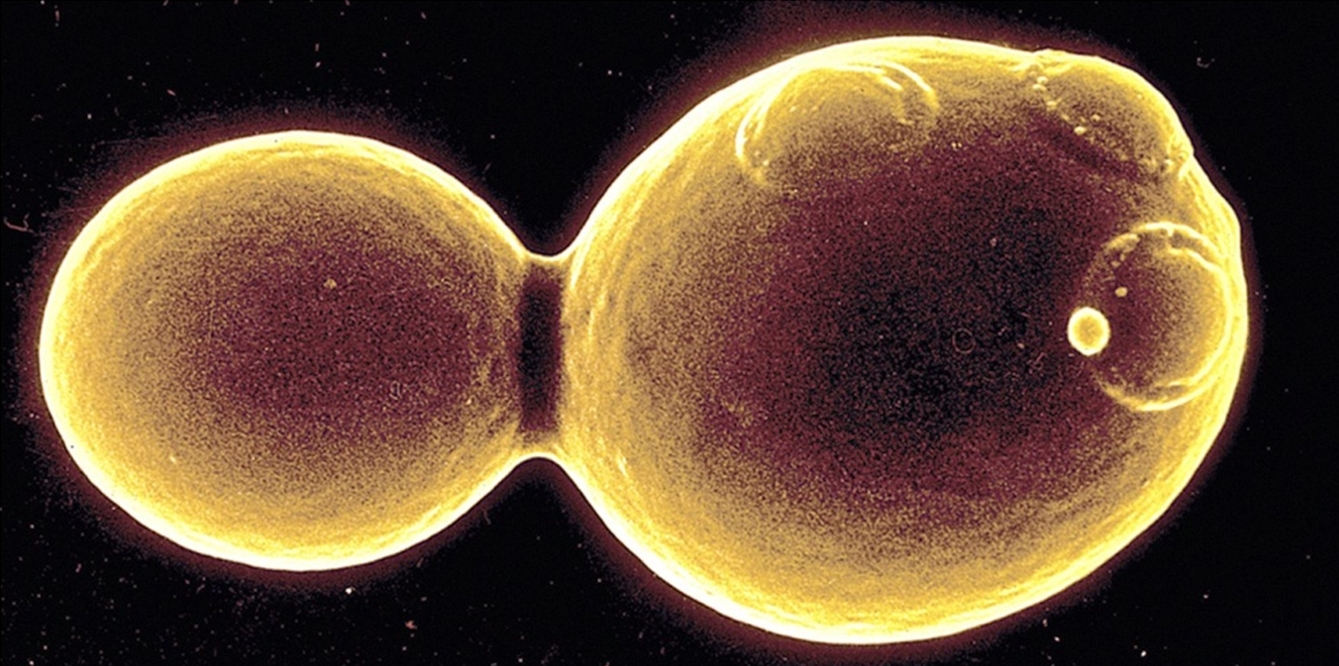
Ciliates
-Use cilium for
sweeping food and
for movement (hair
like)
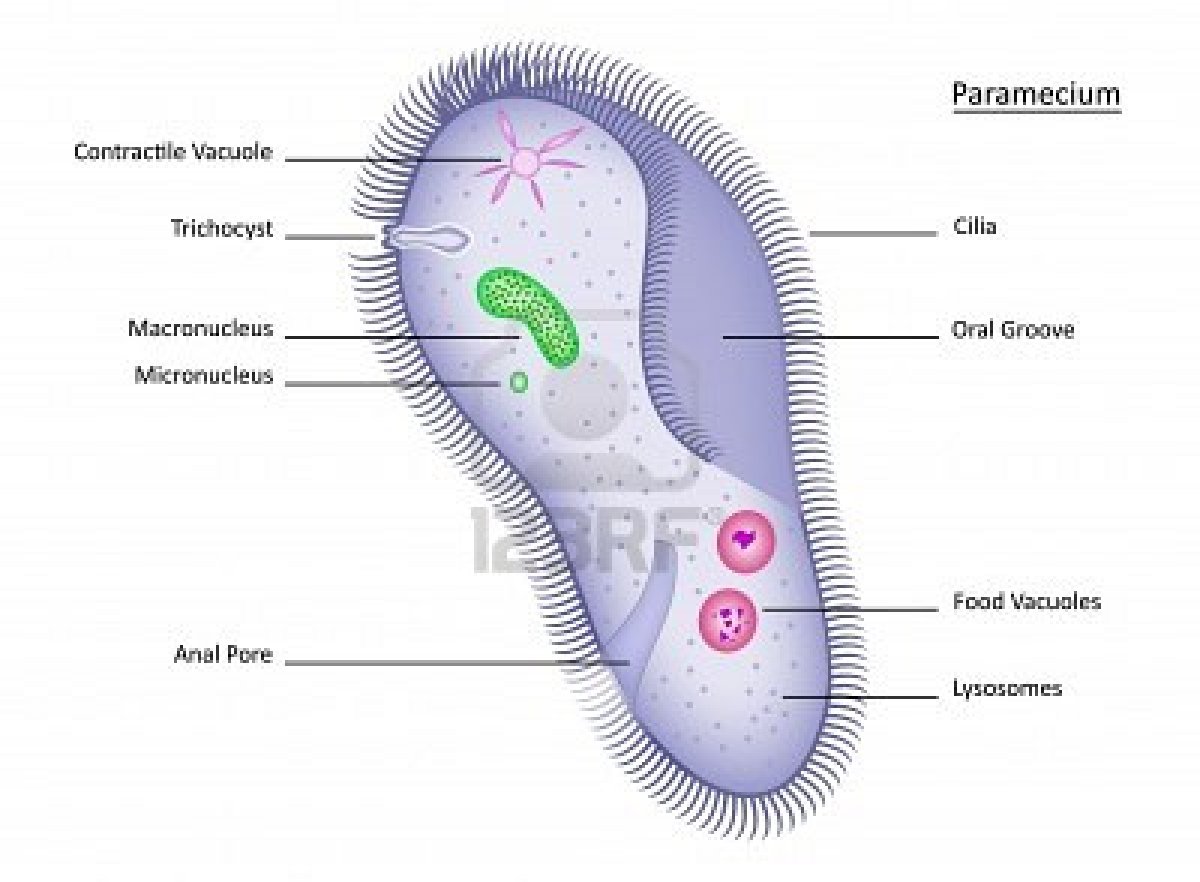
Paramecium
Sporozoans
-parasites of animals,
taking the nutrients they
