Common Ancestor
-DNA as genetic storage
-Ester bonds in cell membranes
Bacteria
-Presence of peptidoglycan in cell wall
Common ancestor of Eukarya & Archaea
-Presence of histones

Eukarya
-Presence of membrane-bound organelles
-Presence of membrane-bound nucleus
Excavata
-Feeding groove
-Secondary Plastids
SAR clade
Stramenopila
-Tripartite flagellar hair
-Secondary plastids

Diatoms

Giant Kelp (Macrocystis pyrifera)

Alveolata
-membranous vesicles on cell membrane
-secondary plastids but dinoflagellates can tertiary plastids
Rhizaria
-filose pseudopodia

Radiolarians
Foraminiferas
Archaeplastida
-primary plastids

rhodophytes (Red Algae)
Common ancestor of chlorophytes, charophytes, and lan plants
-cell walls made of cellulose
-chlorophyll a & b and b-carotene
Common ancestor of charophytes and land plants
-ring-shaped cellulose-synthesizing proteins
-phramgoplast

Southern Magnolia (Magnolia grandiflora)
-common ancestor of land plants
-Sporic life cycle
-embryo
-desiccation-resistant spores
-apical meristems
-gametangia
-sporangia
Common ancestor of Mosses, Hornworts, Lycophytes, Monilophytes, Gymnosperms, Angiosperms
Common ancestor of Hornworts, Lycophytes, Monilophytes, Gymnosperms, Angiosperms
Common ancestor of Lycophytes and Monilophytes, Gymnosperms, and Angiosperms
-Lignin
-Xylem & Phloem
-Leaves
-Dominant sporophytes generation
-Thick waxy cuticle
-Stomata
Common ancestor of Monilophytes, Gymnosperms, Angiosperms
-Megaphylls
Common ancestor of Gymnosperms and Angiosperms
-pollen
-seed
-heterospory
-wood
-ovules
Gymnosperms
-"naked seeds"

Scots Pine (Pinus sylvestris)
Bald Cypress (Taxodium distichum)
Angiosperms
-"enclosed seeds"
-fruit
-endosperm
-ovaries

Southern Magnolia (Magnolia grandiflora)

White Water Lily (Nymphaea alba)

Eastern Marsh Fern (Thelypteris palustris)
-Monilophytes
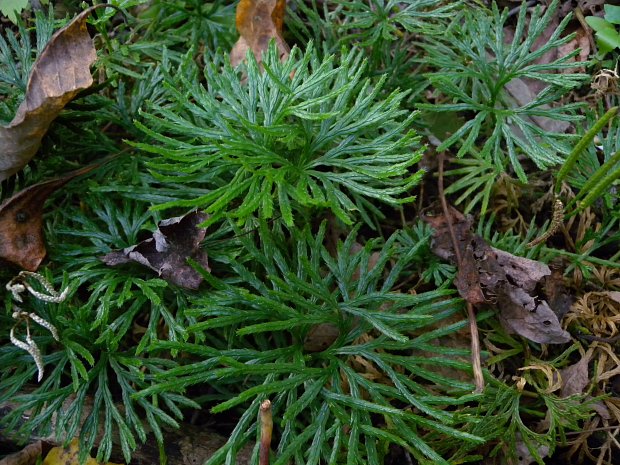

