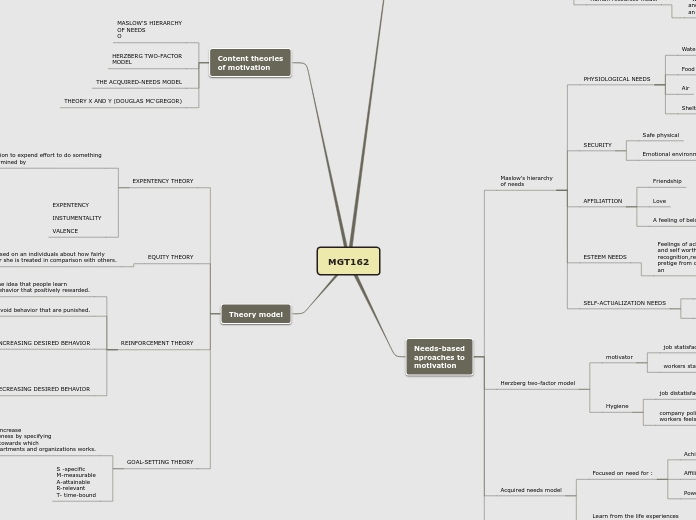
MGT162
motivation
Defination
Forces that moves individuals to take action
Explains why people act they do.
Early view of motivation
Traditional model
FREDERICK W.TAYLOR&
SCIENTIFIC MANAGEMENT
* people were motivated by money
Human relations model
ALTON MAYO &
THE HAWTHORN STUDIES
*people want to feel useful
and important
Human recourses model
Douglas McGregor's theory X and Y
*Workers can contribute the best of their ability
and by encouraging full participation by employees when
an environment are created.
Needs-based
aproaches to
motivation
Maslow's hierarchy
of needs
PHYSIOLOGICAL NEEDS
Water
Food
Air
Shelter
SECURITY
Safe physical
Emotional environment
AFFILIATTION
Friendship
Love
A feeling of belonging
ESTEEM NEEDS
Feelings of achievement
and self worth through
recognition,respect and
pretige from others.
an
SELF-ACTUALIZATION NEEDS
Self-fullfillment
achievement
Herzberg two-factor model
motivator
job statisfaction
workers statisfied with their works
Hygiene
job distatisfaction
company policy( rules and regulartion) makes
workers feels uncomfortable.
Acquired needs model
Focused on need for :
Achievement
Affiliation
Power
Learn from the life experiences
in the culture or country in which
we live.
Theory X and Y
Theory X
Expired by external
motivated by money and promotions
Dislike work
Theory Y
Enjoy work
motivated by appreciation,encouragement
allow employees to participate in decision making.
Content theories
of motivation
MASLOW'S HIERARCHY
OF NEEDS
O
HERZBERG TWO-FACTOR
MODEL
THE ACQUIRED-NEEDS MODEL
THEORY X AND Y (DOUGLAS MC'GREGOR)
Theory model
EXPENTENCY THEORY
Motivation to expend effort to do something
is determined by
effort will lead performance
rewards are attached performance
outcomes/rewards are
value to the individuals.
EXPENTENCY
INSTUMENTALITY
VALENCE
EQUITY THEORY
Focused on an individuals about how fairly
he or she is treated in comparison with others.
REINFORCEMENT THEORY
Based on the idea that people learn
to repeat behavior that positively rewarded.
Avoid behavior that are punished.
INCREASING DESIRED BEHAVIOR
Positive desired behavior
Negative desired behavior
DECREASING DESIRED BEHAVIOR
extinction
punishment
GOAL-SETTING THEORY
A process intented to increase
efficiency and effectiveness by specifying
the desired outcomes towards which
individuals,groups,departments and organizations works.
S -specific
M-measurable
A-attainable
R-relevant
T- time-bound