need from their hosts
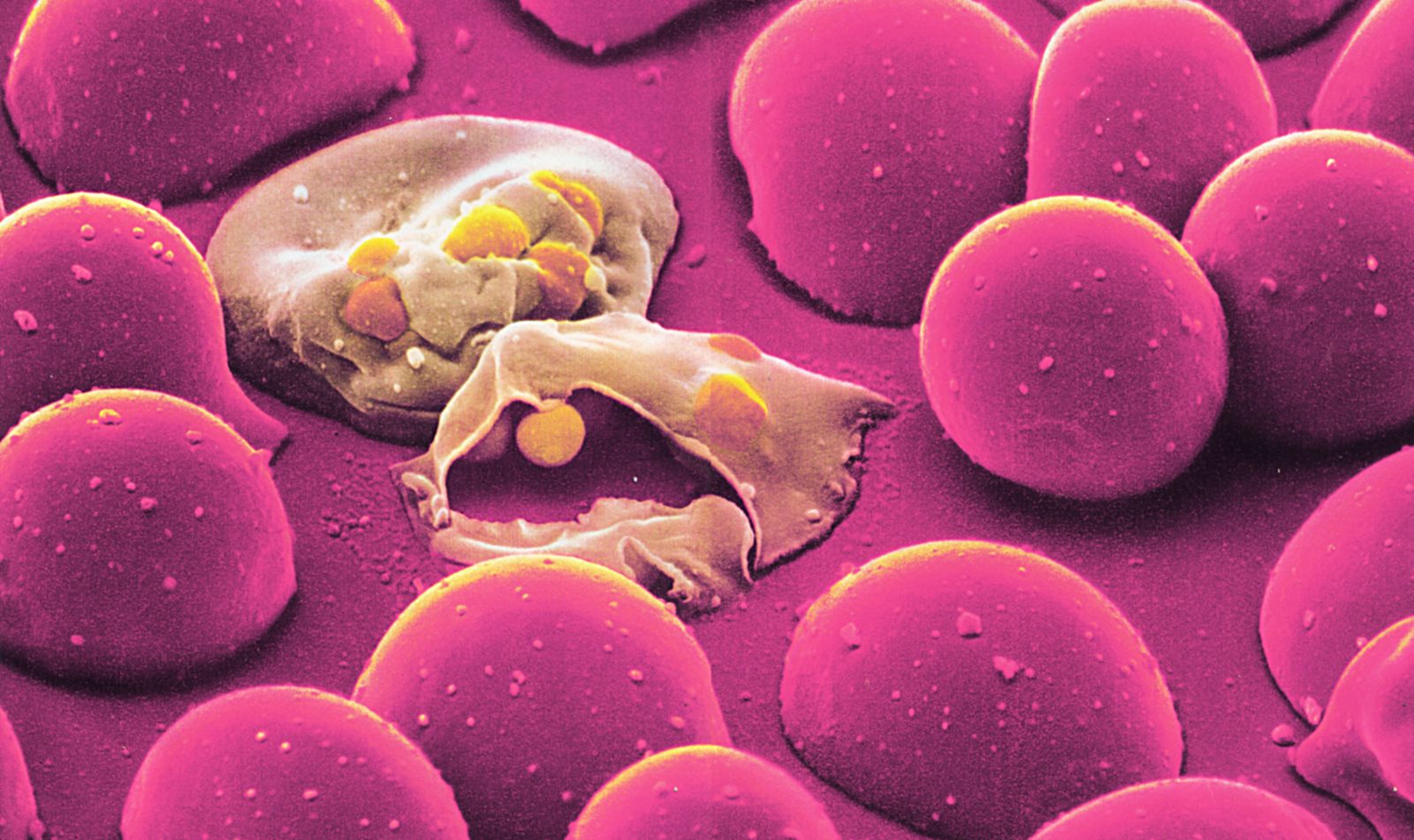
Malaria
Plant-like:
- make their own food
by photosynthesis
Diatoms
-Single celled, aquatic
-Rigid cell walls with an
outer layer of silica
-Asexual reproduction

