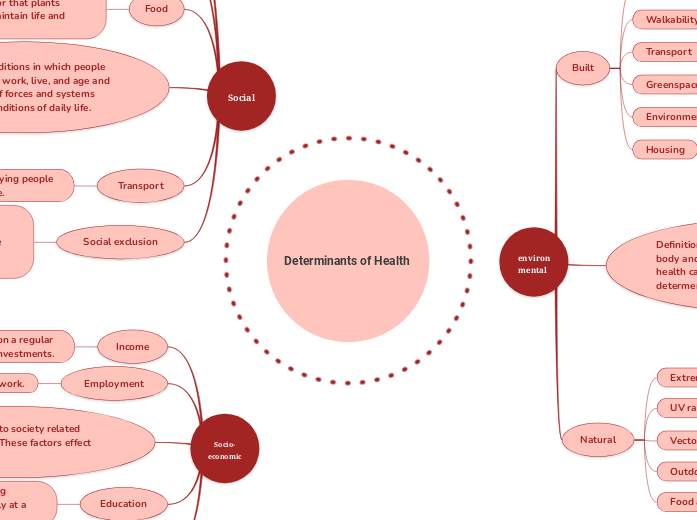
Determinants of Health
environmental
Built
Indoor air quality
Can help body temp, provides oxygen, can cause spread of sickness
Add text
Walkability
Uneven ground can cause people to trip and hurt themselves, saftey hazards,
Add text
Transport
Bad for the enviorment (pollution), encourages the spread of sickness
Add text
Greenspace
Good/bad airflow, can provide places to excersise, can help build social skills like on the playground
Add text
Environmental noise
Can negatively affect wildlife, can also impact hearing and can cause sleep disturbances and high blood pressure
Add text
Housing
Can provide saftey and shelther but also bills, gas leaks and house fires.
Add text
Definition: Anything that acts on the body and can be linked to a change in health can be considered a enviormental determent of health.
Natural
Extreme weather
Droughts, Tsunamis, tornado, fires
Add text
UV radiation
Heat stroke, sun burn/poisoning, can supply you with essential vitamin D, can cause skin cancer
Add text
Vector agents
Can transmit diseases
Add text
Outdoor air quality
Smoke from fires can cause breathing issues
Add text
Food and water quality
Unclean water and bad food quality can cause serious illnesses
Add text
Socio-economic
Income
money received, especially on a regular basis, for work or through investments.
harms children's health, social and emotional wellbeing, and education
Add text
Employment
the state of having paid work.
Unemployment can make it more difficult for individuals to meet their basic needs.
Add text
Definition: Refers to society related economic factors. These factors effect each other.
Education
the process of receiving or giving systematic instruction, especially at a school or university.
Higher crime rates, exposing residents to greater risk of trauma and deaths from violence and the stress of living in unsafe neighborhoods.
Access to services
the ability of people to reach places and services and the ability of places to be reached by people and goods
Add text
Social
Stress
a state of mental or emotional strain or tension resulting from adverse or demanding circumstances.
high blood pressure, heart disease, stroke, obesity and diabetes.
Add text
Early life
The time during which one is a child, from between infancy and puberty
The more adverse experiences in childhood, the greater the likelihood of developmental delays and other problems.
Add text
Food
any nutritious substance that people or animals eat or drink or that plants absorb in order to maintain life and growth.
coronary heart disease, stroke, high blood pressure, atherosclerosis, some forms of cancer, type 2 diabetes, dental caries, gall bladder disease and nutritional anaemias
Add text
Definition: Conditions in which people are born, grow, work, live, and age and the wider set of forces and systems shaping the conditions of daily life.
Transport
a system or means of conveying people or goods from place to place.
rescheduled or missed appointments, delayed care, and missed or delayed medication use.
Add text
Social exclusion
exclusion from the prevailing social system and its rights and privileges, typically as a result of poverty or the fact of belonging to a minority social group.
lowered self-esteem, greater anger, inability to reason well, depression and anxiety, and self-defeating perceptions and behaviours.
Add text