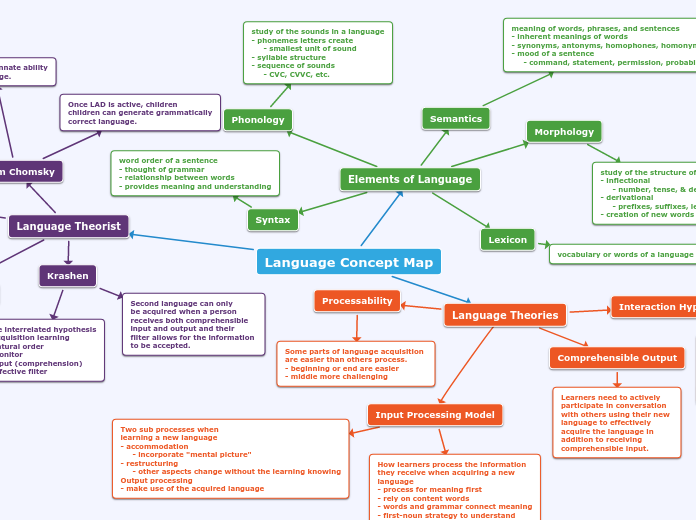
Language Concept Map
Language Theorist
Noam Chomsky
Children have innate ability
to learn language.
Language Acquisition Device (LAD)
- children decipher syntax of their
language through Universal Grammar
Once LAD is active, children
children can generate grammatically
correct language.
B.F. Skinner
Behaviorist theory
- language is learned
through social interaction
Acquired through imitation
and positive reinforcement.
Krashen
Five interrelated hypothesis
- acquisition learning
- natural order
- monitor
- input (comprehension)
- affective filter
Second language can only
be acquired when a person
receives both comprehensible
input and output and their
filter allows for the information
to be accepted.
Lightbrown & Spada
Four major perspective about
second language acquisition
- behaviorism
- innatist perspective
- psychological theories
- sociocultural
Language Theories
Input Processing Model
How learners process the information
they receive when acquiring a new
language
- process for meaning first
- rely on content words
- words and grammar connect meaning
- first-noun strategy to understand
Two sub processes when
learning a new language
- accommodation
- incorporate "mental picture"
- restructuring
- other aspects change without the learning knowing
Output processing
- make use of the acquired language
Comprehensible Output
Learners need to actively participate in conversation with others using their new language to effectively acquire the language in addition to receiving comprehensible input.
Interaction Hypothesis
Comprehensible input through modified
interaction with proficient speakers of a
language is required in order to fully learn
a second language.
- simplified language
- clarifying questions ("Do you understand?")
- repeating what the learner said in correct form
Processability
Some parts of language acquisition are easier than others process.
- beginning or end are easier
- middle more challenging
Elements of Language
Semantics
meaning of words, phrases, and sentences
- inherent meanings of words
- synonyms, antonyms, homophones, homonyms
- mood of a sentence
- command, statement, permission, probability
Morphology
study of the structure of words
- inflectional
- number, tense, & degree
- derivational
- prefixes, suffixes, lexical category
- creation of new words
Lexicon
vocabulary or words of a language
Phonology
study of the sounds in a language
- phonemes letters create
- smallest unit of sound
- syllable structure
- sequence of sounds
- CVC, CVVC, etc.
Syntax
word order of a sentence
- thought of grammar
- relationship between words
- provides meaning and understanding