Fan clubmoss (Diphasiastrum digitatum)
-Lycophytes
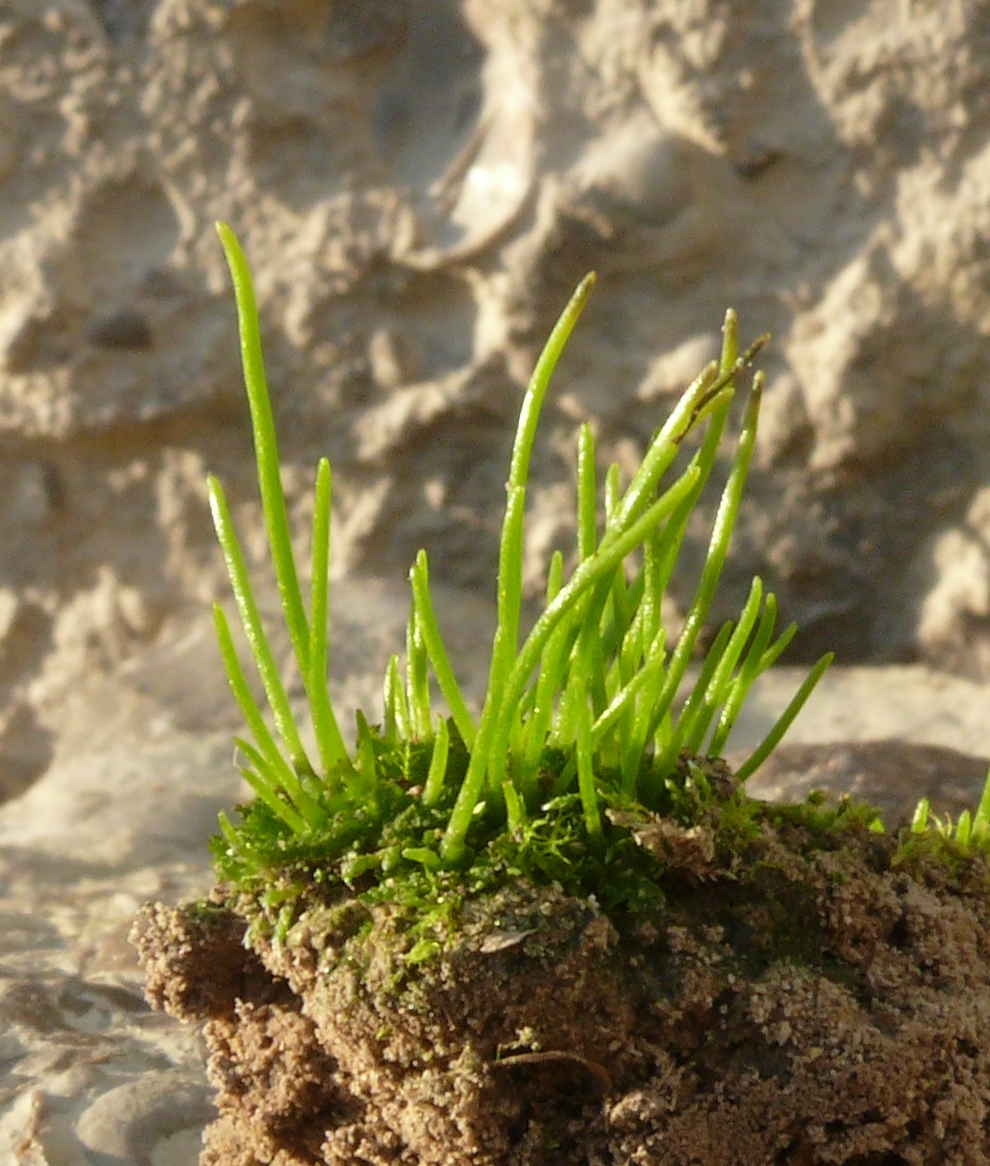

Field hornwort (Anthoceros agrestis)

Woolly Feather Moss (Tomentypnum nitens)

Common Liverwort (Marchantia polymorpha)

