INTERCONECTIVIDAD PRIMER CORTE
PACKET TRACERT
MOBILE TELEFONY HISTORY
It is an electronic communication device, usually of reduced design and based on radio wave
Telephony Generations
0G: Generation 0

It was used from the 50s and 60s onwards. To create a great variety of radio and remote communication devices.
1G: First Generation

Unmanageable size and weight, it worked in an analog way, that is, its transmission and reception of data was supported by a set of radio waves that changed continuously.
2G: Second Generation

It marks the step from analogue to digital telephony, through a series of protocols, improving continuous call handling, more simultaneous links in the same bandwidth.
3G: Third Generation

It was revolutionary in the field of mobile telephony as it led to the appearance of the first cell phones that incorporated a color LCD screen, a fact that opened up an immense range of possibilities in terms of adapting new functions.
4G: Fourth Generation

Greater bandwidth, continuous improvement in technology and the miniaturization and immersion of APPS supported by the internet connection.

It is an education-focused simulation and routing class tool created by the manufacturing company CISCO
Can be used to teach IT concepts
Supports most protocols and technologies
Enables students to explore concepts, experimental behaviors, and test comprehension
Simulates continuous real-time updates of underlying network logic and activities
Facilitates teaching by providing a free multi-user environment allowing instructors to easily teach
Supplements real equipment and allows for expanding learning opportunities beyond the limitations of a physical classroom
OSI MODEL
It is an international ISO reference standard.
PHASES OF THE OSI MODEL

There are orderly levels or phases that allow hierarchical information and the processing models of an information system
7. Application Layer
User functions. Exchange of variables.
Read/Write, Start/Stop
6. Presentation Layer
Data representation. Diagnosis
Coding
5. Session Layer
Synchronization. Request for answers. Establishment, dissolution and monitoring of a session.
Session coordination
4. Transport Layer
Formation, repetition and classification of packages.
Secured packet transmission.
3. Network Layer
Addressing of other networks and flow control.
Communication between two subnets.
2. Data Link Layer
Access method. Collision management. Limitation of data blocks.
CRC-Check. CSMA/CD.
1. Physical layer
Physical means of transmission. Error Test.
Coaxial cable, optical.
TOPOLOGY AND TWISTED PAIR
NETWORK TYPES

Various intercommunication structures in which data networks can be organized.
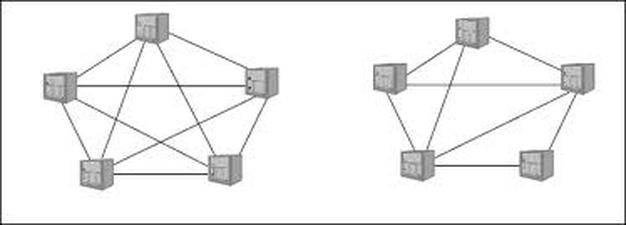
Total and partial interconnection
This type of interconnection provides multiple links between nodes on the network.
Star Interconnection
This type of interconnection provides multiple links between nodes on the network.

Bus interconnection
All nodes are connected to a single transmission medium using transveivers.

Tree interconnection
It is a chain of different bus structures of different length.
Ring interconnection
Se conectan en serie alrededor del anillo, es equivalente a unir los extremos de una red de bus, "Token ring"
TWISTED PAIR

They are the physical medium through which information is transmitted
Cat3
Cat4
Cat5
Cat6
Cat7
ScTP
TELECOMMUNICATIONS HISTORY

In the most important and relevant events in the history of telecommunications

Invention of radio

Invention first cordless phone

First telephone company

The Smarthphones

APPS
Subtopic
interconnectivity devices
Network Devices
According to its place in the OSI model
1-7.Cloud

It is a collection of equipment that is present in the entire OSI model, it is used to search in detail for each of its characteristics, even though it is not direct in the process
3. Routers

It is a device that allows interconnecting computers that work within the framework of a network. Its function: it is in charge of establishing the route that will be allocated to each data packet within a computer network.
2. Media Link
Bridge

In short, a bridge connects network segments forming a single subnet (it allows connection between computers without the need for routers). It works through a table of MAC addresses detected in each segment to which it is connected.
Switches

It is a logical digital device for interconnection of equipment so its function is to interconnect two or more hosts in a similar way to network bridges, passing data from one segment to another according to the destination MAC address of the frames in the network and eliminating the connection after the connection is completed.
1. Physics

A hub (HUB) is the device that allows centralize the wiring of a computer network, to later be able to expand it.
A WiFi repeater, also called a WiFi amplifier or adapter, is one of the devices that you can find to extend the coverage of your home network
Hubs
A hub (HUB) is the device that allows
centralize the wiring of a computer network, to later be able to expand it.
Data flow

Focuses on the way frames are propagated through the network
It is the movement of packets between layers 1,2 and 3 of the OSI model, so that the data is encapsulated to be effective.
The data is encapsulated in layer 1 through IP with an output and in layer 2 with a source and destination MAC address.
Means of link
Today's networks use three types of media to interconnect devices to send data throughout the system.
Metallic Threads (Copper)
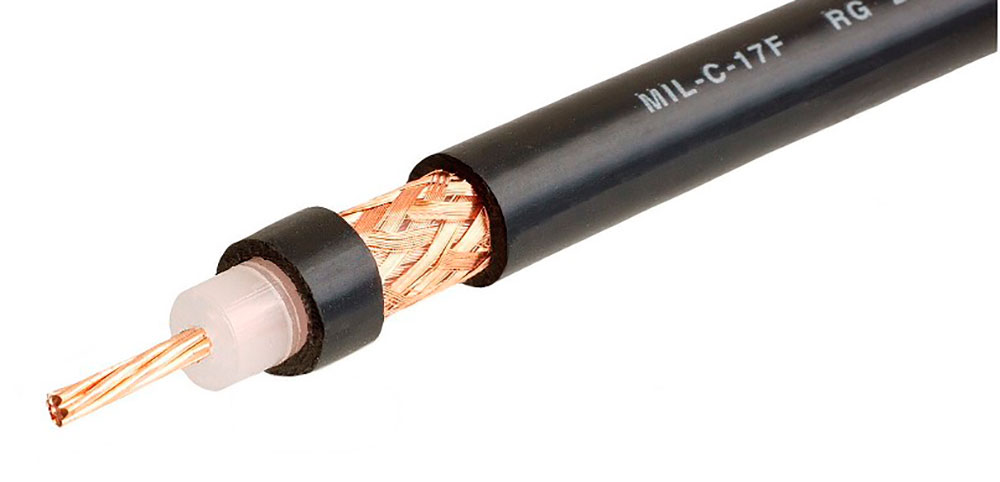

Information is encoded through electromagnetic pulses that match legible patterns.
Wireless Transmission

Electromagnetic wave patterns allow you to integrate patterns showing the various values in bits
Johan Santiago Romero Duarte - 644392 Interconectividad
UTP
100 meters and BASE-T data transport speed (10 Gbps)
They handle a speed range between 10 MHz and 600 MHz