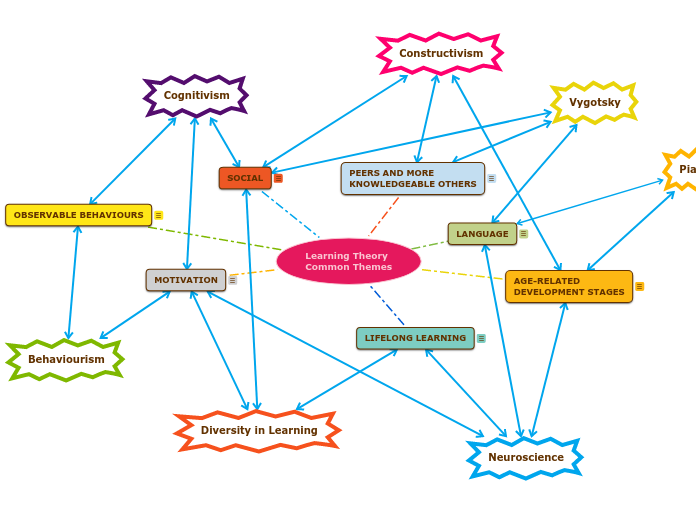
Learning Theory
Common Themes
AGE-RELATED
DEVELOPMENT STAGES
Piaget:Order of operations (sensorimotor, preoperational, concrete operations, formal operations)Neuroscience:Consolidation (development of synaptic responses) and brain development over time.Constructivism:Equilibration - knowledge shift from one stage to another (cognitive constructivism)
OBSERVABLE BEHAVIOURS
Behaviourism:Assumption that human behvaiour is predictableExplicit behaviours can be observed and measuredSocial Cognitive Theory:Can learn by watching (observational learning) and observing the consequences of an action by someone else (vicarious reinforcement)
SOCIAL
Social Cognitive Theory:Social modellingTriadic reciprocal responseVygotsky:Dynamic interdependence of social and individual processesCollaborative learningScaffoldingConstructivism:Interactions with peers and teachers is essentialCooperative learningScaffoldingInternalization occurs more effectively when there is social interaction.Diversity in Learning:cMOOCs collaboration and networkingScaffolding
MOTIVATION
Cognitivism:Material and self-evaluative incentivesBehaviourism:Pavlov's response to stimuliNeuroscience:Information is processed through filters to gain attention, which is influenced by perceived importance, novelty, intensity and movement.Growth mindsetDiversity in Learning:Collaboration in cMOOCs leading to increased motivation to participate and add to discussion
PEERS AND MORE
KNOWLEDGEABLE OTHERS
Vygotksy:Guided participationZone of proximal developmentCollaborative learningConstructivism: Social Constructivism = ideas constructed though interaction with teacher and/or peers
LIFELONG LEARNING
Neuroscience:Much is learned through observationConsolidation + memory + application = learningDiversity in Learning:Wide reaching availability of MOOCsMOOCs as free learning
Neuroscience
Behaviourism
Vygotsky
Constructivism
Cognitivism
Diversity in Learning
Piaget
LANGUAGE
Piaget:Stages of operations include language and communication as key identifiersVygotsky:Culture and language in human development is essential.Semiotic Mediation - key to all aspects of knowledge construction. Through language, counting, art, writing, schemes, maps, mnemonic techniques, etc.Importance of language and culture on learning.Inner speech is integral to learning and thinkingNeuroscience:Language is key to learning and involves a number of processes from multiple parts of the brain.