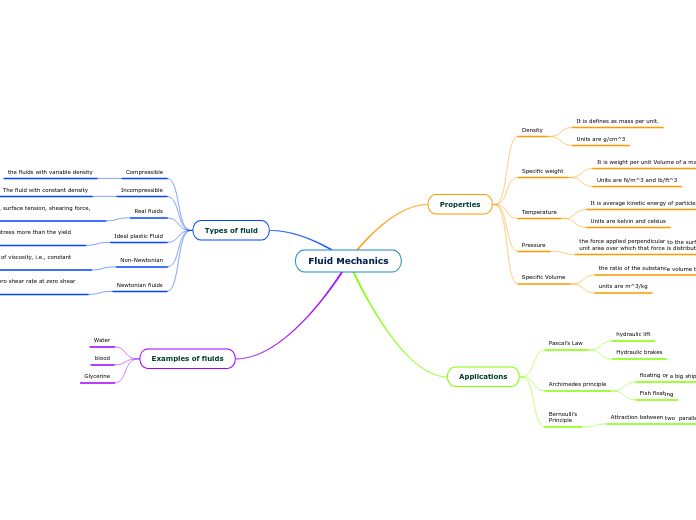
Fluid Mechanics
Properties
Density
It is defines as mass per unit.
Units are g/cm^3
Specific weight
It is weight per unit Volume of a material
Units are N/m^3 and lb/ft^3
Temperature
It is average kinetic energy of particles in an object
Units are kelvin and celsius
Pressure
the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed
Specific Volume
the ratio of the substance volume to mass
units are m^3/kg
Applications
Pascal’s Law
hydraulic lift
Hydraulic brakes
Archimedes principle
floating of a big ship
Fish floating
Bernoulli’s
Principle
Attraction between two parallel moving boats
Types of fluid
Compressible
the fluids with variable density
Incompressible
The fluid with constant density
Real fluids
fluids which have viscosity, surface tension, shearing force, and compressibility
Ideal plastic Fluid
A fluid having the value of shear stress more than the yield value
Non-Newtonian
It does not follow Newton's law of viscosity, i.e., constant viscosity independent of stress
Newtonian fluids
It has constant viscosity, with zero shear rate at zero shear stress.
Examples of fluids
Water
blood
Glycerine