Day 3 4/27
Brain Changes
- not fixed
Subtopic
Subtopic
Subtopic
Retention
- Space out Study/review later
Subtopic
Learning vs. Memorizing
- Retrieval Strategies
Subtopic
Gender Differences
Subtopic
Trend that girls try harder than boys
Subtopic
Growth Mindset
Statistics show that people in poverty do perform less in school and stuff, so how true is this?
Your environment should have an influence, maybe it isn't 100% about passion. My thoughts
Anyone can be freed from poverty. Anyone can pass a class.
5/2 "The fact that one region of the brain is shrinking in teenage girls while the same region is growing in teenage boys doesn’t mean that boys are smarter than girls, or that girls are smarter than boys. It just means that girls and boys are different. Differences do not imply an order of rank." Different is good, it is how we learn.
Learning capabilities are not set by the circumstances you are born in. You need to have a growth mindset. With your push towards learning, you will be able to learn more. Money and your genes don't make you smart. It's your passion.
Learning capabilities are not set by the circumstances you are born in. You need to have a growth mindset. With your push towards learning, you will be able to learn more. Money and your genes don't make you smart. It's your passion.
5/2
I think it useful to that we are more invested and more likely to remember information when we have context for the situation. Knowing this we can help our students remember and apply top principles when we help them see when the information
fits in with everything else
05/02/2018 From Boys Adrift and question stood out to me when a man said,"We had to walk. Even in the snow. And I'll Tell you one thing. When you've walked three miles in the snow to get to school, you make darn sure you learn something. You don't want that long walk to be for nothing. I think it motivates you." So how do you think the generations
The method of retrival through consolidation
Floating topic
Day 4 4/30
Maslows Hierarchy of needs
I like the idea of growth mindset, but just for the sake of argument, I like the ideas that Alfie Kohn has against this idea.. "All we have to do is get kids to adopt the right attitude, to think optimistically about their ability to handle whatever they’ve been given to do. Even if, quite frankly, it’s not worth doing." He is basically saying that in the educational setting growth mindset is just another fad that is aimed at changing the students instead of facing the bigger issue such as quality of curriculum or teaching pedagogy. https://www.alfiekohn.org/article/mindset/
Retrival
Type of Learner
Rule Learner
Reasons why males are preforming
left favorably in today's society
Study of males and females:
Fine motor skill challenge where both genders were told it was for sewing and the males did worse than the females. Then males were told that it was for a more manly task and they did better than the females
- Spaced Repition
Interleading Practice
Spacing out varies activities i.e. Learning something then doing something else (art) then retrieving what you learned
Stereotypes
Example Learner
Principles
More surface level of learning:
tend to abstract the underlying principles or "rules" that differentiate the examples being studied.
tend to memorize the examples rather than the underlying principles: lack the grasp of rules needed to classify or solve it
5/2
Voting Topics
Floating topic
5/3
Anxiety
Trait Anxiety
Attribute for anxiety is high:
naturally uptight and stressed
With somebody across multiple situations: Physical Makeup
State Anxiety
When as certain cituation causes stress
i.e. Taking a test or turning in homework
Debilitating Anxiety
Performance is hindered because of stress. When Trait anxiety is present then state anxiety is thrown on top of that.
Facilitating Anxiety
Add anxiety to the situation to have it go well.
bad
Good
stress
External thing that messes with internal anxiety
Anxiety
internal
5/7
egocentrism
Defining Characteristic: True all/majority of the time for all/majority of instances
Correlational Characteristics: True some of the times for some instances
prototype: Most appropriate example based off of the defining Characteristics; Defining characteristic clearly visible; common in the students environment
Mammal
Defining Characteristics: fur, suckle their young, warm blooded
Correllational Characterstic: Sometimes they fly (bat), can live on land, some can swim (whale),
5/11
positive example: An instance where the the example meets the defining characteristics
negative example: An instance that does not meet the charactersitcs
positive example: Monkey
negative example: snake