Charophytes (Braun's stonewort (Chara braunii))
-zygotic life cycle

Chlorophytes (Green Algae)
Unikonta
Amebozoa
-movement with pseudopodia

slime molds
Opisthokonta
-single posterior flagellum on swimming cells

Fungi
-multicellularity
-absorptive heterotrophy
-cell wall
-zygotic life cycle

Fly Agaric (Amanita muscaria)
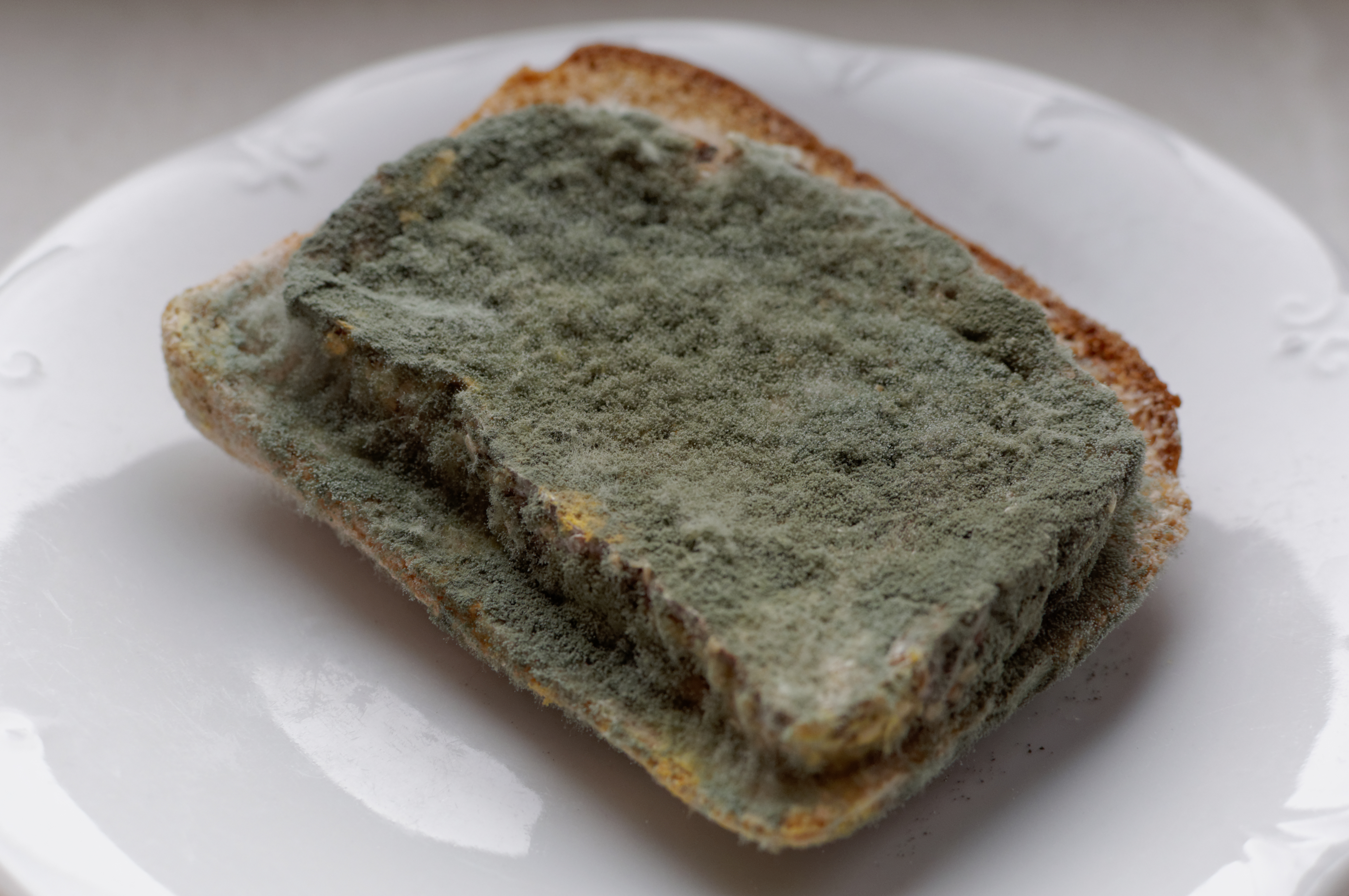

Black Bread Mold (>Rhizopus stolonifer)
Common Ancestor of Choanoflagellate and Animals
Animals
American Black Bear (Ursus americanus)
-multicellularity
-absorptive heterotrophy
-mobility
-complex organ systems
-gametic life cycle

Porifera
-Asymmetry
-No tissues
Eumetazoa
-Tissue
-Symmetry
Bilateria
-triploblasty
-bilateral symmetry
-cephalization
Deuterostomia
-radial & indeterminate cleavage

Chordata
-notochord
-dosal nerve cord
-pharyngeal slits
-endostyle
Common ancestor of vertebrates & urochordates
Vertebrates
-cranium
-vertebral column
Gnathostomes
-jaws
-bony skeleton

