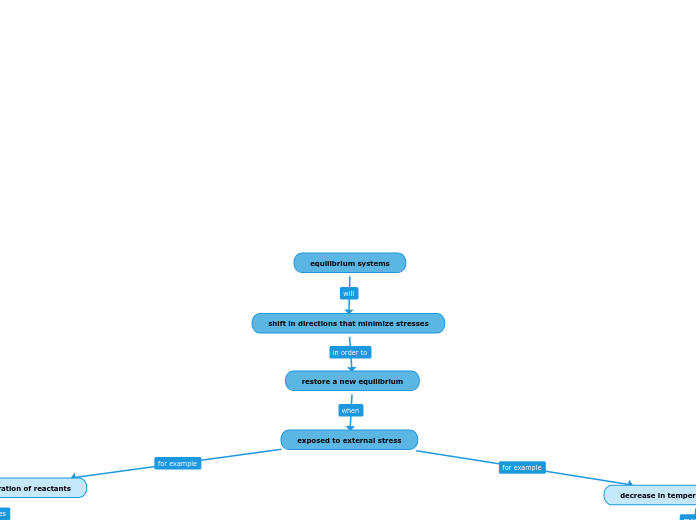
equilibrium systems
shift in directions that minimize stresses
restore a new equilibrium
exposed to external stress
increase of concentration of reactants
more collisions
reactant particles
the forward reaction is favored
an increase of products
the system reaches a new equilibrium
the equilibrium law
changes in concentration
the reactants are favored
K << 1
the denominator of the fraction (reactants) is greater than the numerator
the equilibrium constant "K" of the system remains the same
a new equilibrium is achieved with different concentrations of chemicals
the products are favored
K >> 1
the numerator of the fraction (products) is greater than the denominator
changes in temperature
the forward reaction is endothermic and temperature increases
K increases
the system shifts to increase the product side (numerator)
the equilibrium constant "K" of the system changes
a new equilibrium is achieved with a new temperature of the system
the value of the equilibrium constant is only temperature dependent
the forward reaction is exothermic and temperature increases
K decreases
the system shifts to increase the reactant side (denominator)
decrease in temperature of the system
the system must shift
produce more energy
the exothermic reaction side is favored
an increase of the release of energy