phatic communication
Negative Transfer
When you use previous knowledge and apply it to something, but it is incorrect i.e. when learning kickball a child shows that they can do a controlled soccer dribbling instead of drilling the ball
Positive Transfer
when you use previous knowledge and it is correctly applied to the new situation.
How to promote Positive Transfer:
Explain topic more in depth
corrections
spaced out transitions with time in between things that are similar and can easily be confused
Under-Generalization
Category is defined as too narrow
Over-Generalization
Category is defined as too broad
may 22, bryce thingy
Attribution Theory
3 variables
2: Is the failure attributed to something controllable or uncontrollable?
3: Stable or unstable
Stable: under any circumstance
unstable: Just happens in one instance i.e. "I got lucky"
How to diagnose success or failure
mastery orientation
want to master a specific task. keeps trying and learning all about the subject. not simply preparing for a performance, but looking to master a task. more skill focused.
performance orientation
tend to choose easier tasks in order to perform it better. As soon as performance is lower, this person tends to quit. prepares just for the performance, more status focused
lesson to teach:
preasses: what do you think makes a good jump shot?
defining characteristics, correlational
prototype
learning styles
Lifetime development Milestones Piaget, Erickson
1 stage: Sensorimotor stage (birth to age 1)
Subtopic
Piaget: Cognitive and biological
Erickson: social
help develope in more than just a cognitive way: Moral, ethical, etc. PIaget and erickison stages
learned helplessness
maybe teach him how to do his own practice. How to get the best out of practicing by yourself. Might be in zpd because at that age all I did was huck up shots, but to teach him different drills and what not could help.
Piaget
Know stage names (ie. sensory motor stage) and know certain key milestones
Subject:
To help Bryce understand his interests and maybe explore new topics.
Age-Level:
age 12: Piaget Late childhood and early adolescence Erickson: Industry vs. Inferiority and Identity vs. (role) confusion
Generative Topic:
Purpose:
During this period, they explore possibilities and begin to form their own identity based upon the outcome of their explorations. Failure to establish a sense of identity within society ("I don’t know what I want to be when I grow up") can lead to role confusion. Role confusion involves the individual not being sure about themselves or their place in
society.
Pre-Assessment:
During the Preassessment it was clear that Bryce had a whole bunch of different interests. Maybe a good question to ask if he knows what future job that he wants. Maybe he wants to know about small motor because it will help him with his future job idea.
He said that he knew how a car engine works but wants to know more about a smaller engine and proper maintenance for that.
during lesson pre-assessment:
Understanding Goals: What they will understand by the end of lesson. Kind of like knowing the steps to do something (i.e how to serve a tennis ball)
I want Bryce to understand how a small engine works compared to a car engine. and also how to take care of small engines. This is a good lesson to understand differences and see comparisons. Be aware of negative transfers that may come because of this.
Performance Goals: What they will actually be able to do by the end of the lesson. The actual execution of the goal, (i.e if they are able to actually hit a serve in)
Bryce will be able to learn more about what makes a small engine work and he will be able to take apart the separate components and put them back together. Through study of the individual parts, Bryce will be able to understand
Concept order:
Brain
Neurons
Dendrite
axon
myelin Sheath
Mirror Neuron
when someone yawns,
you want to yawn.
copy emotions of those
around you
Lobes
Frontal Lobe
motor skills, voluntary movement
Parietal Lobe
monitors bodily senses (heat, pain)
Temporal Lobe
senses: hearing, memory
Occipital Lobe
visual information
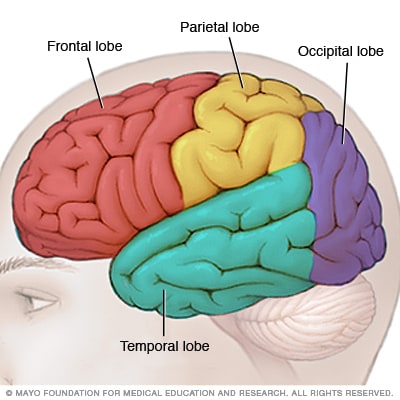
Subtopic
Limbic System
Amygdala
Hippocampus
short term memory into long term

Subtopic
Imaginary Audience
debilitation and sometimes facilitating.
kind of like a created state where you almost feel like you are being judged.
Like when you walk in front of a large crowd and feel like they are all watching you.
Sensory Register
registers the senses
takes in senses first recording of memory process
Control Language vs. Information Language
Control: giving a command to do something
i.e. "we are going to do this"
Information Language: less direct way of asking something. give reasons and such
Personal Theory
Look at environment for understanding of things around them.
can be accurate or way off
Construction of a schema basked off personal experiences
Howard Gardener Multiple Intelligence

Subtopic
Subtopic