Chondrichthyes
-bony skeleton lost
-cartilaginous skeleton in extant species
Osteichthyes (bony fishes)
-lungs/lung derivatives
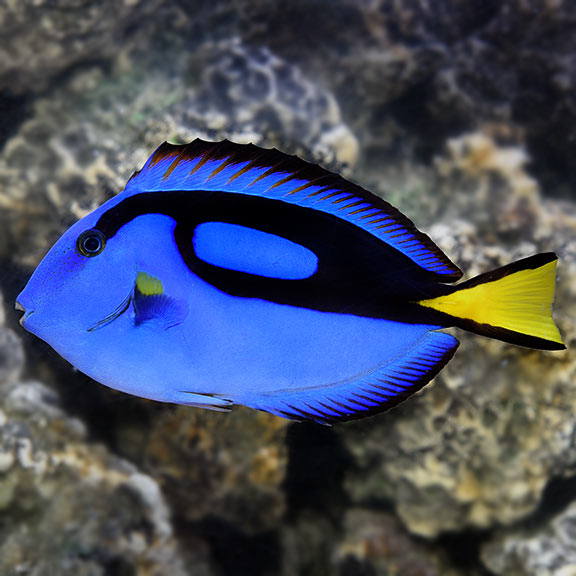

Ray-finned fishes (Actinopterygil)

Lobe-finned fishes (Sarcopterygii)
-skeleton extends into the fin
Common ancestor of lungfishes & tetrapods
Tetrapods
-4 limbs with digits

Amphibians
-non-amniotic egg
Amniotes
-amniotic egg
Mammals
-hair
-milk
-endotherm
Common ancestor of Marsupials & Eutherians

