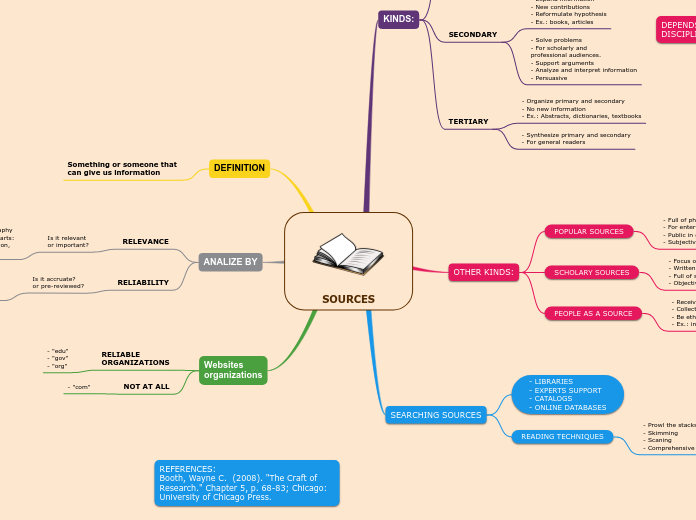
SOURCES
KINDS:
PRIMARY
- Original material
- Basis for others work
- First-hand evidence
- Ex.: Surveys and academic researches
- "Raw data"
- Discoveries
- Text studied
- Used to test hypothesis
- Authoritative
SECONDARY
- Analyze primary ones
- Expand information
- New contributions
- Reformulate hypothesis
- Ex.: books, articles
- Solve problems
- For scholarly and
professional audiences.
- Support arguments
- Analyze and interpret information
- Persuasive
TERTIARY
- Organize primary and secondary
- No new information
- Ex.: Abstracts, dictionaries, textbooks
- Synthesize primary and secondary
- For general readers
OTHER KINDS:
POPULAR SOURCES
- Full of photos
- For entertainment
- Public in general
- Subjectivity and opinions
SCHOLARY SOURCES
- Focus on academy
- Written by specialist
- Full of scientific information
- Objectivity and reliable facts
PEOPLE AS A SOURCE
- Receive memories
- Collect opinions
- Be ethical
- Ex.: interview, survey, experiment.
SEARCHING SOURCES
- LIBRARIES
- EXPERTS SUPPORT
- CATALOGS
- ONLINE DATABASES
READING TECHNIQUES
- Prowl the stacks
- Skimming
- Scaning
- Comprehensive reading
DEFINITION
Something or someone that
can give us information
ANALIZE BY
RELEVANCE
Is it relevant or important?
- Relevant bibliography
- Skim important parts:
Abstract, introduction,
conclusions, so on.
RELIABILITY
Is it accruate?
or pre-reviewed?
- Be skeptical
- Scholar authors
- Up-to-date
- Cited before
Websites
organizations
RELIABLE
ORGANIZATIONS
- "edu"
- "gov"
- "org"
NOT AT ALL
- "com"