Dinoflagellates
- Have two flagella

Gonyaulax catenella
Euglenoids
-Have chloroplasts and conduct
photosynthesis, they also have
flagella and can absorb nutrients
-Autotrophs in sunlight and
heterotrophs in the dark
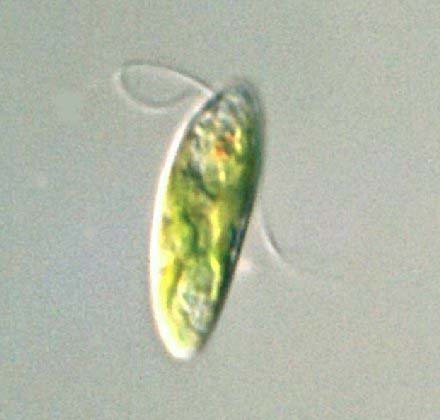
Euglena gracilis
Plantae
Seedless Vascular
-Gametophytes were reduced
to tiny, short-lived structures that depend on moisture to carry out sexual reproduction.

Whisk ferns (Phylum Psilotophyta)

Club mosses (Phylum Lycophyta)

Horsetails (Phylum Sphenophyta)
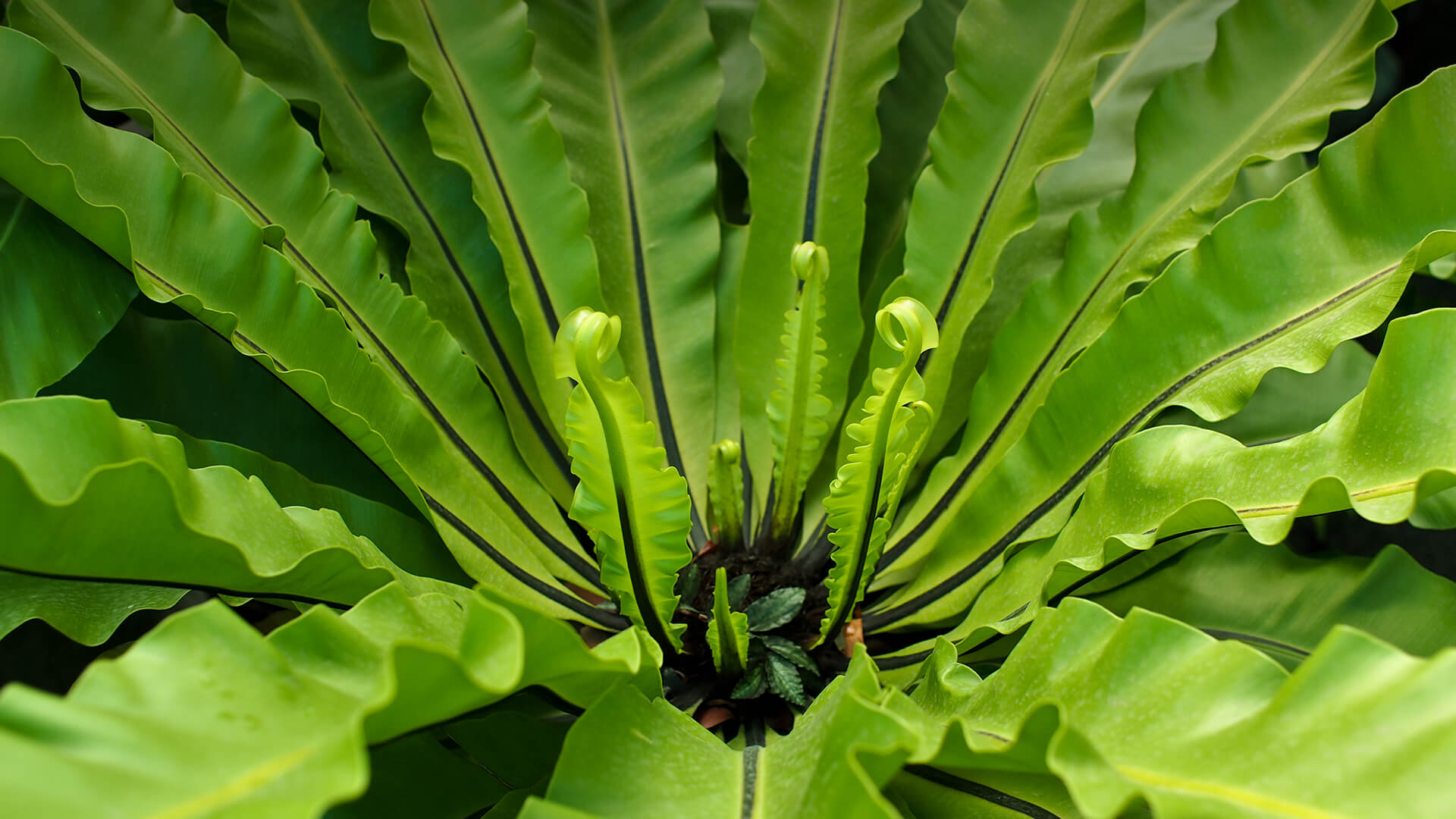

Ferns (Phylum Pteridophyta) •
Non-Vascular: Bryophytes
-These plants do not have vascular tissue,
and they are dependent on the processes
of diffusion and osmosis to transport nutrients

Mosses (Phylum Bryophyta)

Liverworts (Phylum Hepatophyta)

Hornworts (Phylum Anthocerophyta)
Seed producing vascular
Gymnosperms
-Seeds that are exposed
on the surface

Coniferous trees
Angiosperms
-Reproduce using flowers,
and their seeds are contained
in a fruit

Birch trees
Main topic
Life - the existence of an organism
Evolutionary Milestones
Nerve cord
Paired gill slits
Most advanced organs and
systems
Chordata
Tunicates
Cephalochordates
Vertebrates
Agnethanos
Gnathostomata
Adaptation to Terrestrial Lide
Fish:have a skeleton of cartilage
rather than bone.
Amphibians:Use their moist skin to
assist in gas exchange
Reptiles:Have body scales that create
a waterproof barrier that helps prevent
dehydration in dry air
Birds: Endothermic (constant body temperature)
and has four chambers to the heart
Mammals: Females have mammary glands
(produces milk), have developed brains and
hair has multiple functions
Monotremes
Marsupials
Placenta mammals
Developed mantle that
surrounds internal organs
contains organ
system
Simplest Human:
developed stomach
Uses flagellates and cilia
to control water flow
an
Bilateral Symmetry: can
be divided along one plane
to make two equal parts
Developed germ layers
Developed centralized
nervous system
ne
Radial Symmetry: can be
divided along any plane
Developed nervous system
Developed digestive tract
Segmentation: division
of the body in repetitive
segments
Developed closed
circulatory system