Eutherians
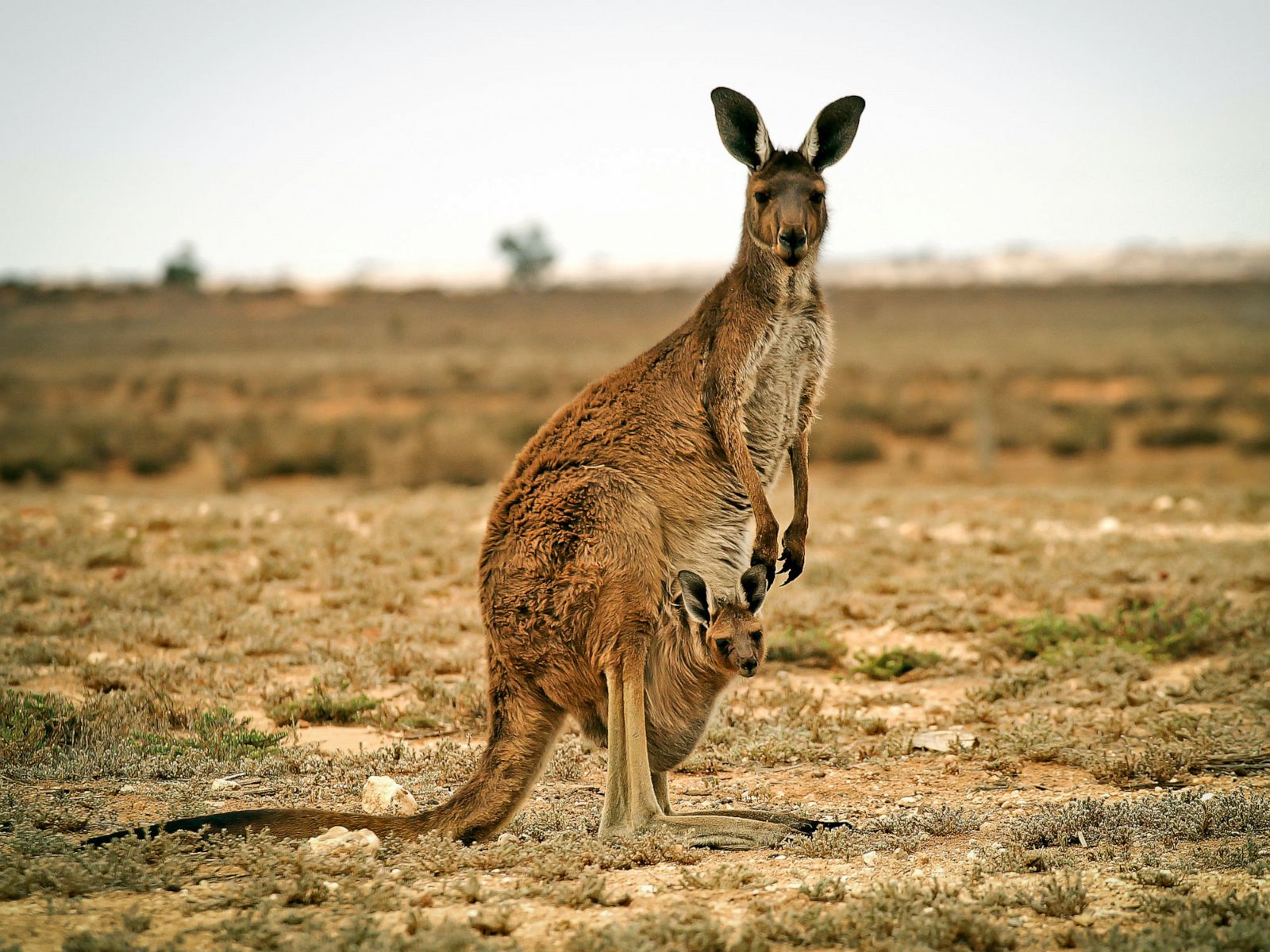

Marsupials

Monotremes
-egg-laying mammals

Reptiles
-ectotherm
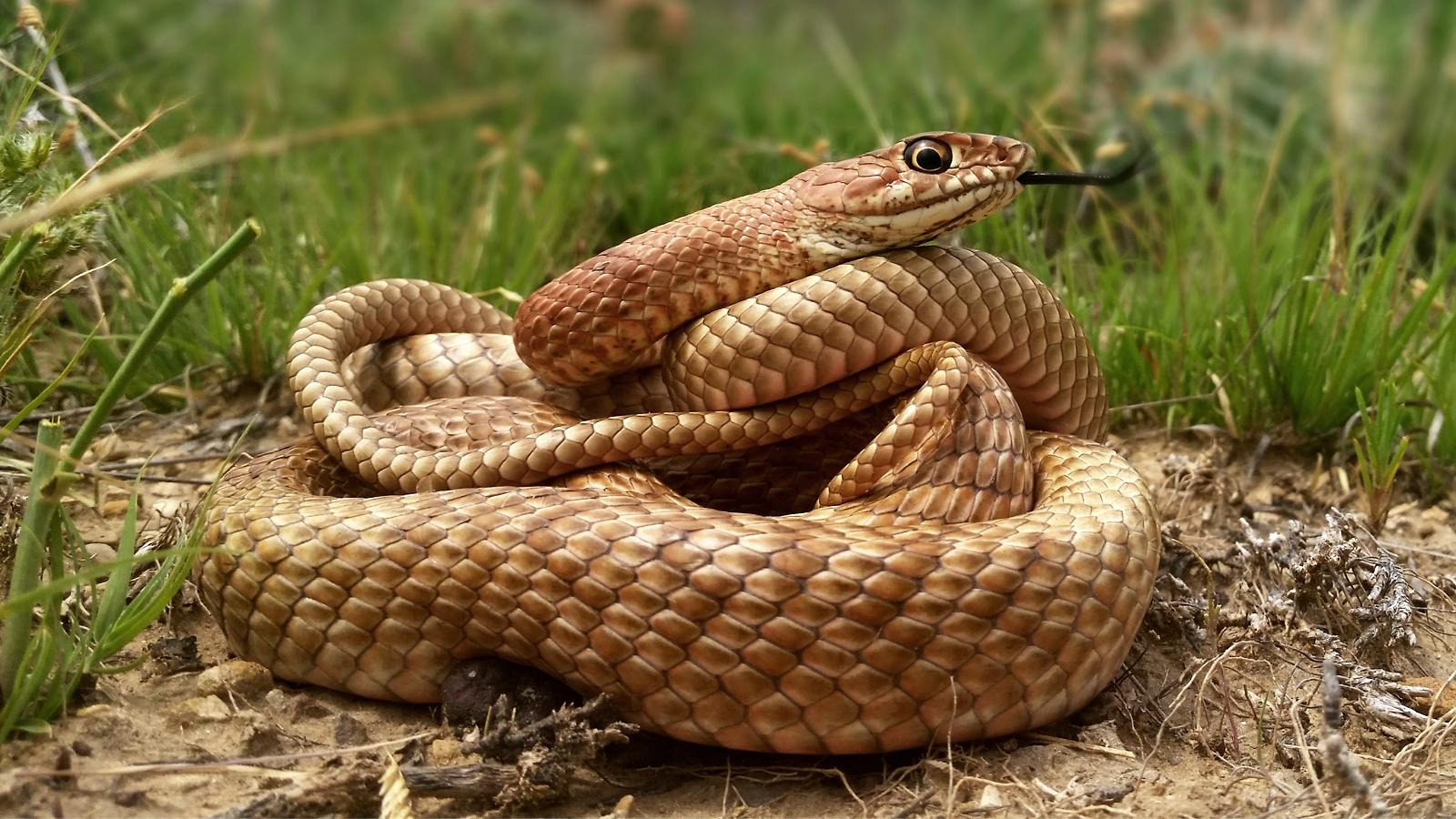

Lepidosaurs (snakes, lizards, amphisbaenians)
Archosaurs

Turtles
Common ancestor of birds & crocodilians
Birds (Aves)

Crocodilians

Lungfishes

Coelocanths
Agnathans (Cyclostome)

Petromyzontida (lampreys)

