Macromolecules by Chloe Sharp
carbohydrates
monosaccharide
single carbon base
building on the other carbohydrates
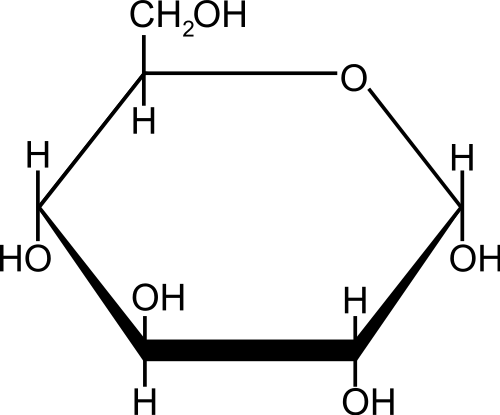
glucose
energy production
cellular respiration

fructose
plants

galactose
disaccharide
two bases
two molecule joined together
dehydration synthesis
chemical process

sucrose
white table sugar
glucose and fluctose

maltose
glucose and glucose
malt products (malt sugar)

lactose
glucose and galactose
dairy products (milk)
polysaccharide

starch
hydrolysis
enzymes and amylase
amylose
maltose
many bases
chains of 3 or more molecules joined together
dehydration synthesis

chitin
arthropods

cellulose
plants
structure

glycogen
liver
energy storage
proteins
translations
cytoplasm
ribosome

amino acids

non-ionized form and ionized form
peptide bonds
transcriptions
RNA
DNA
RNA polyamerase
information
nucleus
structures

secondary structure
B-pleated sheet
a-helix
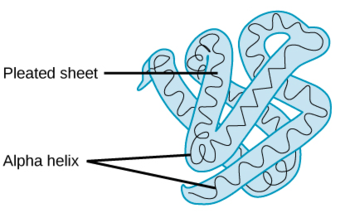
tertiary structure
pleated sheets
quaternary structure
a-chain
B-chain
Fe2+
heme

primary structure
lipids

triglycerides
dehydration synthesis
glycerol and fatty acids
calories

phospholipids
amphipathic
tail and head
hydrophobic and hydrophillc

fats
Subtopic

steroids
medical
hormones

waxes
ear wax
bacteria
plants and animals
characteristics
C-H energy rich bonds ideal for storage
non-polar
hydrophobic; therefore clump together in water
not a true polymer; can't link sub units over and over again
hydrogen than carb
long chain carbon,hydrogen,oxygen
nucleic acids
phosphodiesterase bond
covenant bonds
two hydroxide groups
phosphate groups
instructions for proteins

DNA

RNA
information
pentose sugars

deoxyribose

ribose
bases
purine bases

adenine

guanine
pyrimidine bases

thymine

uracil
broken down
hydrolysis
enzymes