Myxini (hagfish)
Urochordata
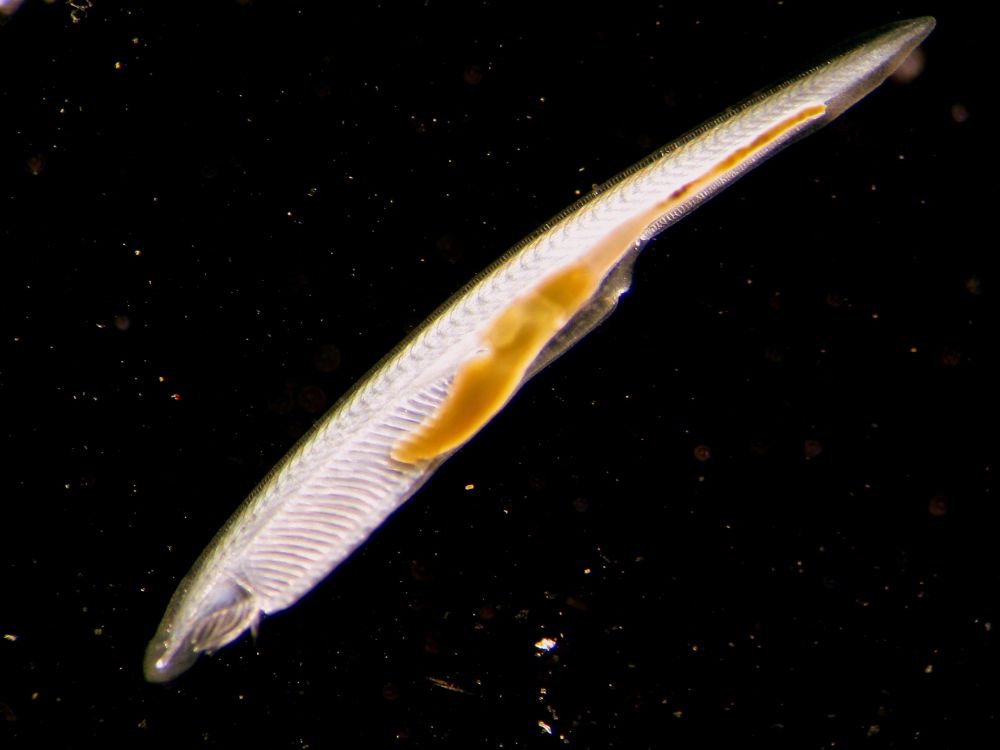

Cephalochordata
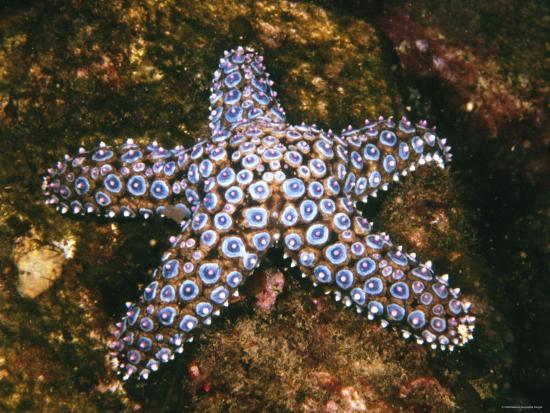

Echinodermata
-"spiny skin"
-water vascular system
-adults radially symmetrical, larvae are bilaterally
symmetrical
-no brain
-complete digestive tract
Holothuroidea
-sea cucumbers
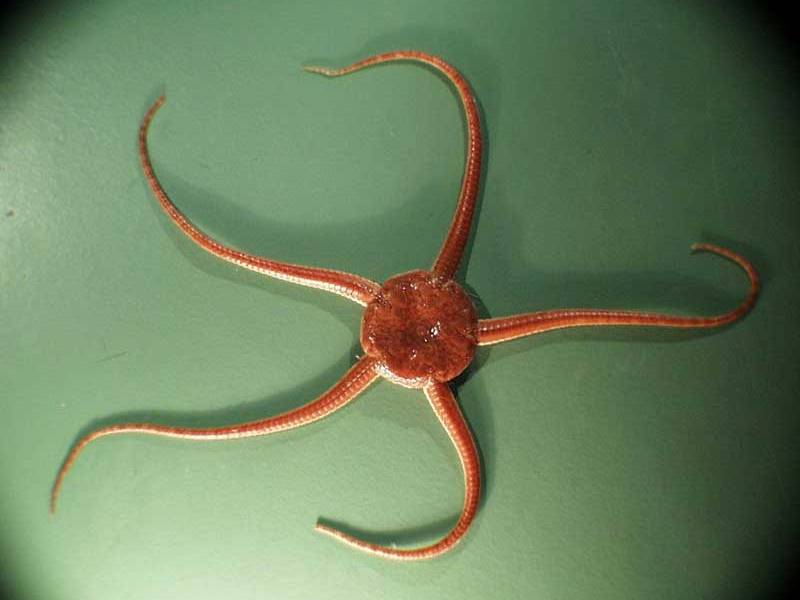
Ophiuroidea
-brittle stars
Echinoidea
-sea urchins & sand dollars

Asteroidea
-sea stars
Protostomia
-spiral & determinate cleavage
-blastopore becomes mouth
Lophotrochozoa
-lophophore and/or trocophore larvae

Platyhelminthes
-acoelomates
-incomplete digestive tract
-no respiratory or circulatory systems

Free-living Rhabditophorans
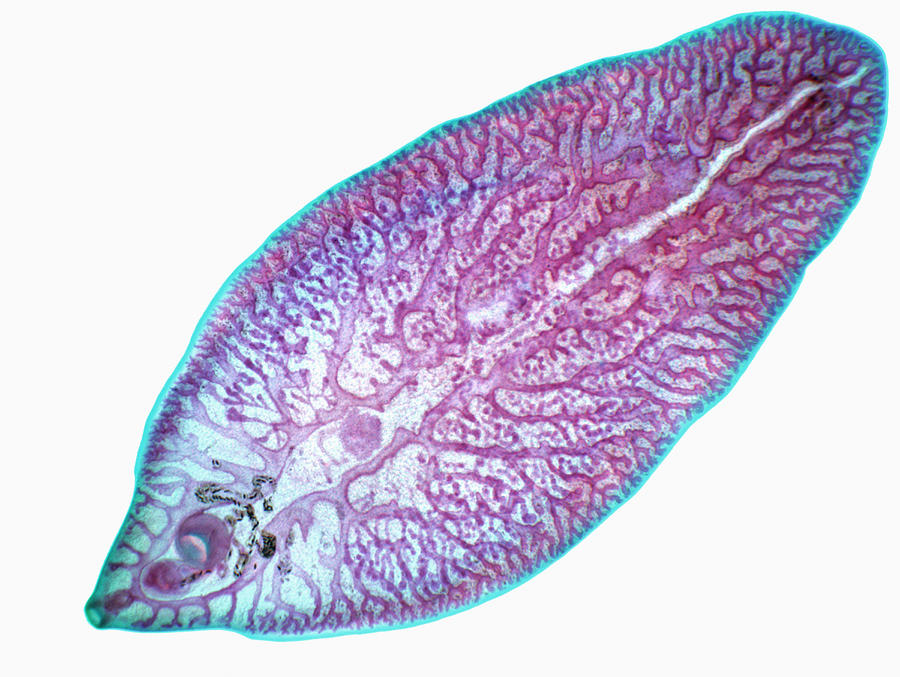
Trematodes
-parasitic
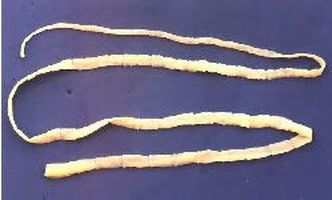
Tapeworms (cestoda)
-parasitic
-no digestive tract
Common ancestor of Mollusca & Annelids

Annelida
-segmented worms
-closed circulator system
-complete digestive tract

Mollusca
-soft-bodied
-foot, visceral mass, mantle
-coelomates
-organ systems

Gastropoda

Cephalopoda
-reduced or absent shell (except nautilus)
-closed circulatory system
Bivalvia
-2 part shell
Ecdysozoa
-ecdysis
-metamorphosis (most)

Arthropoda
-"jointed foot"
-segmented
-exoskeleton made of chitin
-complete digestive tract
-open circulatory system

Pancrustaceans

Crustaceans
-cephalothorax

Hexapoda
-six legs
-insects
-many have wings (crucial to their success as a group)
-head, thorax, abdomen

Chelicerates
-cephalothorax & abdomen
-4 paris of walking legs, pedipalps, chelicerae

Nematoda
-round worms
-free-living & parasitic
-cuticle
-pseudocoelom
-complete digestive tract
/492542401-56a5f70d5f9b58b7d0df4ff5.jpg)
Cnidaria
-radial symmetry
-diploblasty
Medusozoa

Hydrozoa
-alternates between polyp & medusa

Scyphozoa
-usually only medusa

Anthozoa
-usually only polyp

Choanoflagellates
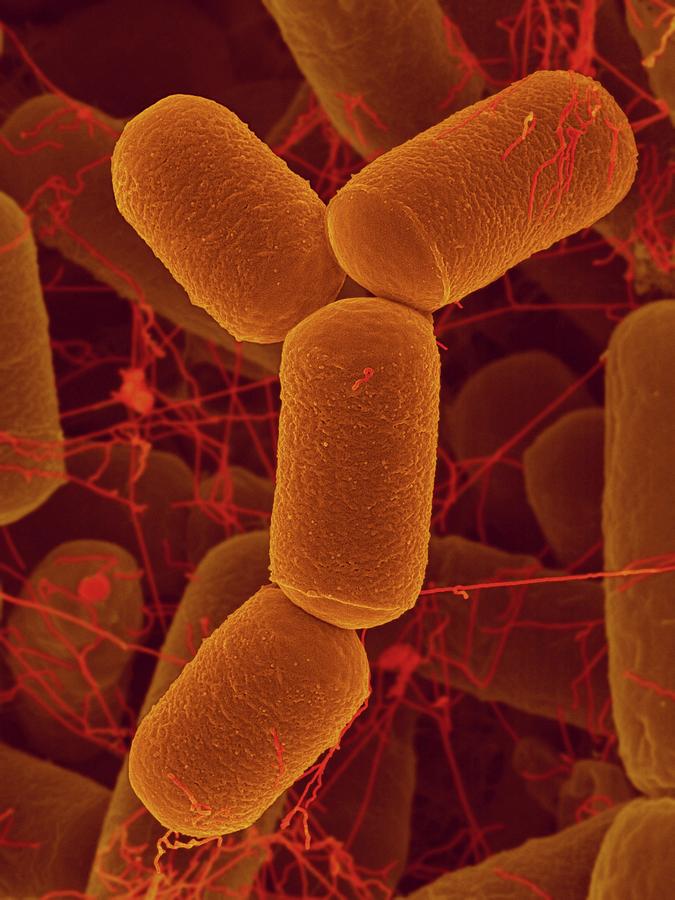
Archaea
-Ether bonds in cell membranes (derived from esther bonds)